Embed presentation
Downloaded 45 times


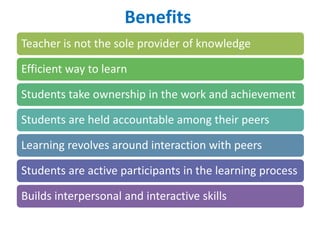
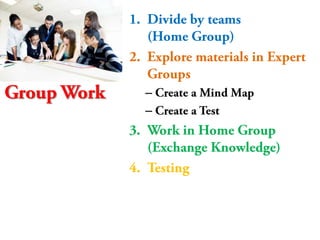




The jigsaw technique is a teaching method invented by Elliot Aronson in 1971 where students are divided into groups and each student is assigned a subtopic to learn. Students then join "expert" groups with students from other home groups learning the same subtopic. After researching their subtopic, students return to their home groups to teach their peers what they have learned. The benefits of this technique include that the teacher is not the sole provider of knowledge, it is an efficient way for students to learn, and it promotes accountability and interaction among peers during the learning process.







