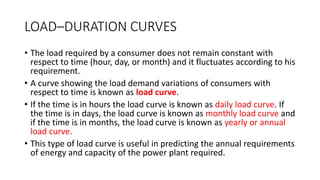
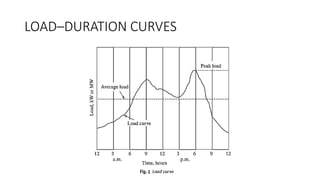
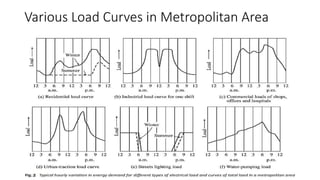
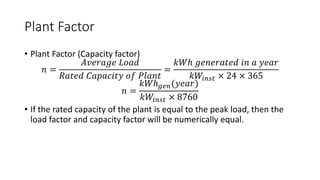
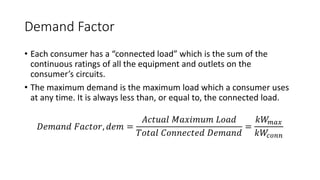
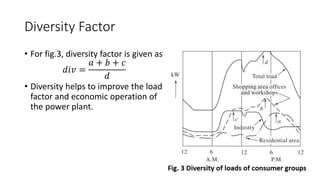
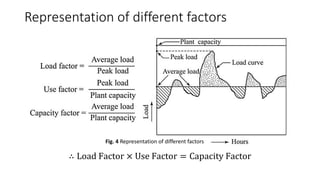
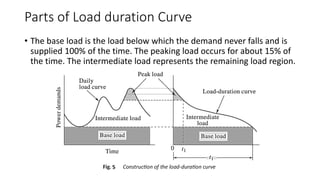
The document provides an in-depth discussion on load-duration curves and factors influencing power plant planning. It outlines the importance of load curves in predicting energy requirements, methods for determining total installed capacity, and various factors like load, demand, and diversity factors in electricity supply. The document emphasizes the economic operation of power plants, the significance of unit sizes, and the categorization of load types into base load, intermediate load, and peaking load for effective energy generation.