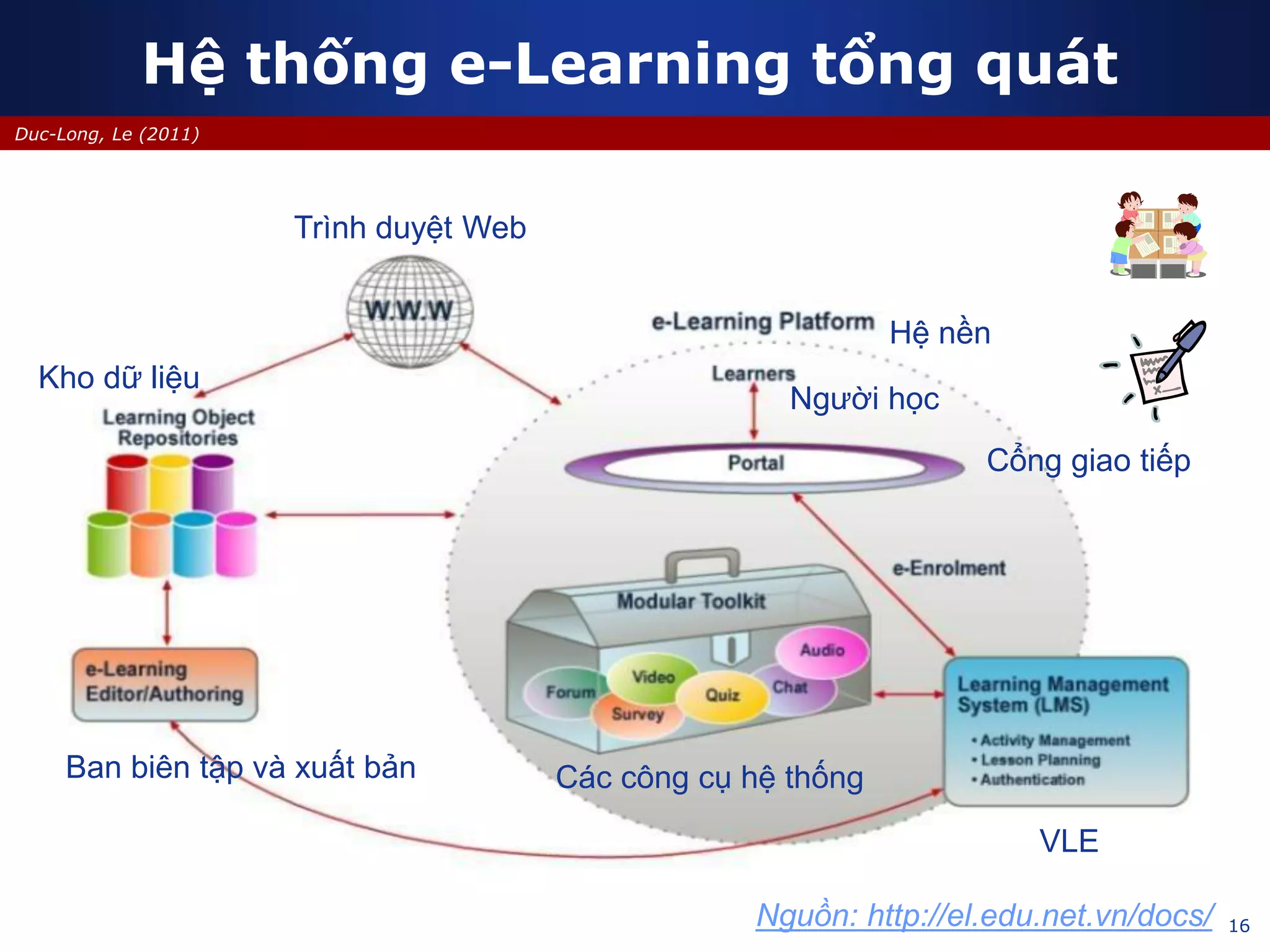
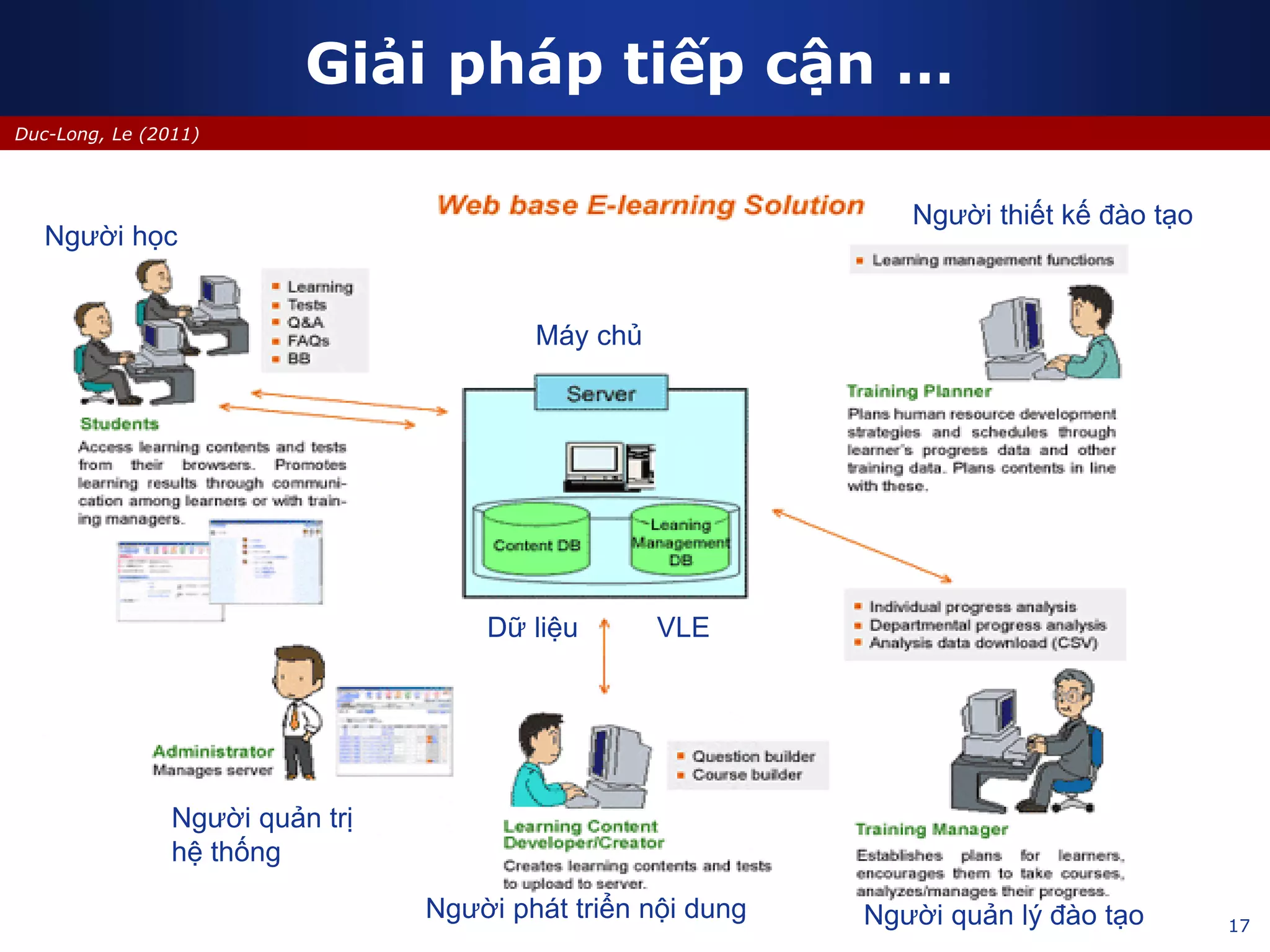
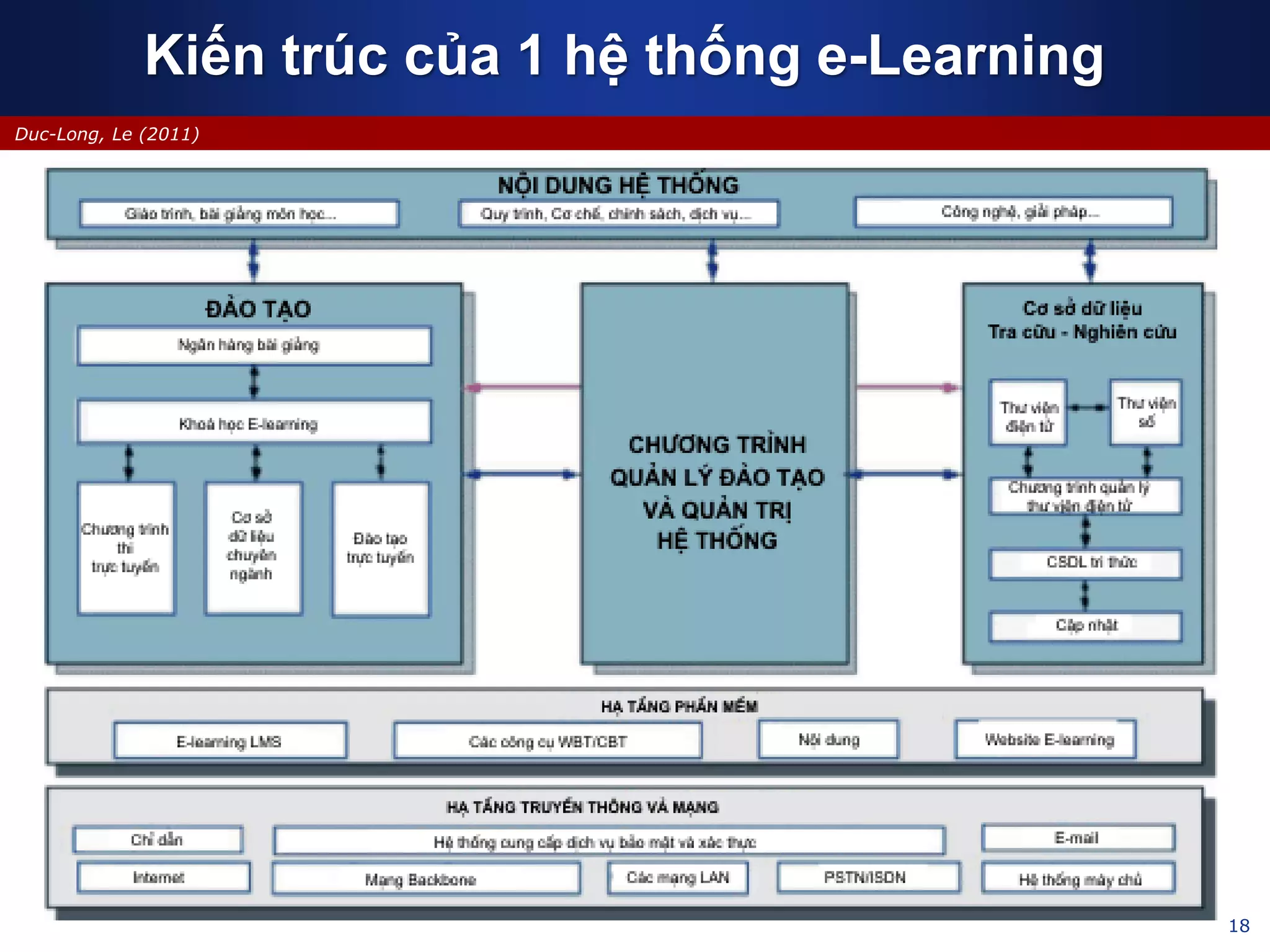
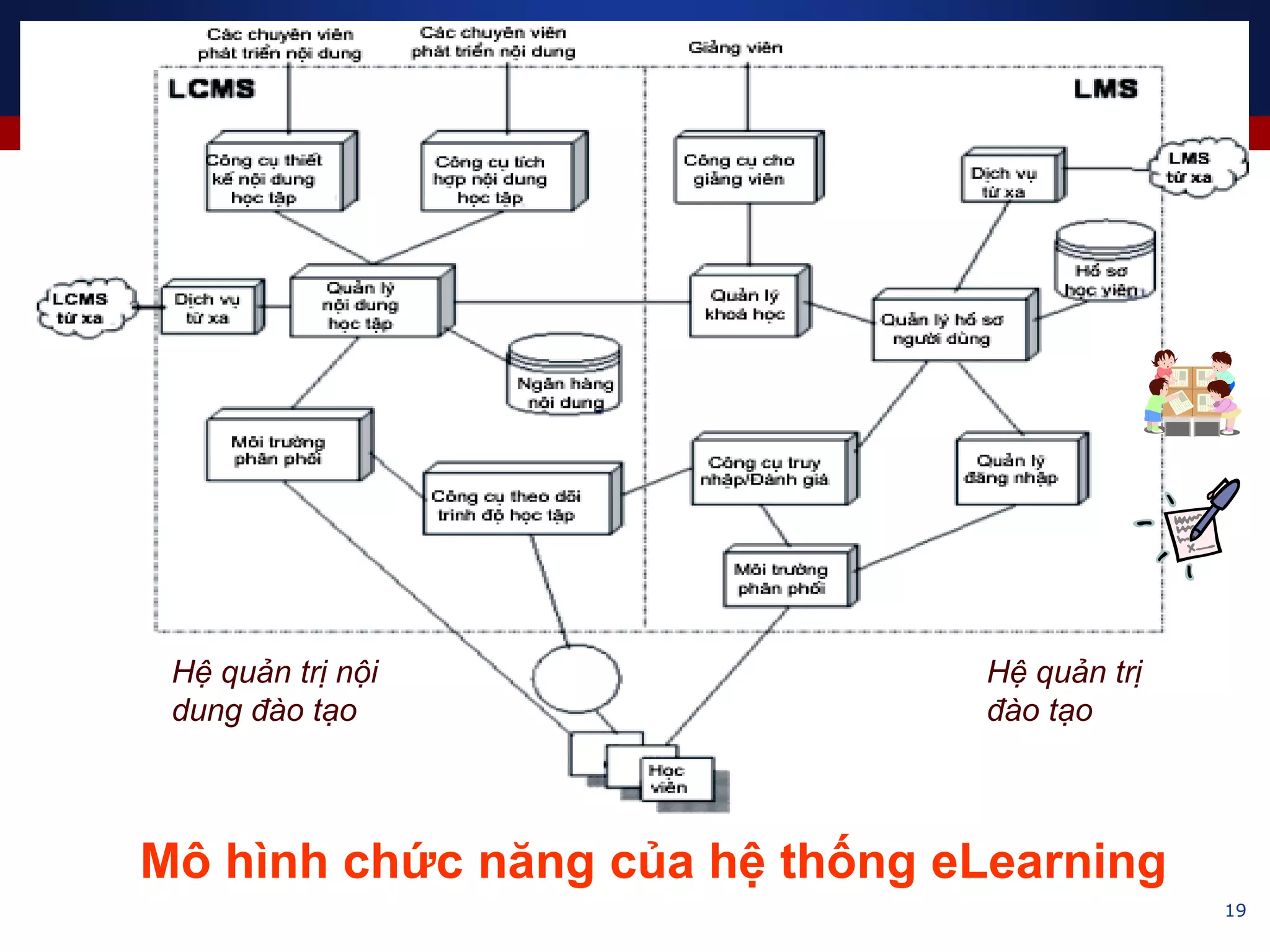
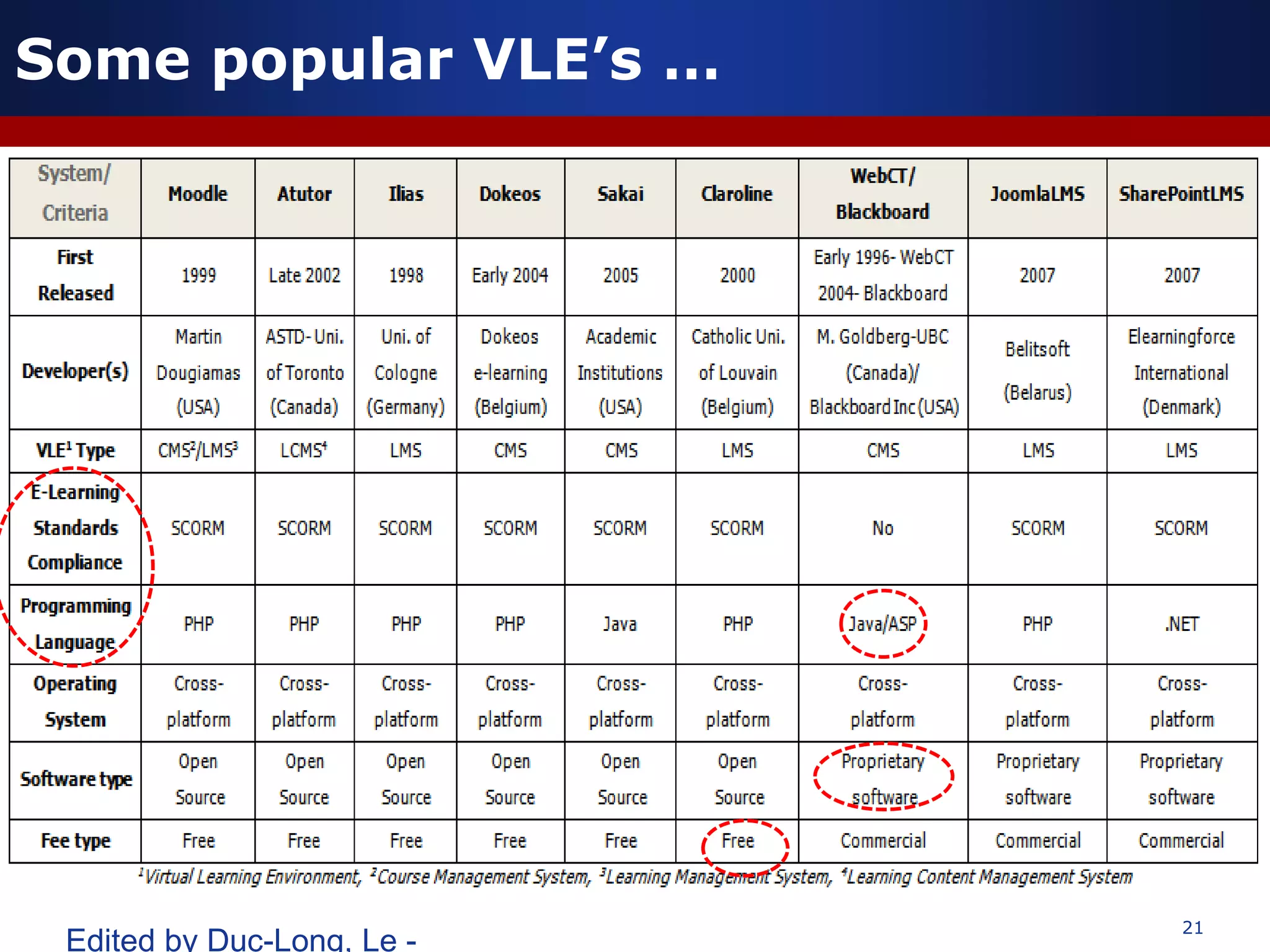
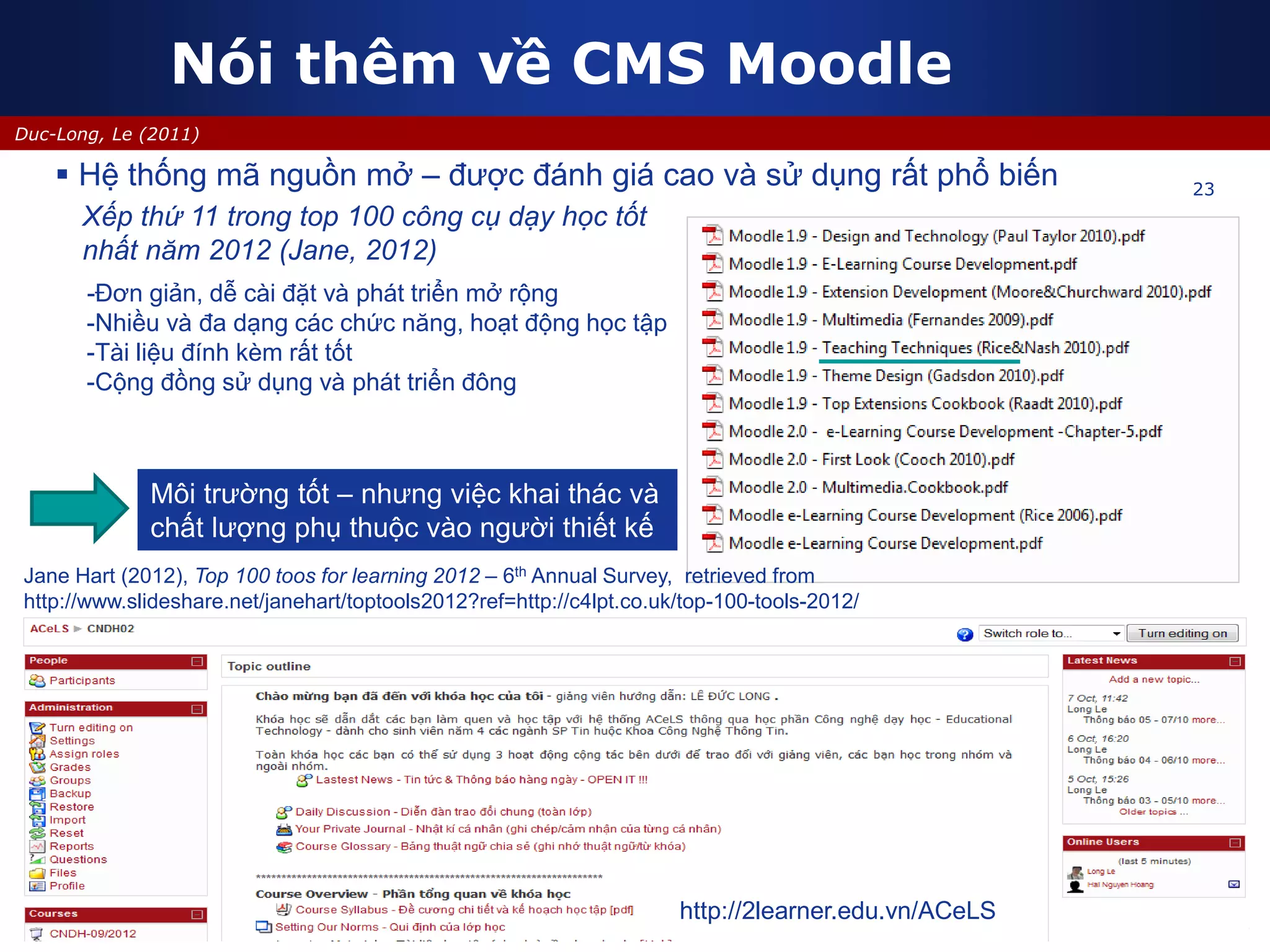
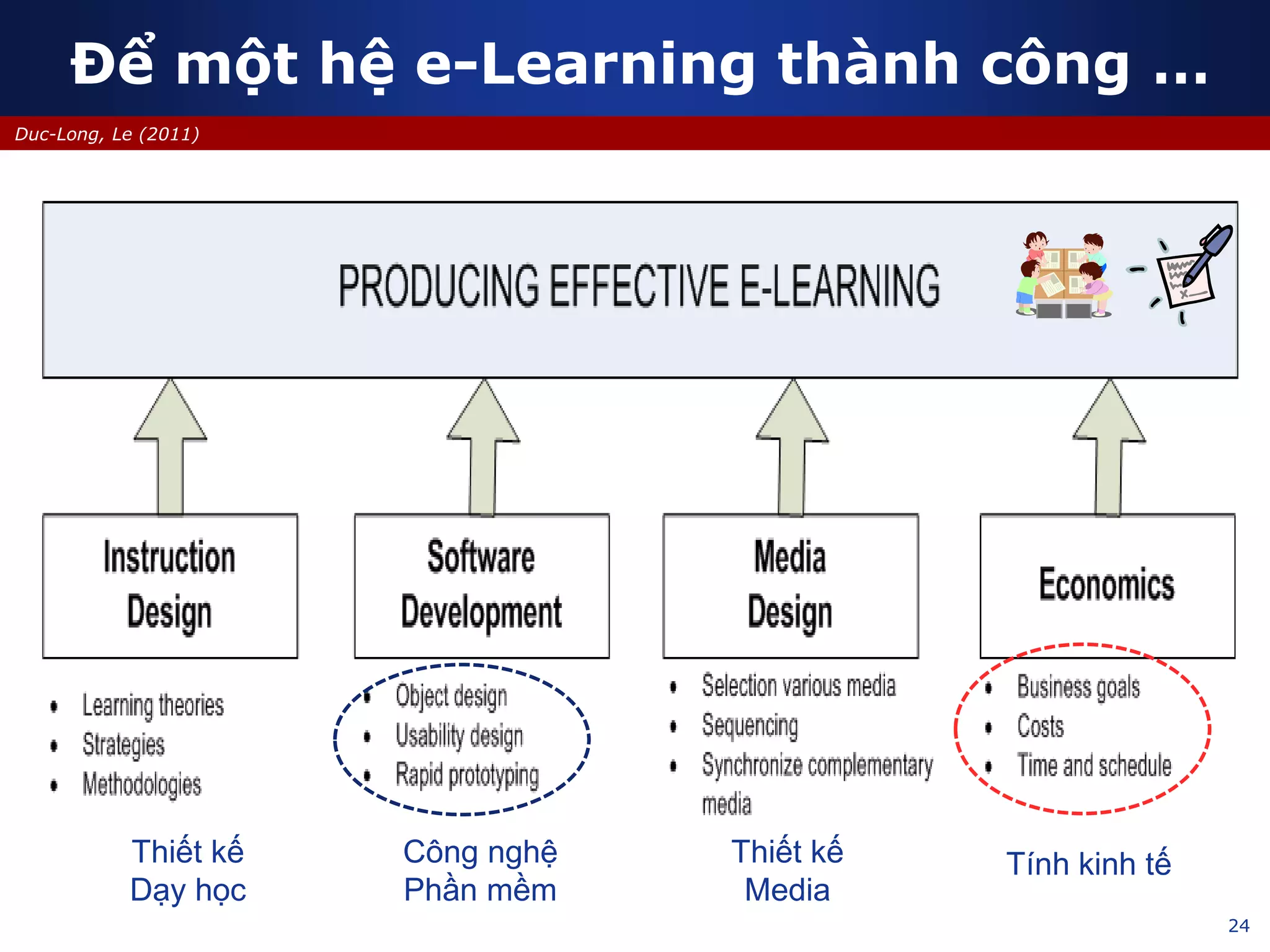
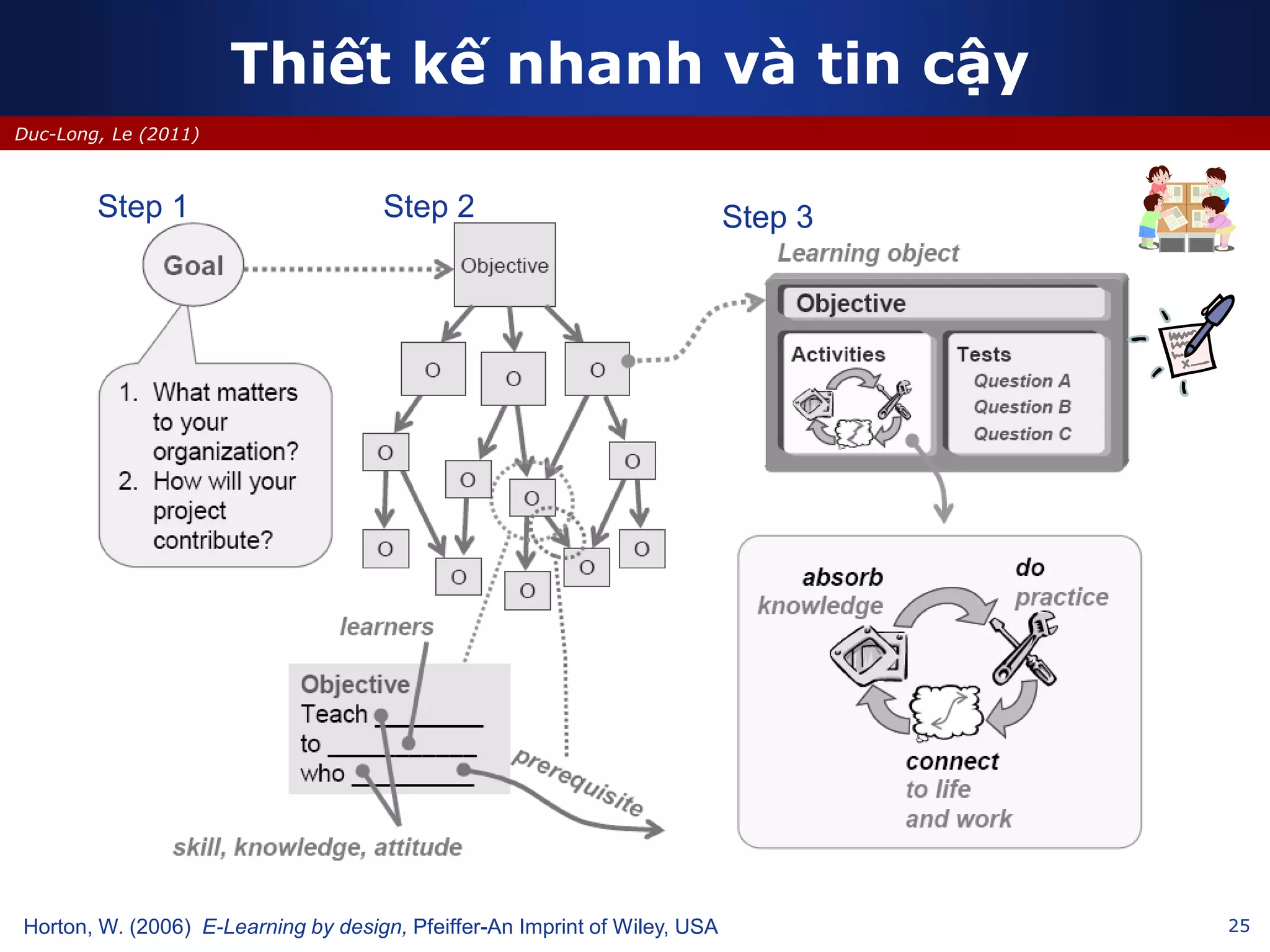
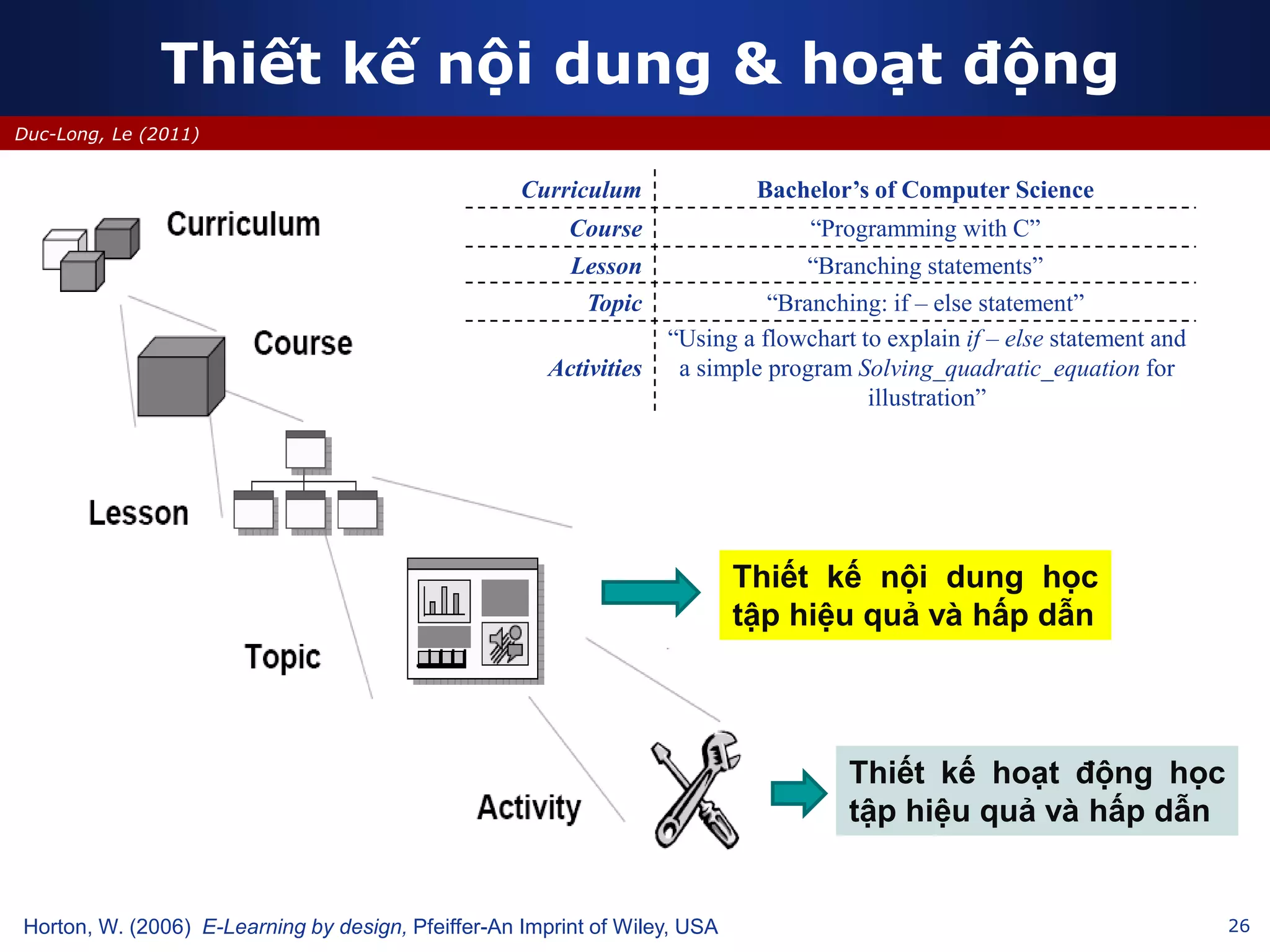
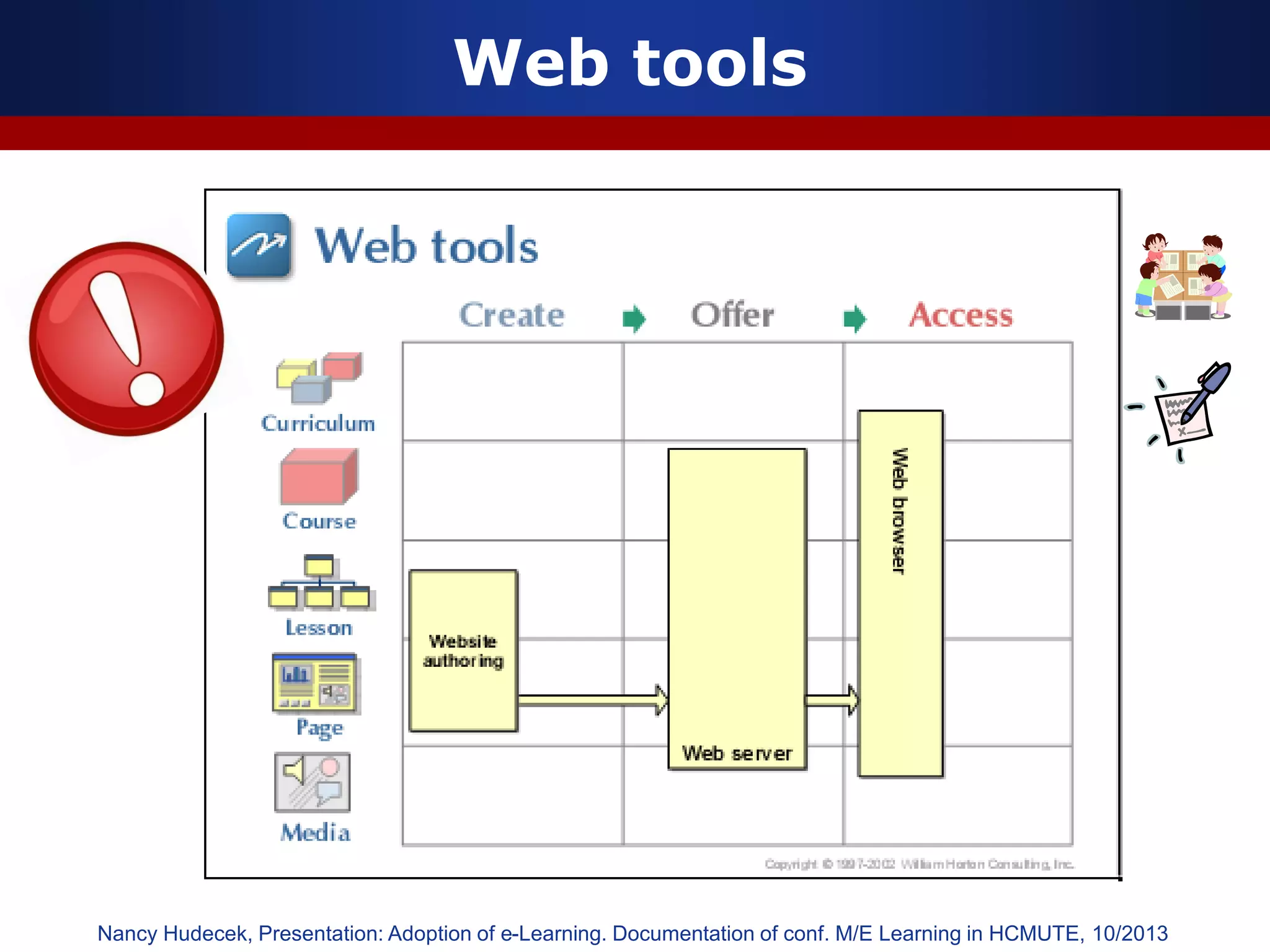
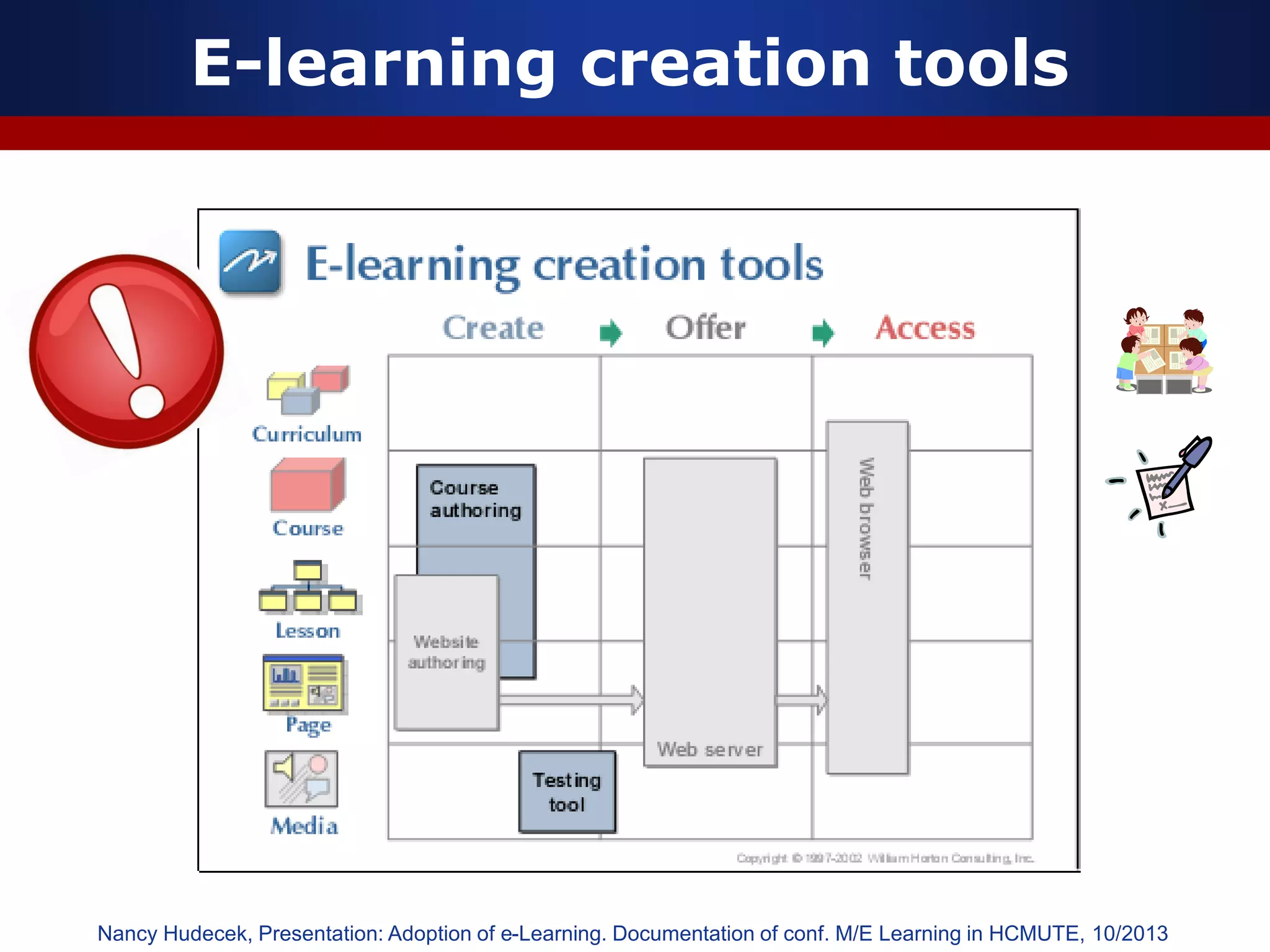
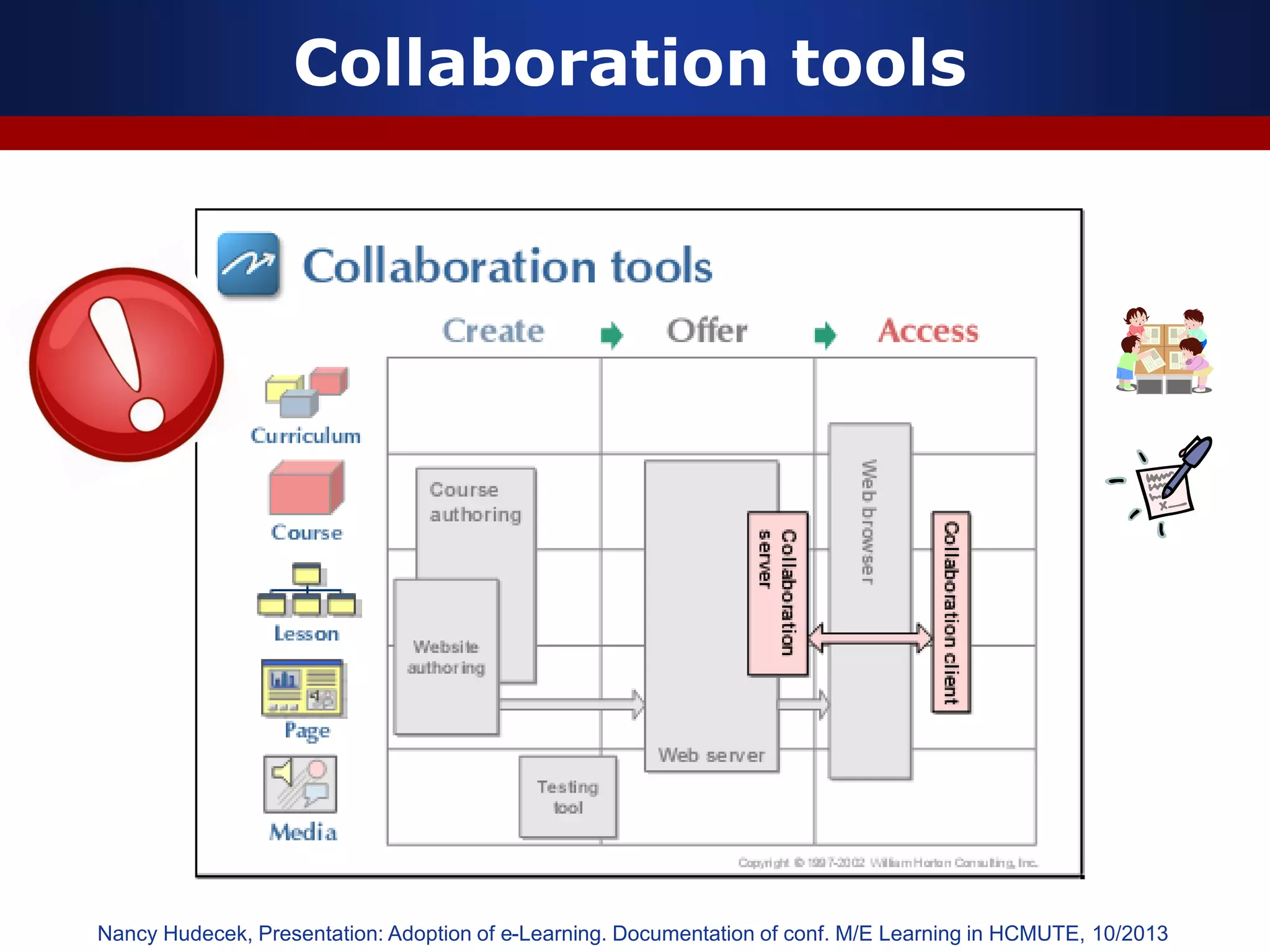
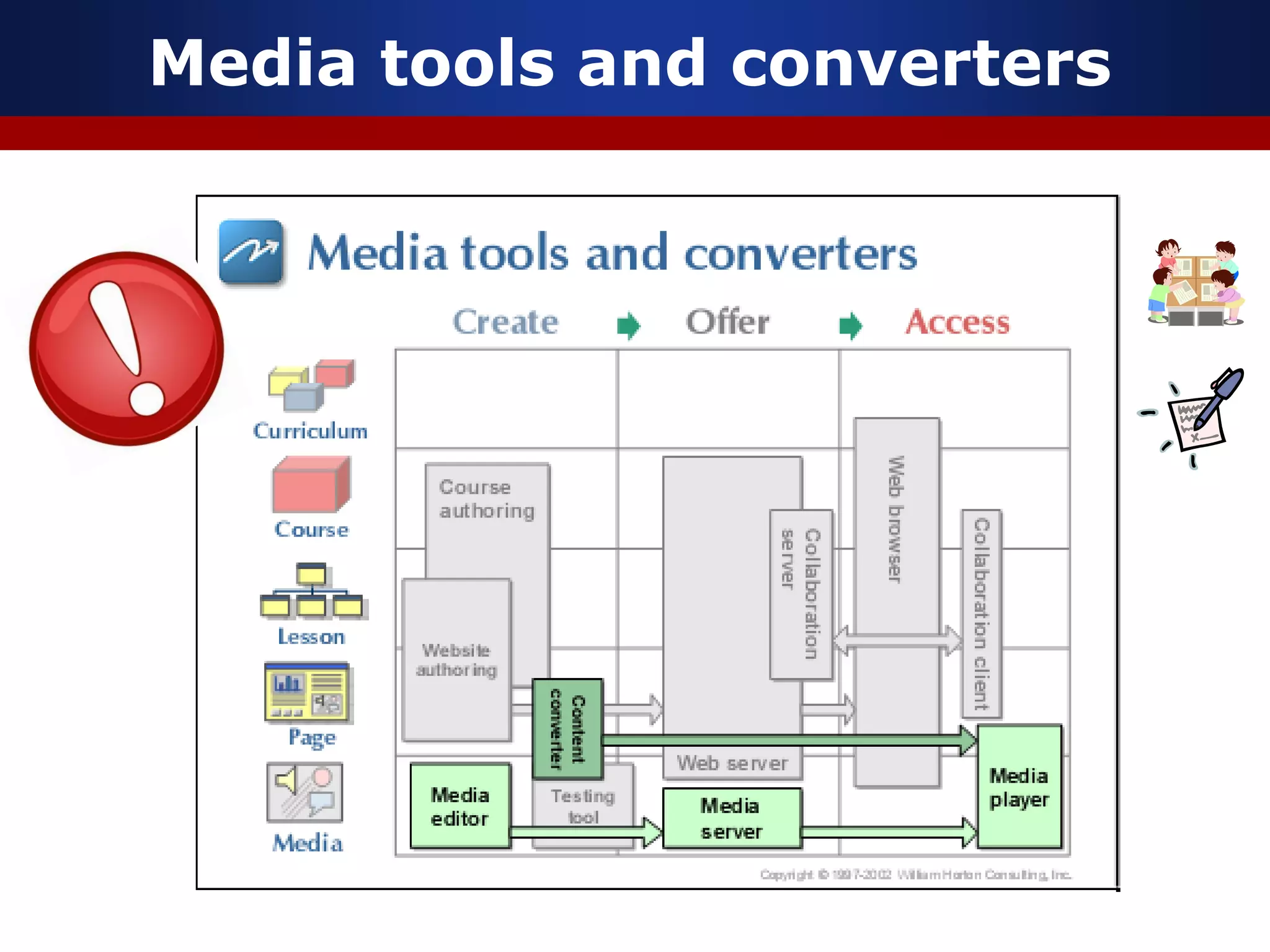
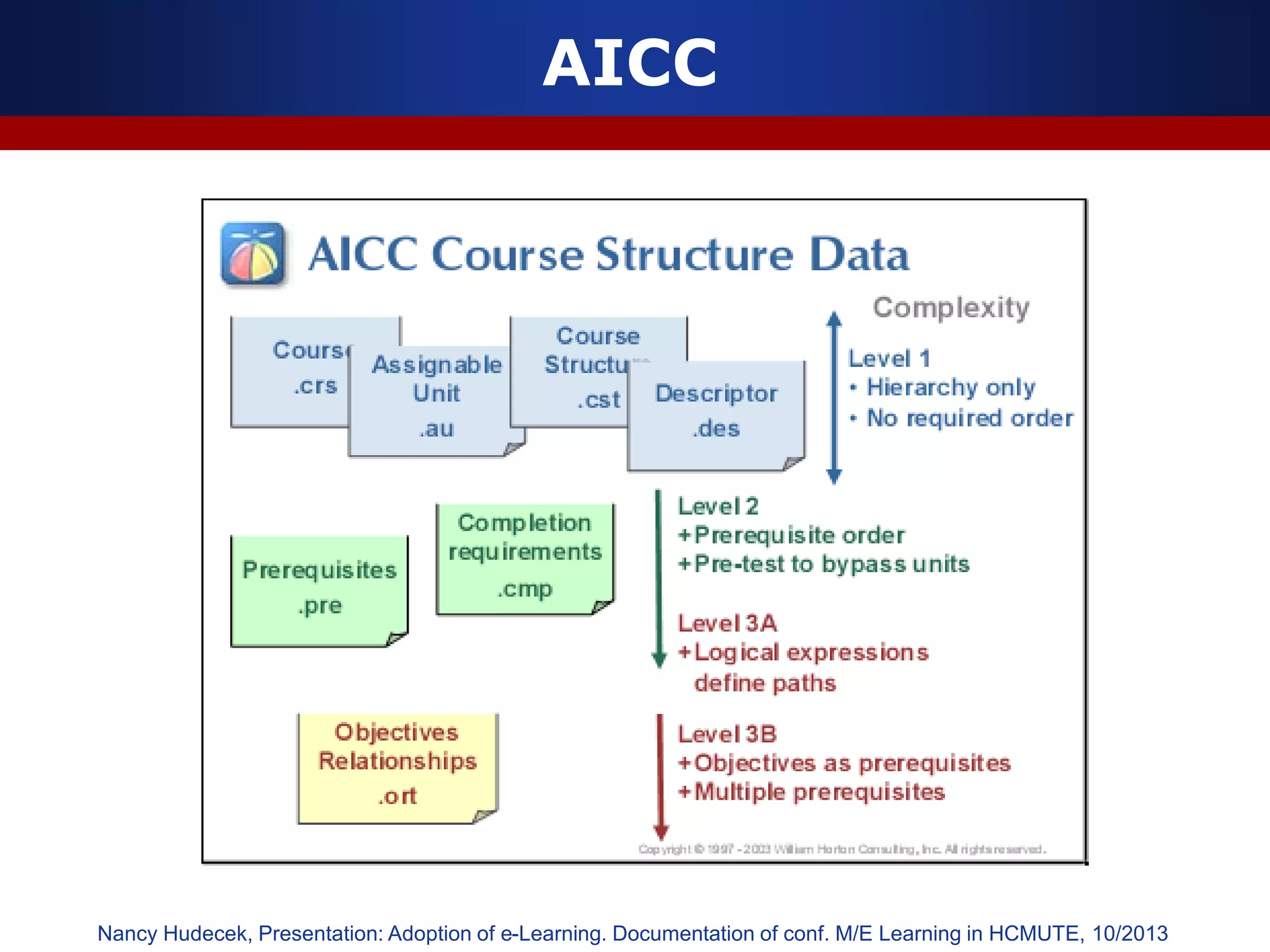
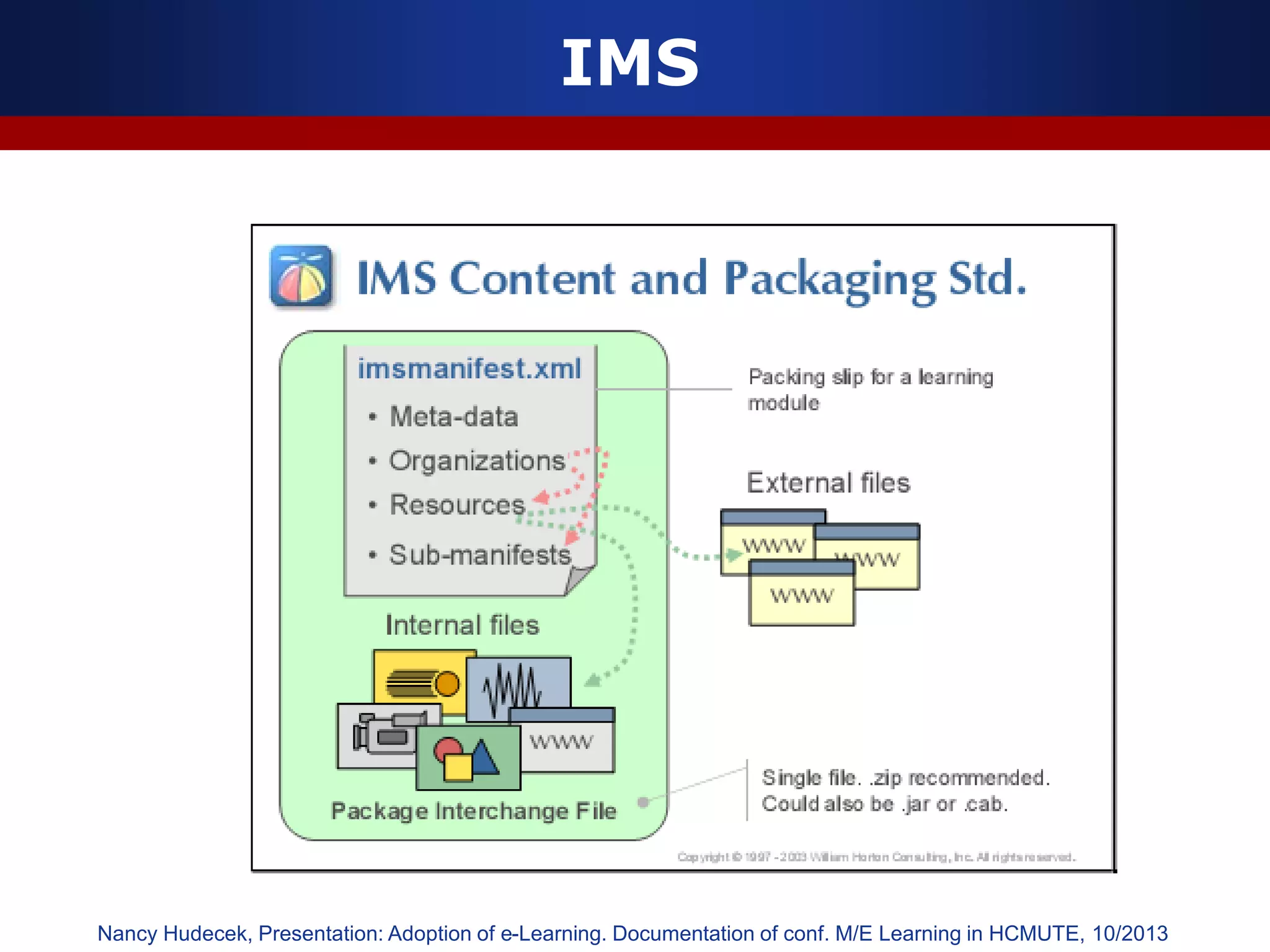
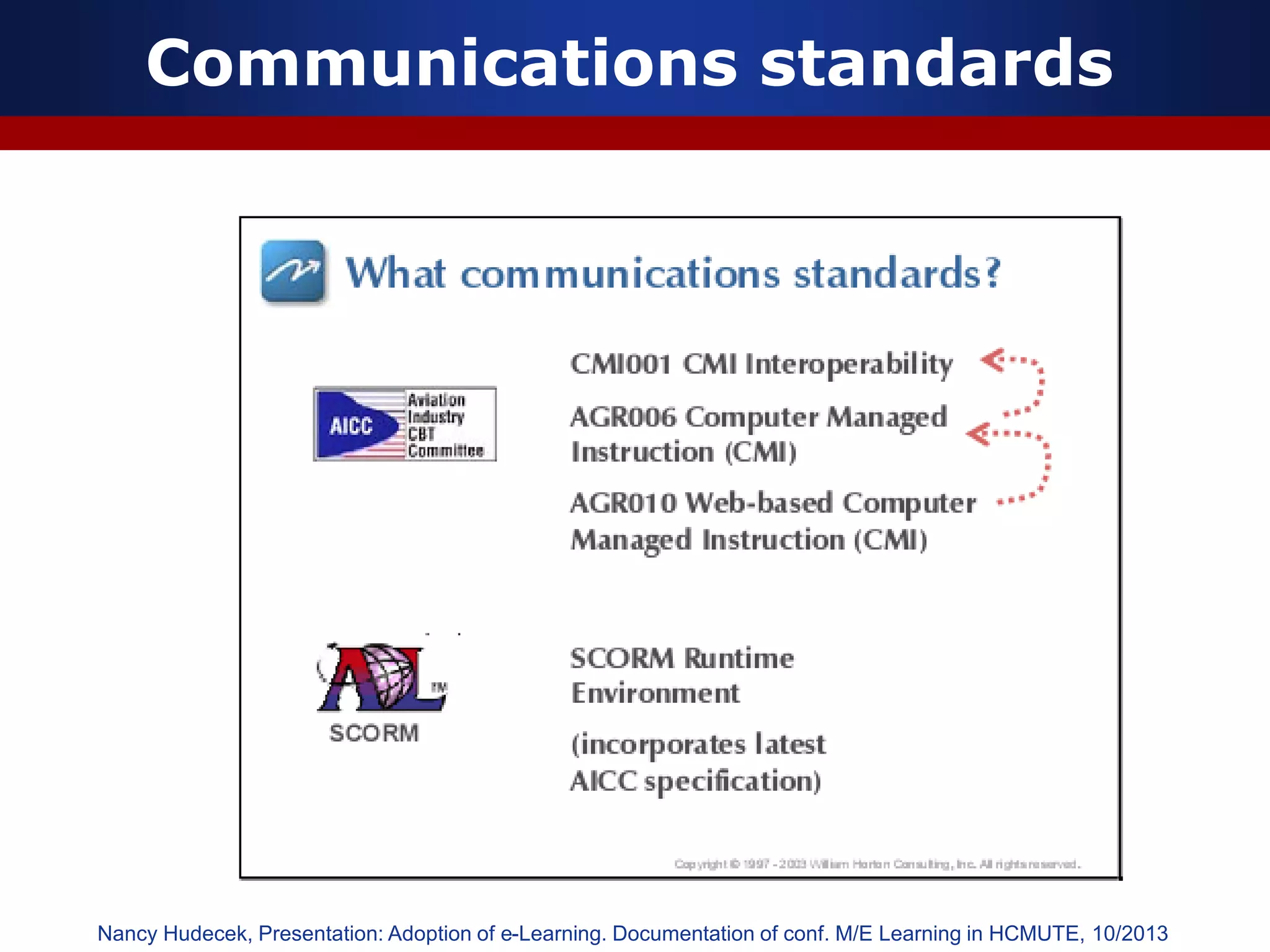
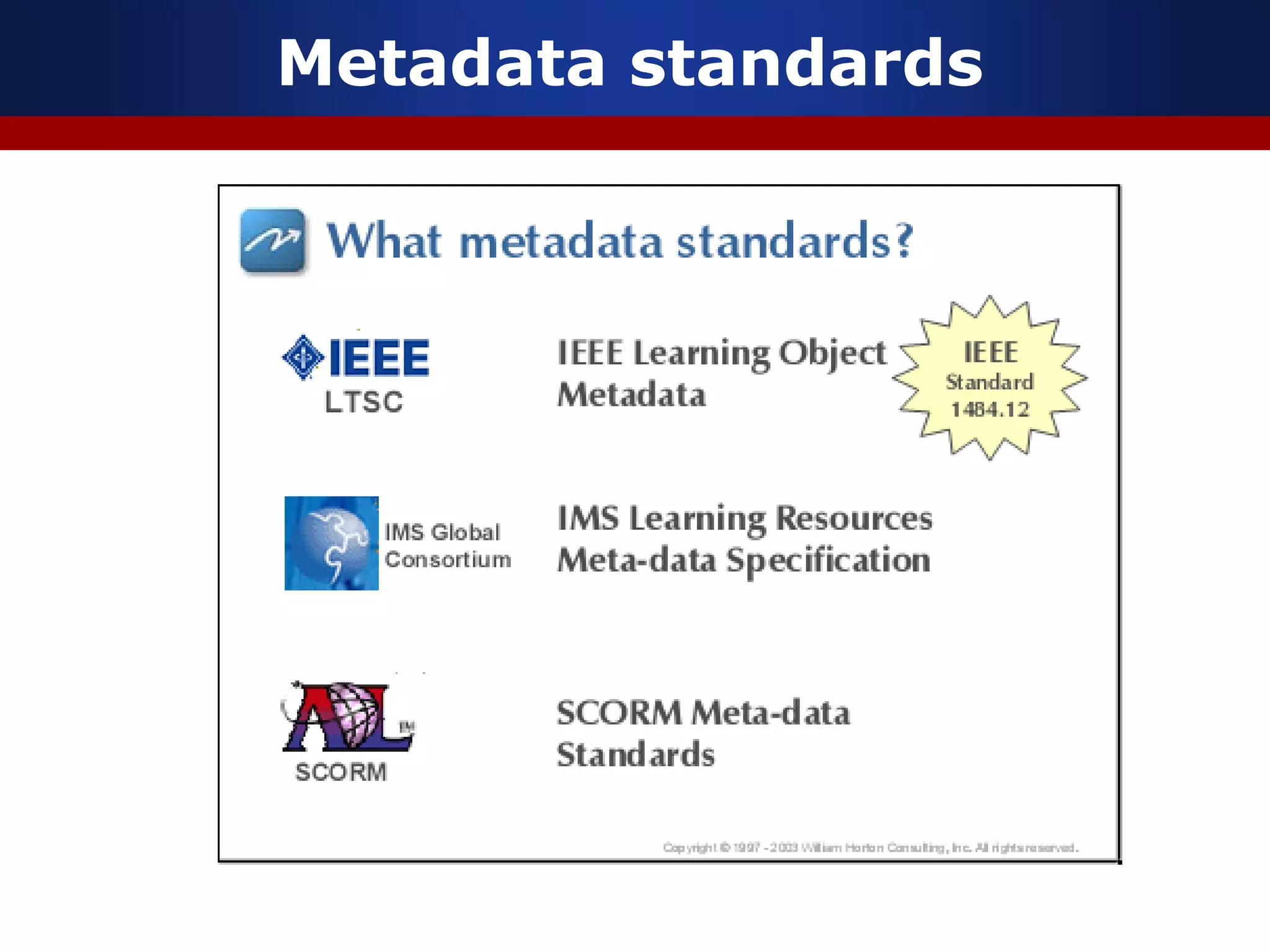
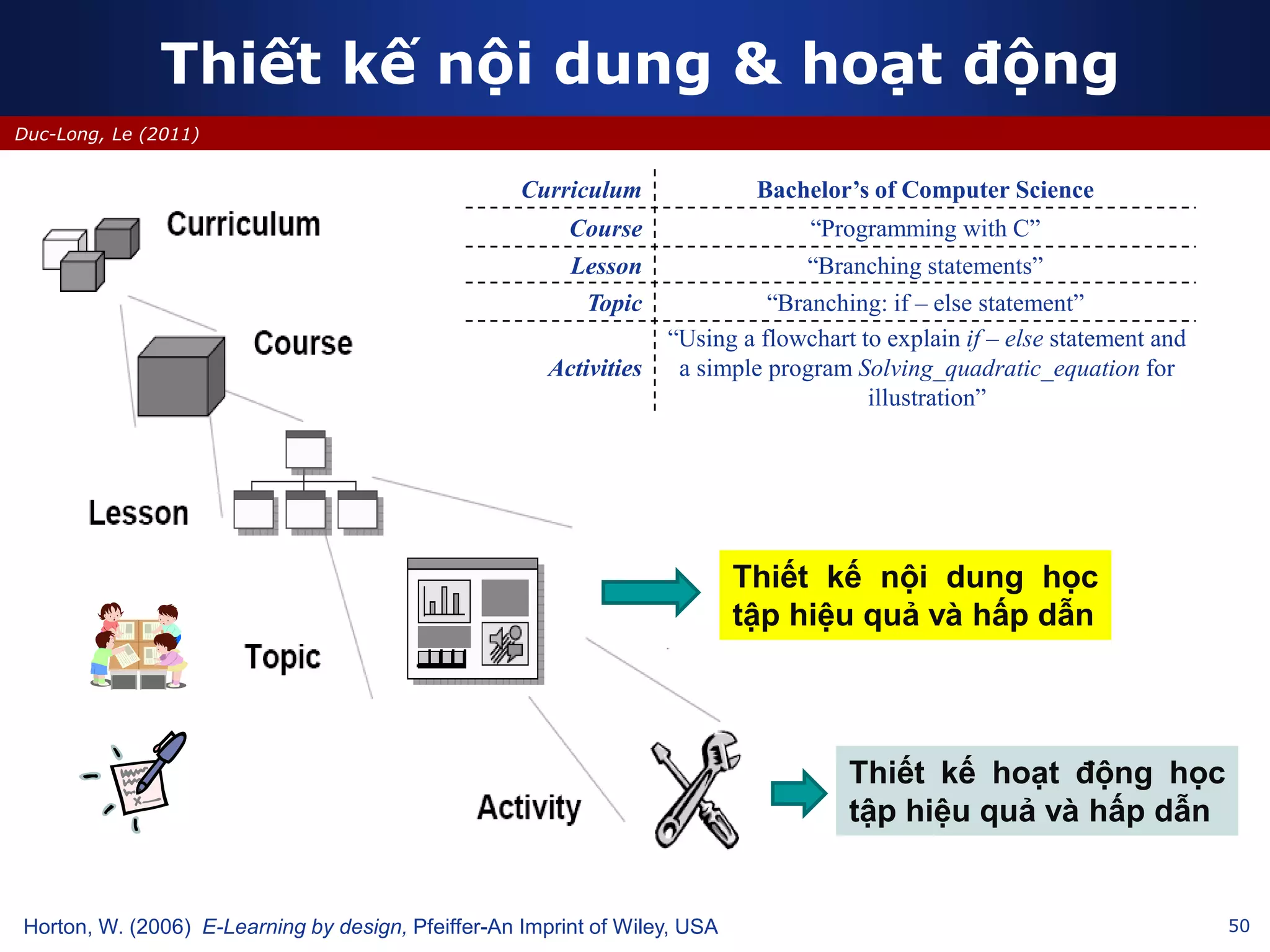
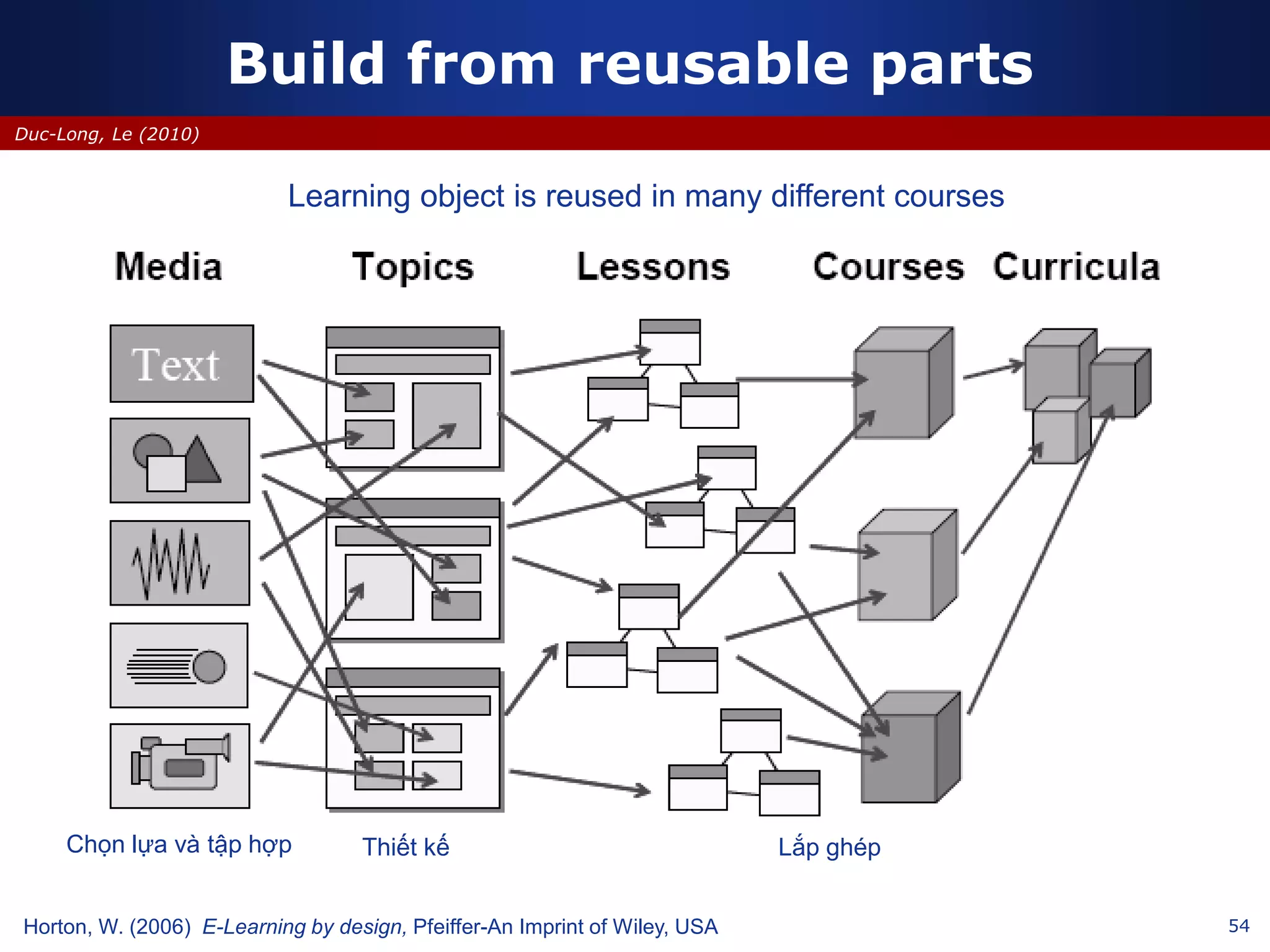
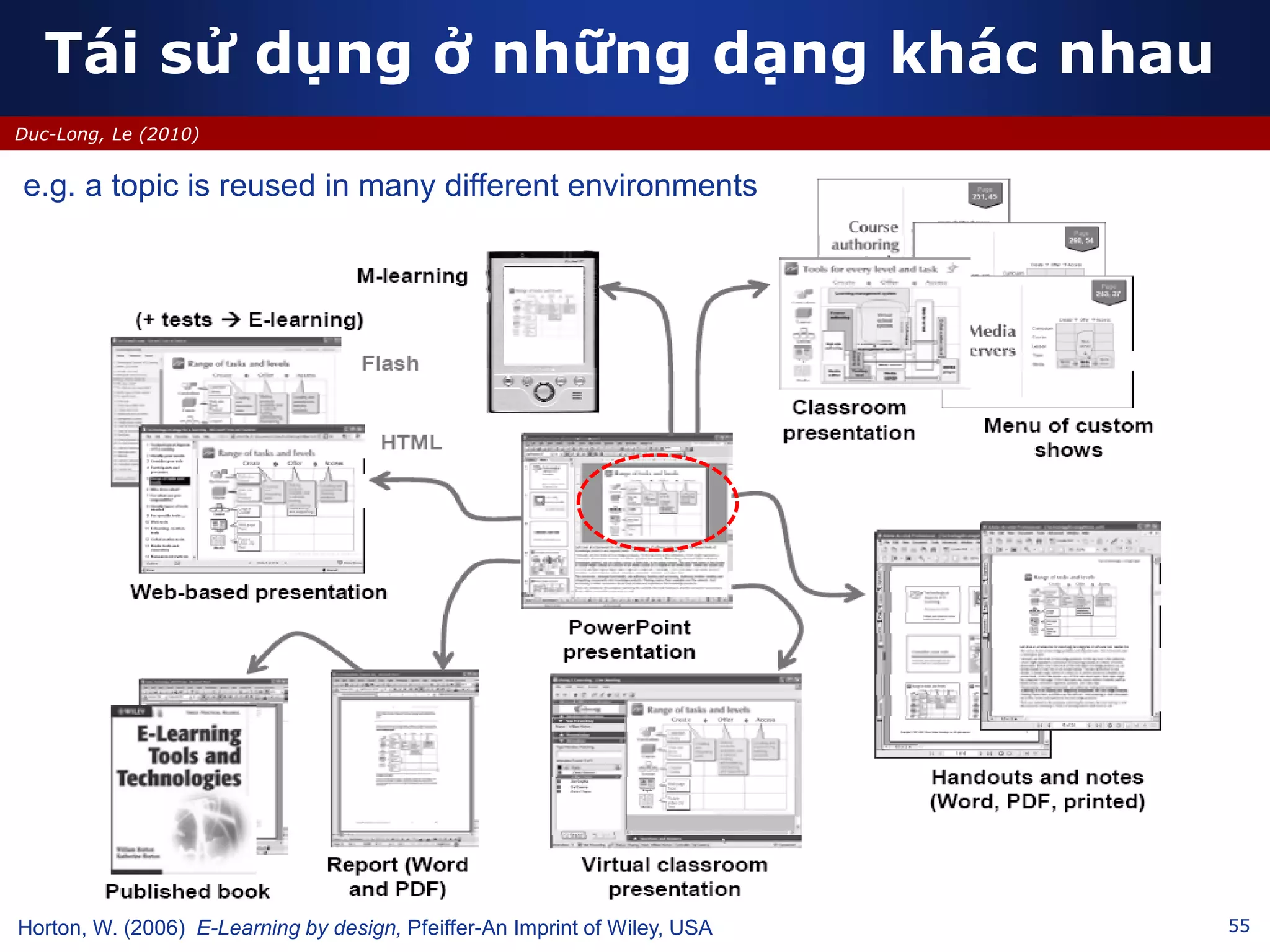
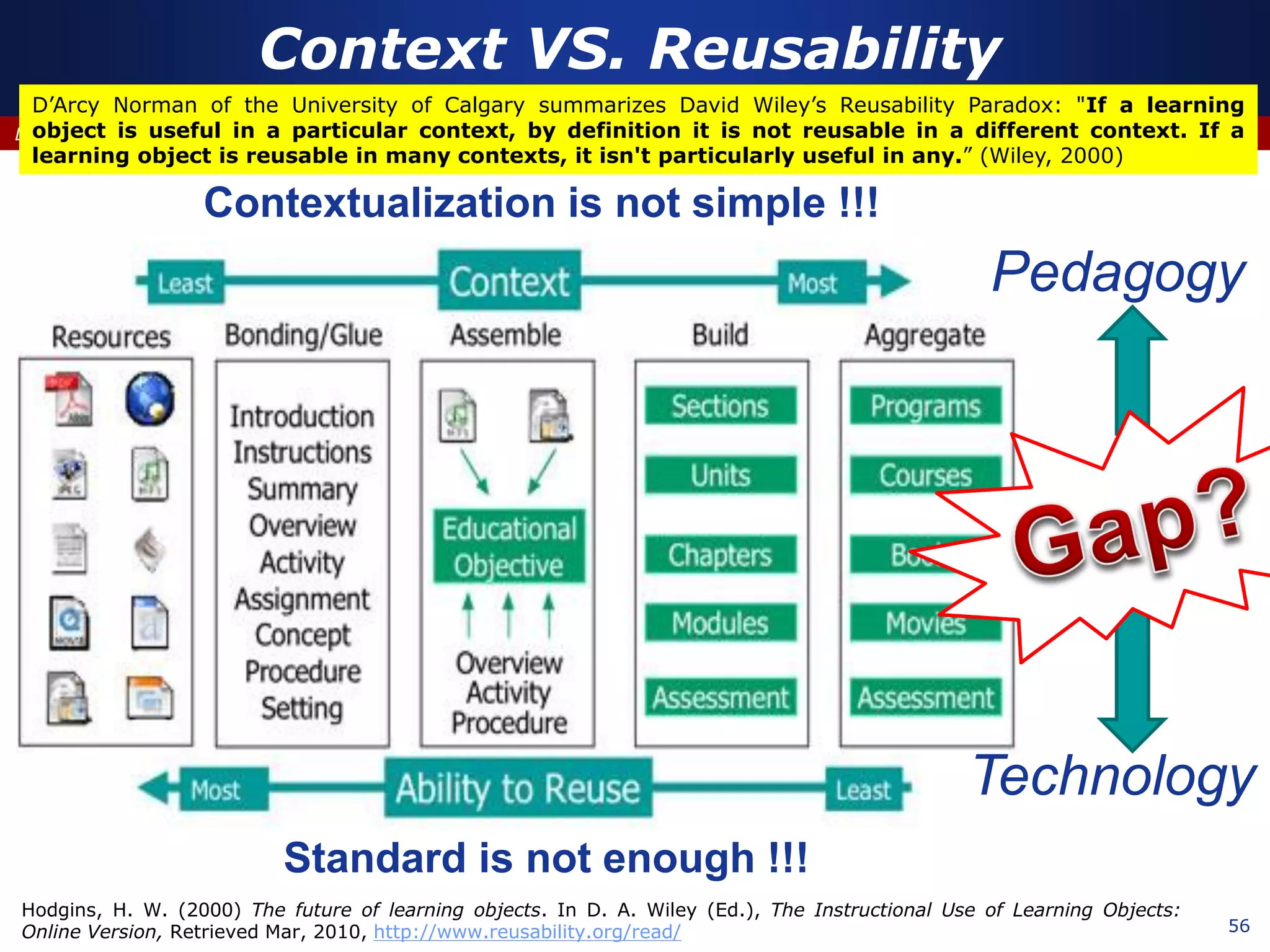
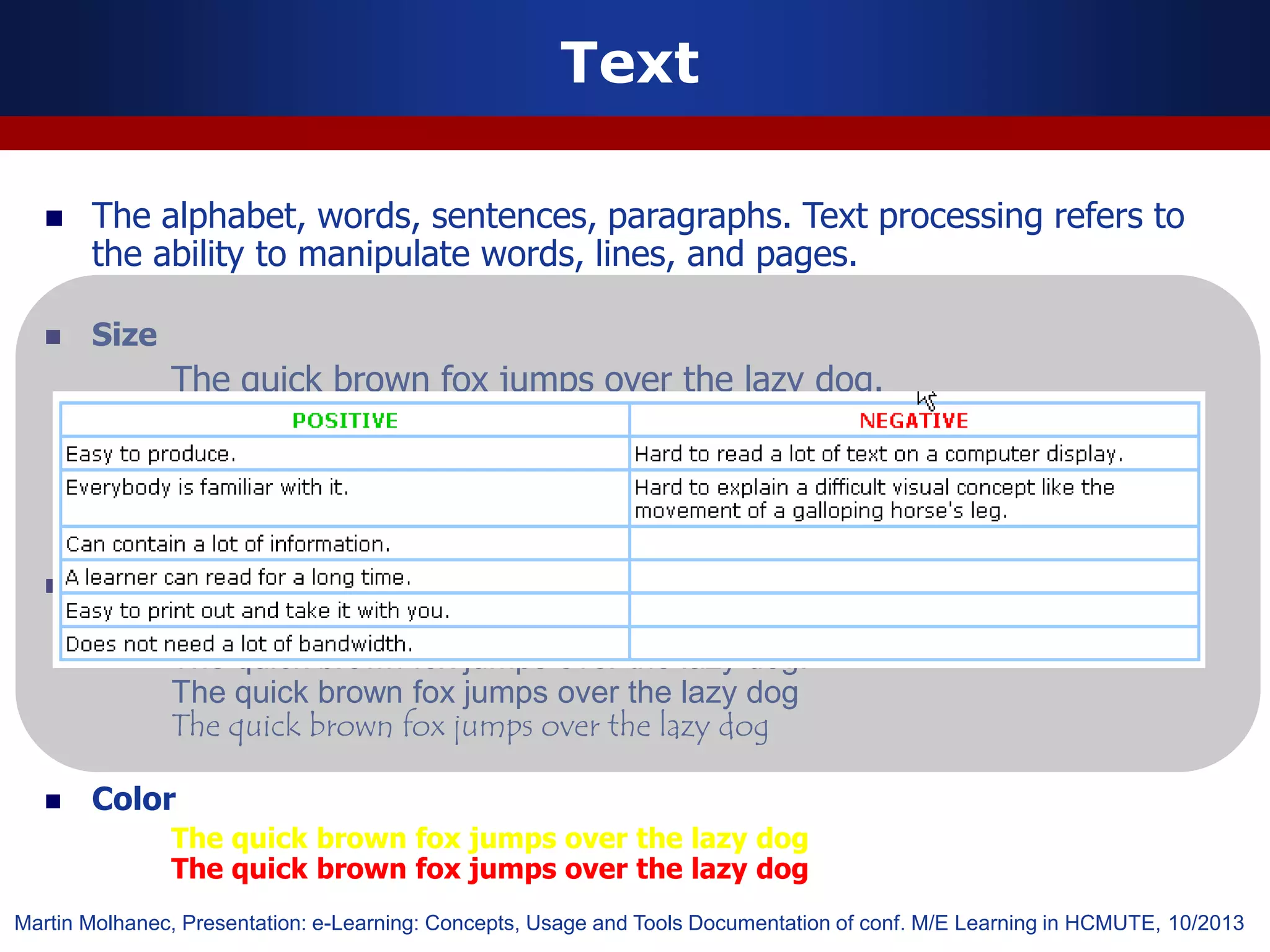
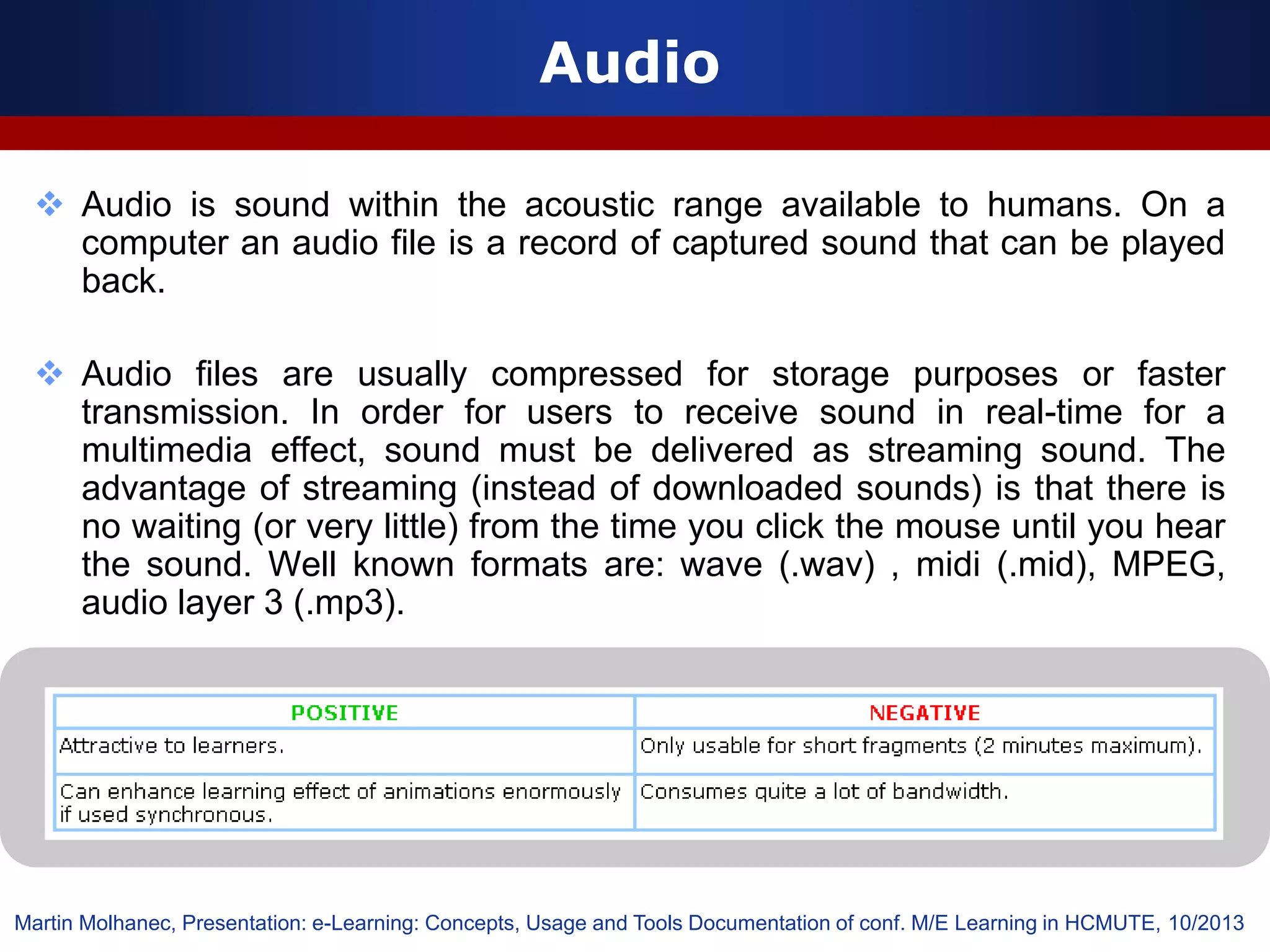
This document discusses e-learning and virtual learning environments (VLEs). It begins by defining a VLE as a computer-mediated environment for online education. Popular VLE platforms mentioned include Moodle, Atutor, Ilias, Dokeos, Sakai, and Blackboard. The document then discusses the key components of an e-learning system, including a learning management system, content management system, learning content management system, and more. It emphasizes that for an e-learning system to be successful, attention must be paid to technology, software, design, pedagogy, media, and economics. Effective content and activity design are also highlighted as important factors.