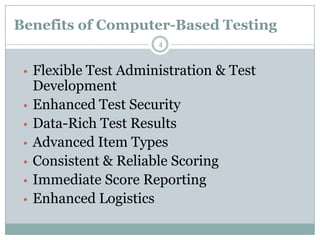
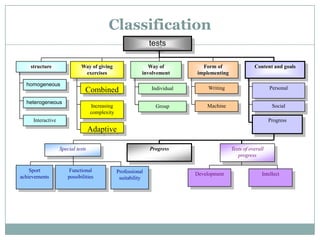
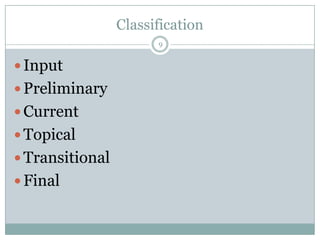
This document discusses computer-based assessment (CBA), also known as computer-based testing. CBA involves administering tests electronically, where responses are recorded and assessed using computers. The document outlines the benefits of CBA, such as flexible administration, enhanced security, and immediate scoring. It also describes different types of tests, including objective and subjective tests, and provides guidelines for developing valid and reliable CBA tests. Key aspects addressed include defining learning objectives, structuring test questions, designing an assessment, and evaluating the validity of the final computerized test.