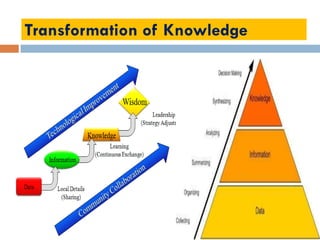
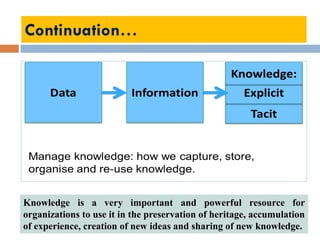
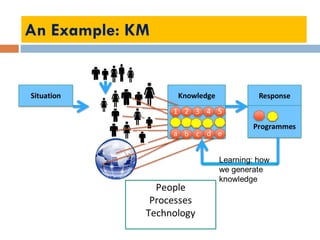
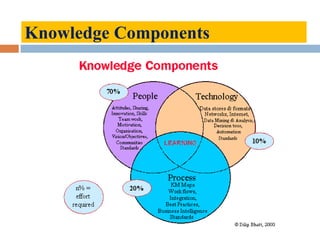
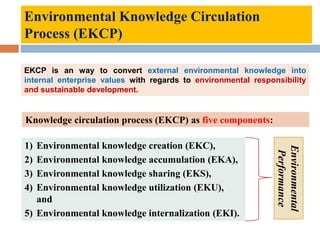
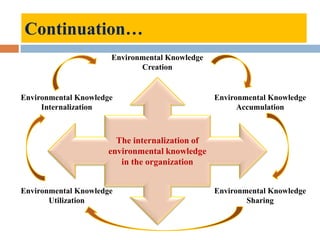
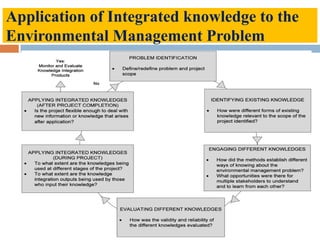
This document outlines a lecture on environmental knowledge management. It begins by defining knowledge management as the systematic collection of activities to generate, distribute, organize, store, access, and apply knowledge. It then discusses the processes of knowledge transformation and the components of knowledge. Environmental knowledge management is introduced as combining the management of explicit and tacit environmental knowledge in an organization to control environmental impacts. The key differences between environmental knowledge management systems and environmental management information systems are explained. Environmental knowledge circulation process and its five components are also outlined. Finally, the document discusses some potential results of effectively applying environmental knowledge management, such as improvements in areas like water and energy use, pollution control, and waste management.