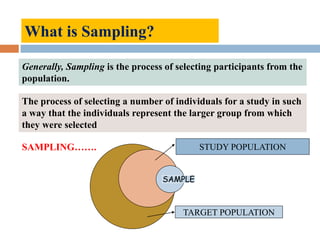
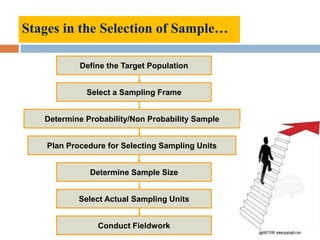
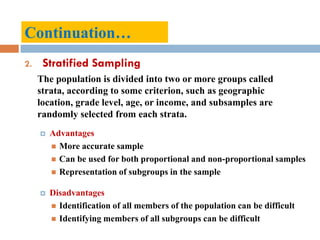
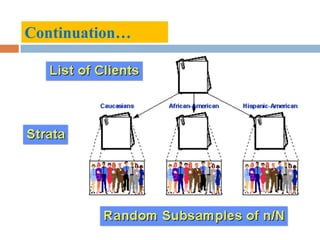
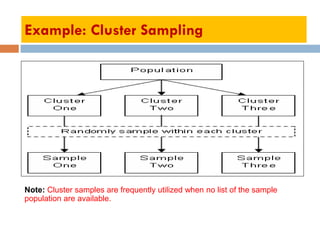
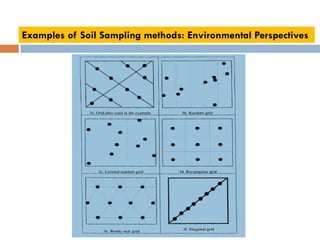
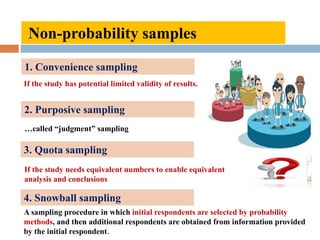
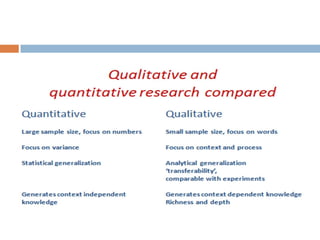
The document discusses sampling and analysis methods from an environmental science perspective. It defines a sample as a subset of a population that is used to make inferences about the entire population. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling which uses random selection, and non-probability sampling which does not use random selection. Some specific sampling methods discussed include random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, cluster sampling, convenience sampling, purposive sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. Ethical considerations for data collection like informed consent and confidentiality are also covered.