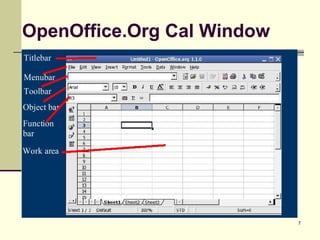
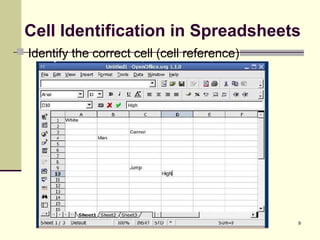
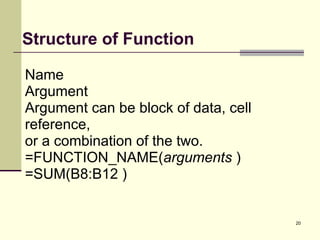
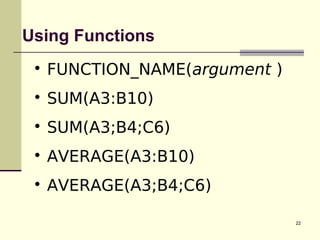
This document introduces spreadsheets and Microsoft Excel. It discusses the basics of spreadsheets including their use for organizing and analyzing large amounts of data. Key concepts covered include the spreadsheet layout, using cell references in calculations, operators like addition and subtraction, and functions like SUM and AVERAGE. Examples provided demonstrate creating a simple spreadsheet to track university expenses and using cell references and functions to calculate totals.