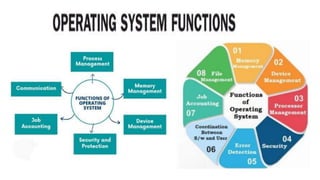
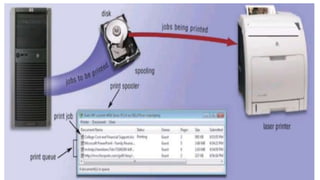
This document provides information about system software and operating systems. It defines system software as instructions that control and maintain computer programs and devices. It identifies two main types of system software as operating systems and utility programs. It then describes key functions and examples of operating systems, including stand-alone, network, and embedded operating systems. It also discusses some common standalone utility programs.