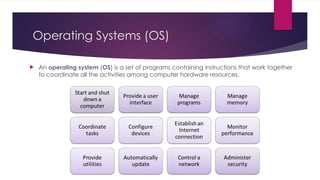
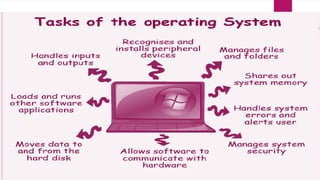
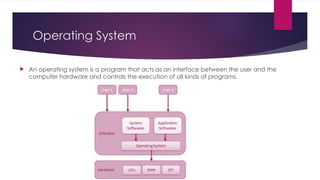
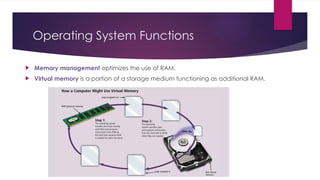
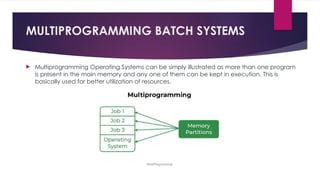
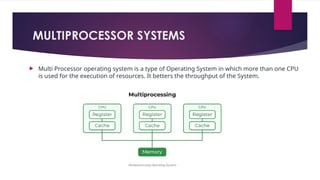
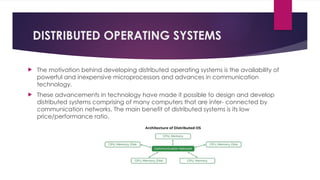
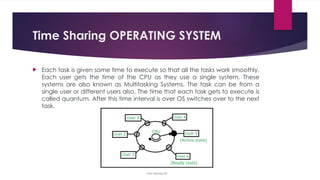
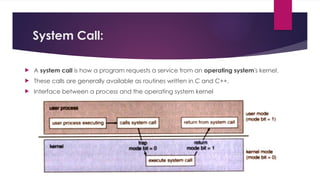
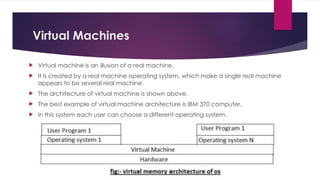
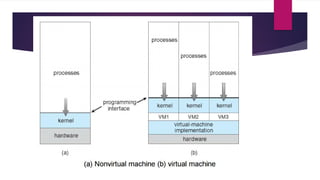
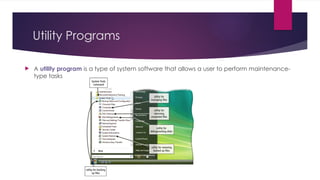
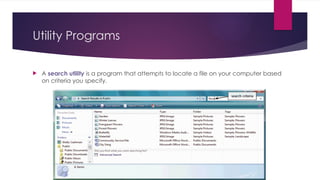
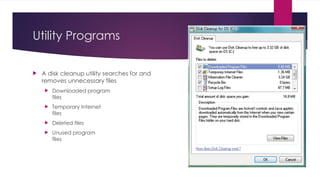
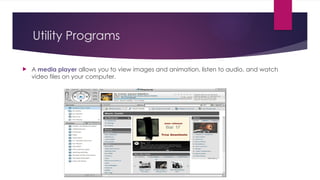
The document provides an overview of operating systems (OS), detailing their definition, functions such as memory and file management, security, and hardware control. It describes various types of OS including batch systems, multiprogramming systems, and real-time systems, along with their features and disadvantages. Additionally, it outlines utility programs that assist users in maintaining their systems, highlighting functions like file management, disk cleanup, and media playback.