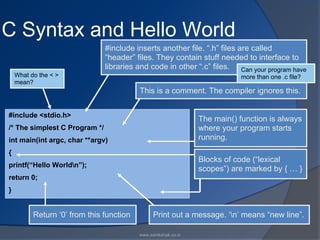
The document discusses key concepts in the C programming language including its popularity due to being robust, efficient, fast, and portable. It describes C's character set including alphabets, digits, and special symbols that can be used to form constants, variables, and keywords. Constants represent values that do not change, while variables represent unknown values. Keywords are reserved words in C that are predefined like int, long, struct, etc. The document also discusses the structure of a C program including comments, preprocessor directives, declarations, functions, and executable statements. It provides an example of a simple "Hello World" C program to print that message.


![Character Set
● A character can a number, alphabet, or
any special symbol to represent
information
Alphabets A, B, ….., Y, Z
a, b, ……, y, z
Digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Special symbols ~ ‘ ! @ # % ^ & * ( ) _ - + =
|{}[]:;"'<>,.?/
www.eshikshak.co.in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3gettingstartedwithc-110822101504-phpapp01/85/Lecture-3-getting_started_with__c_-3-320.jpg)