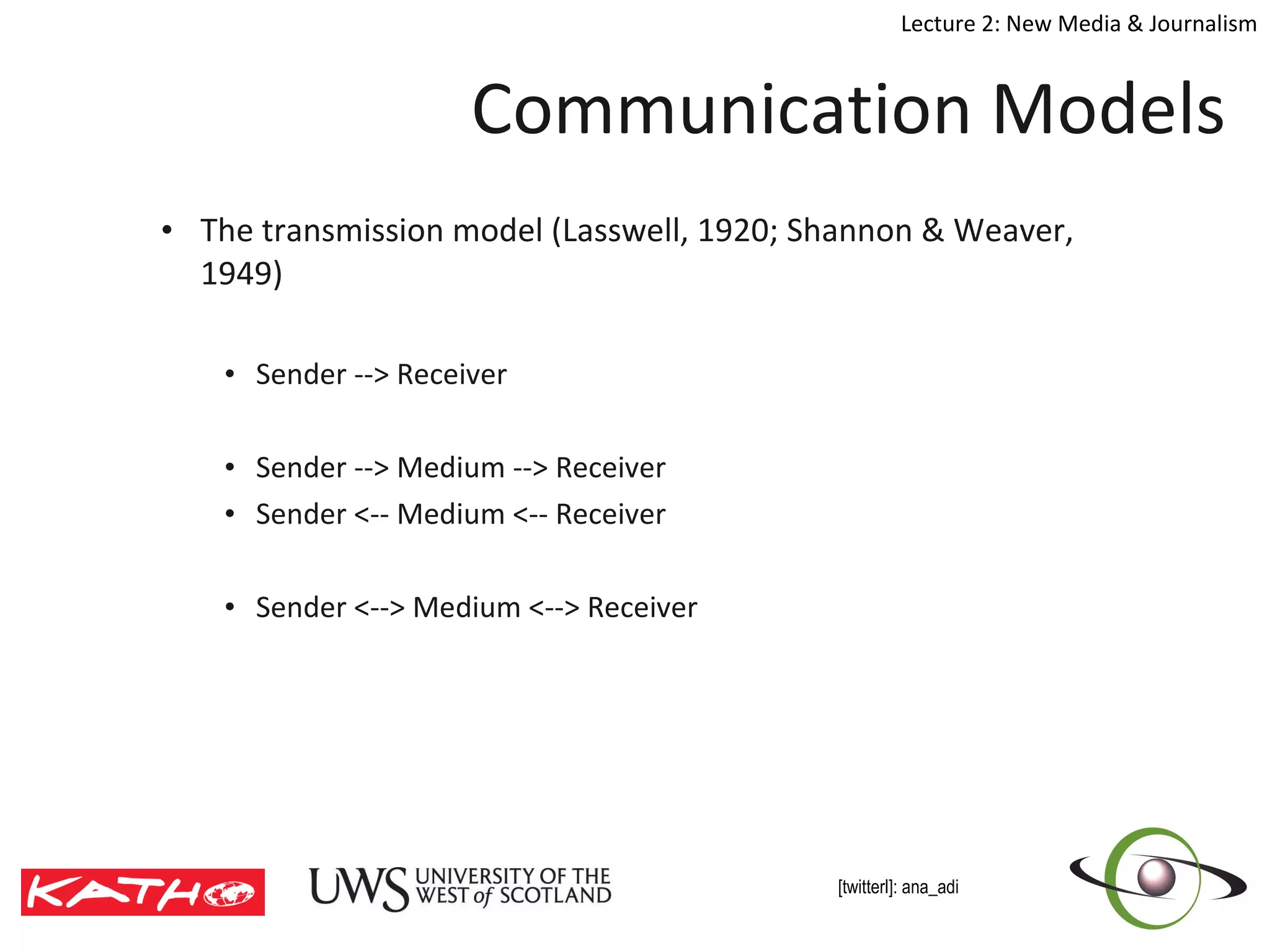
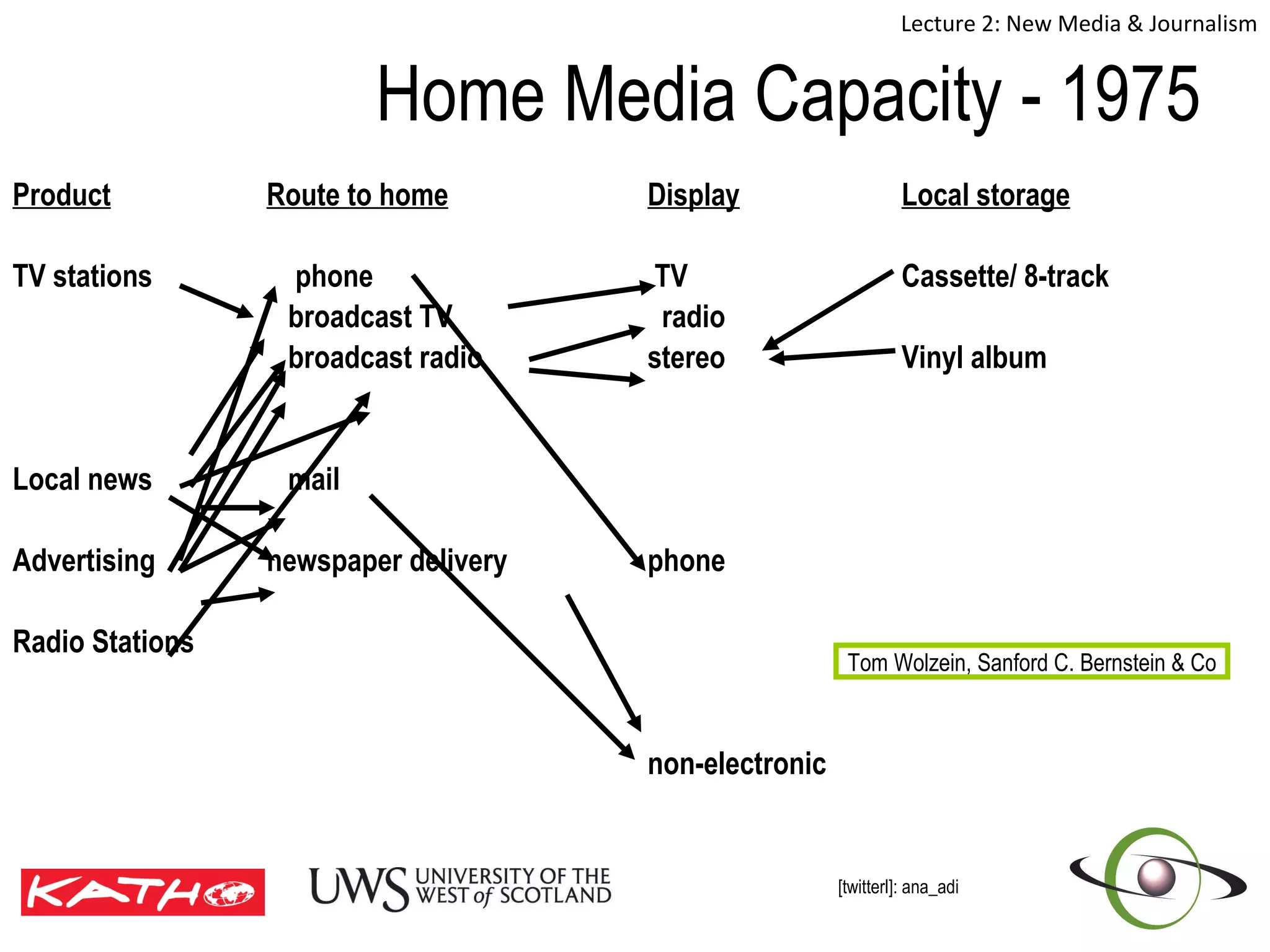
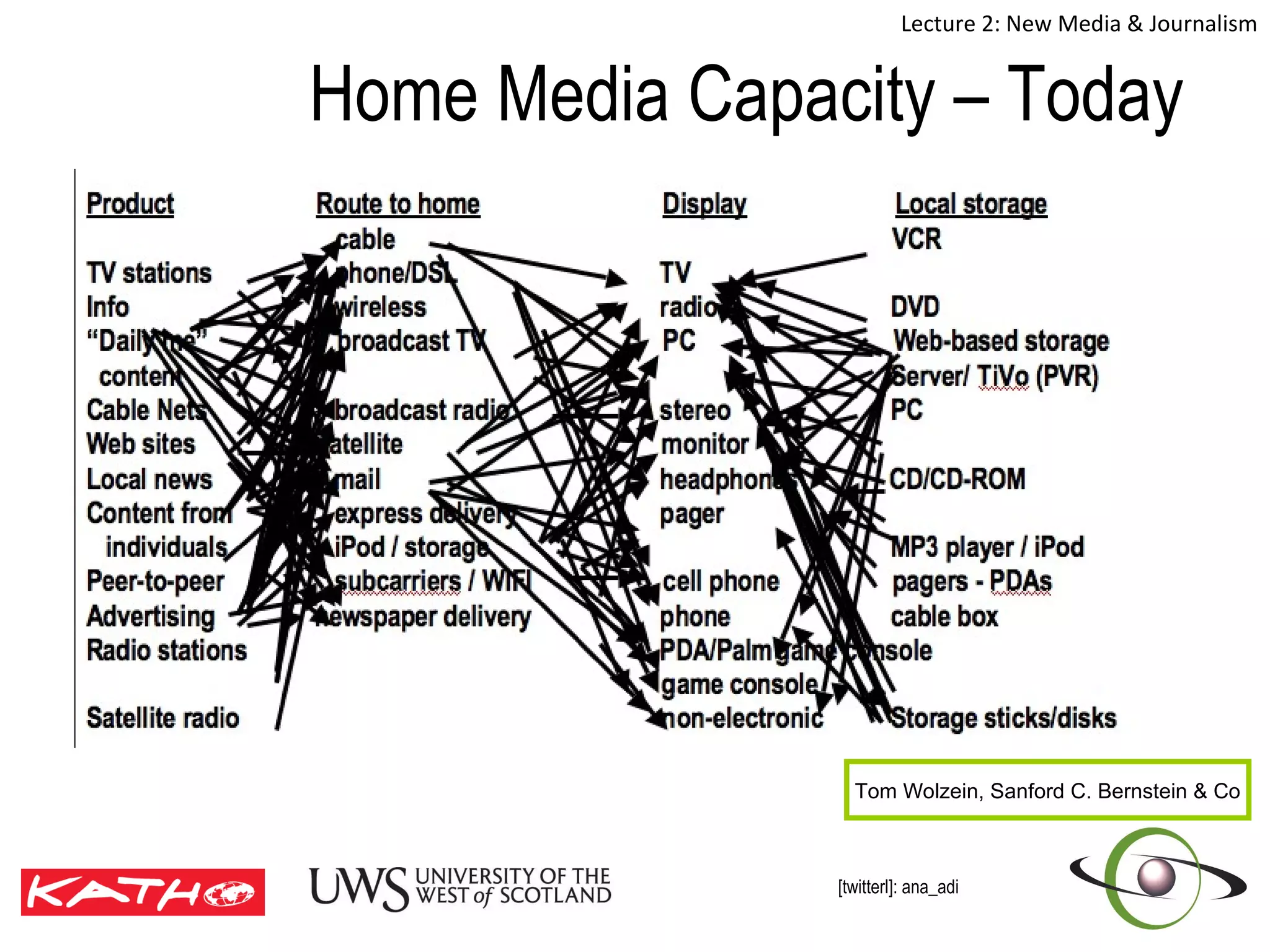
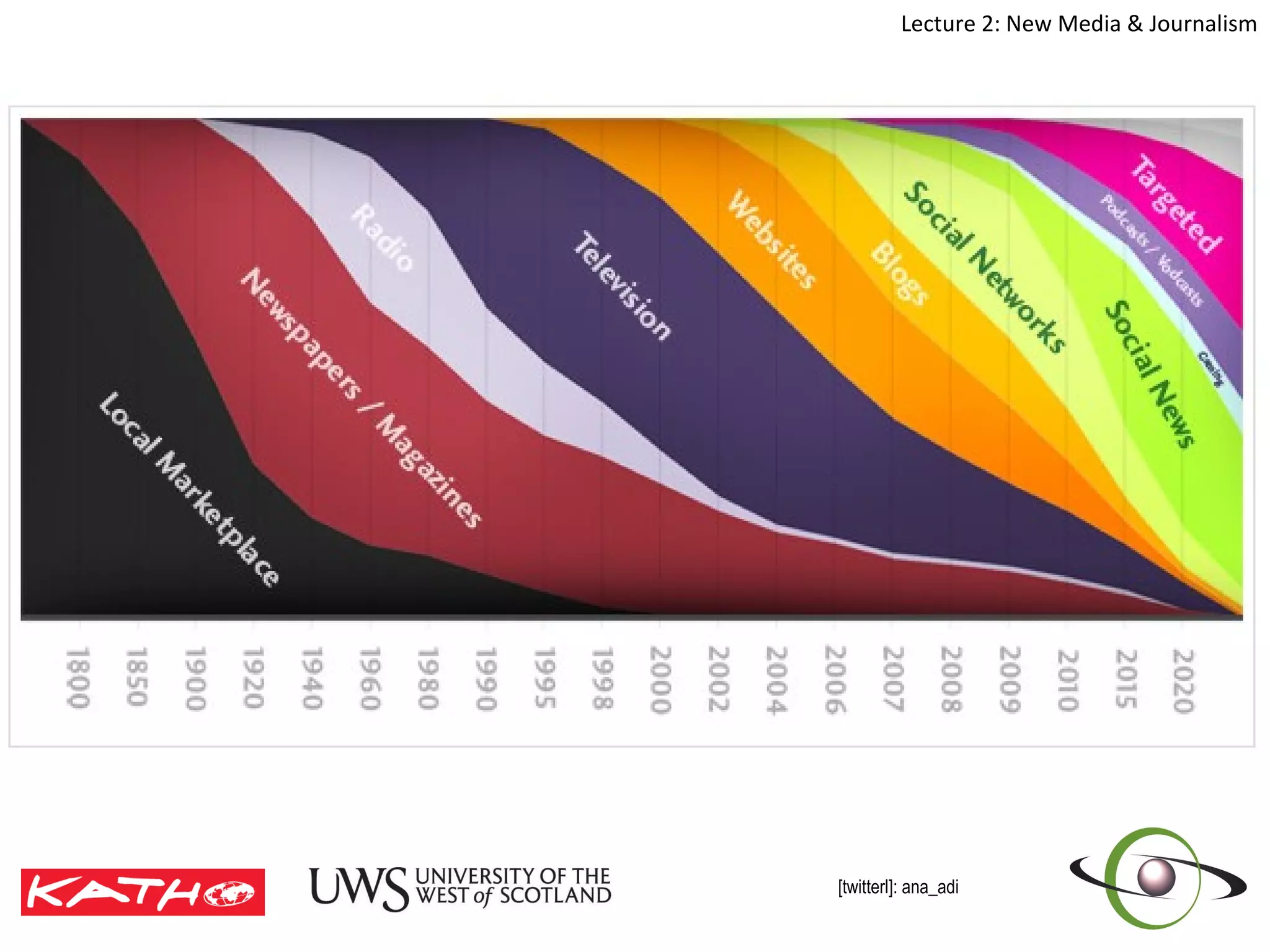
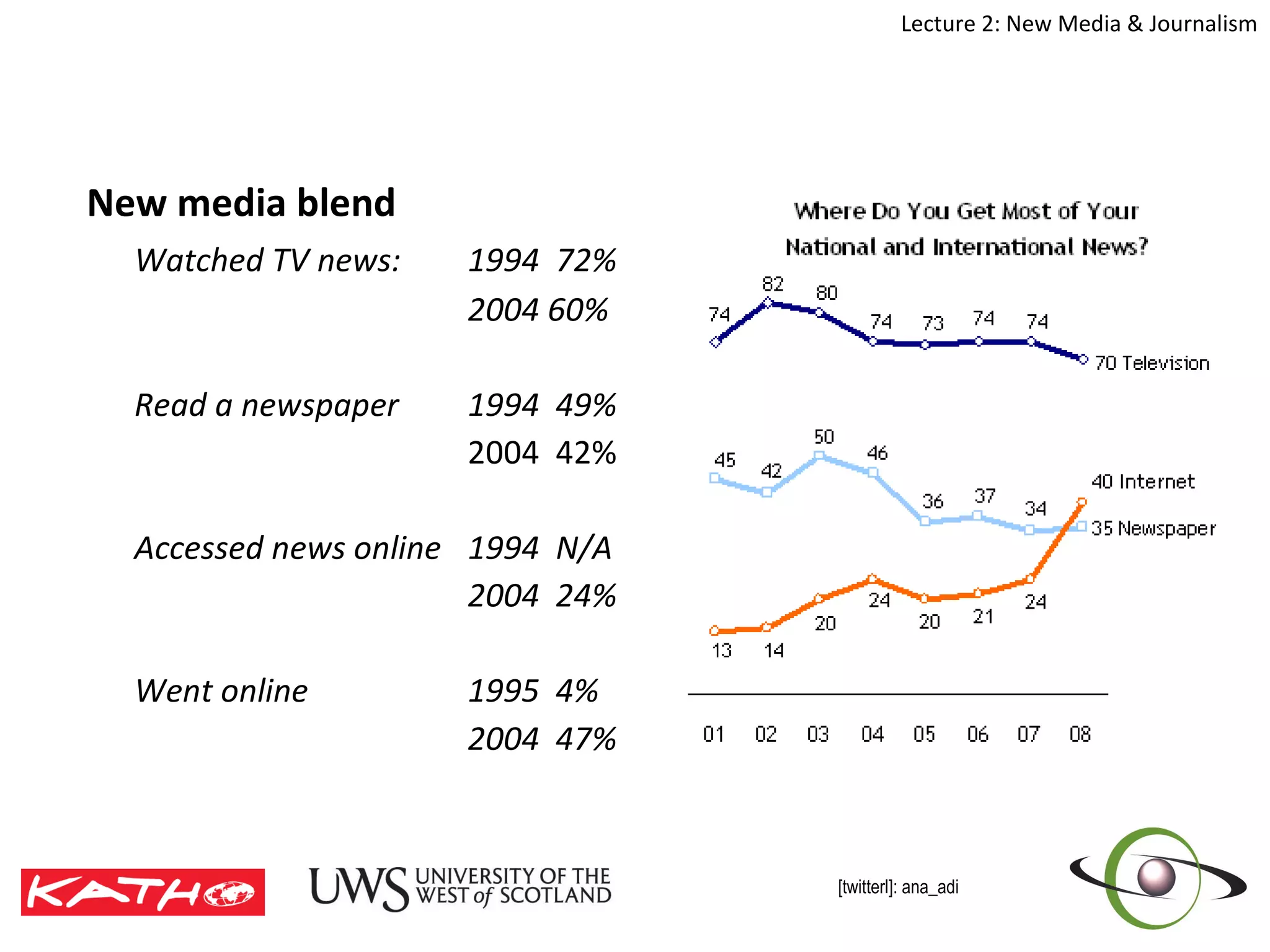
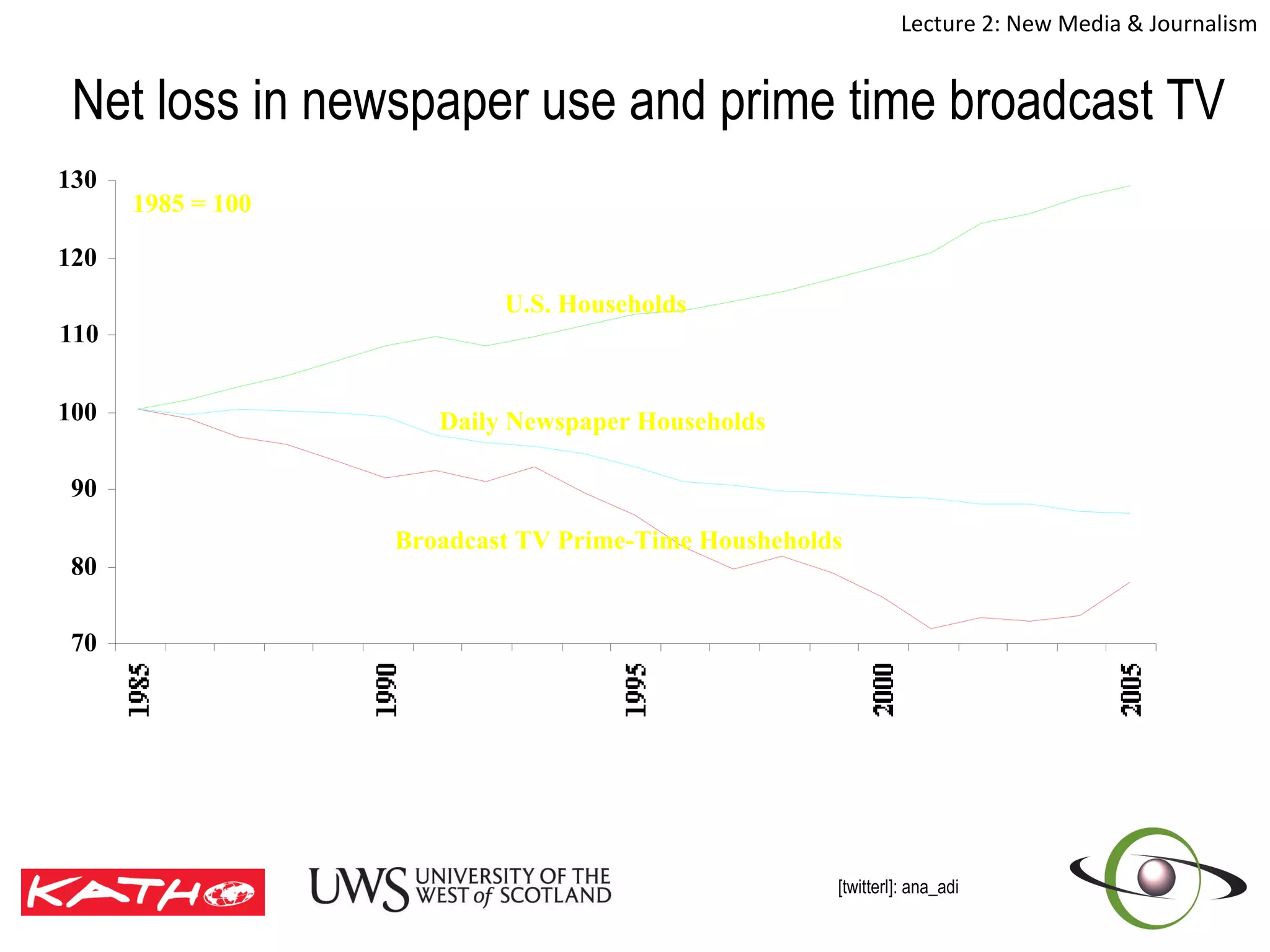
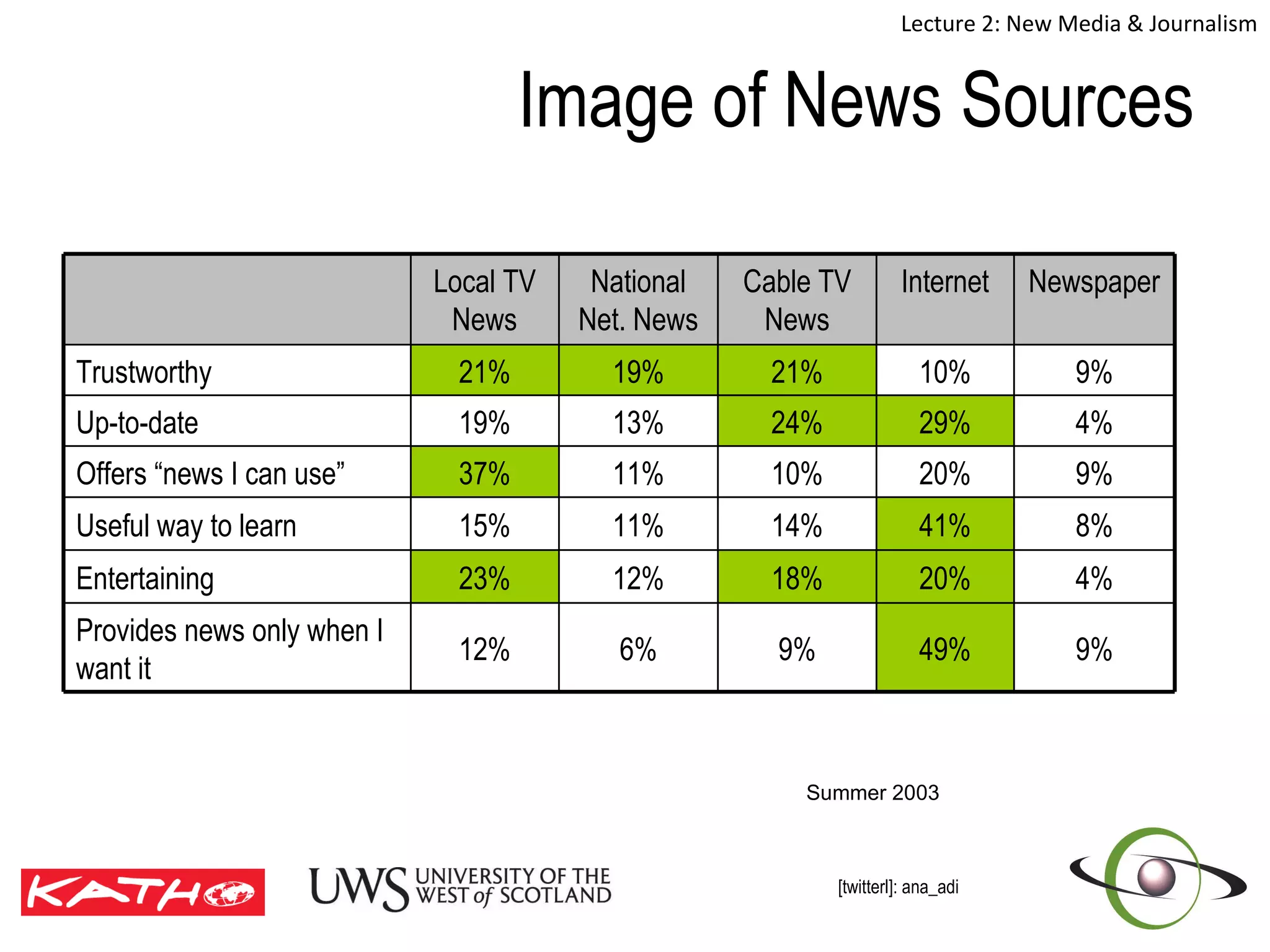
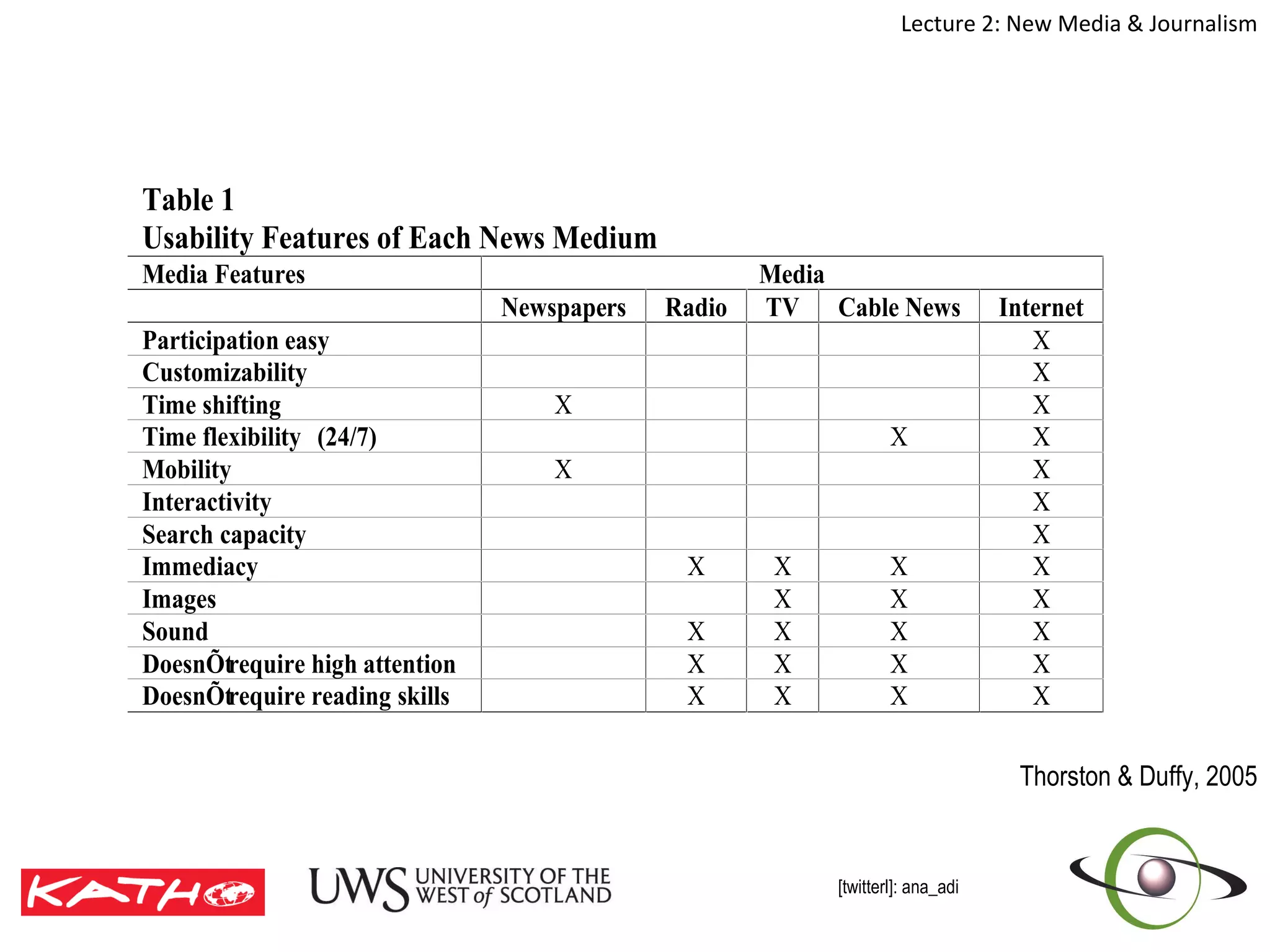
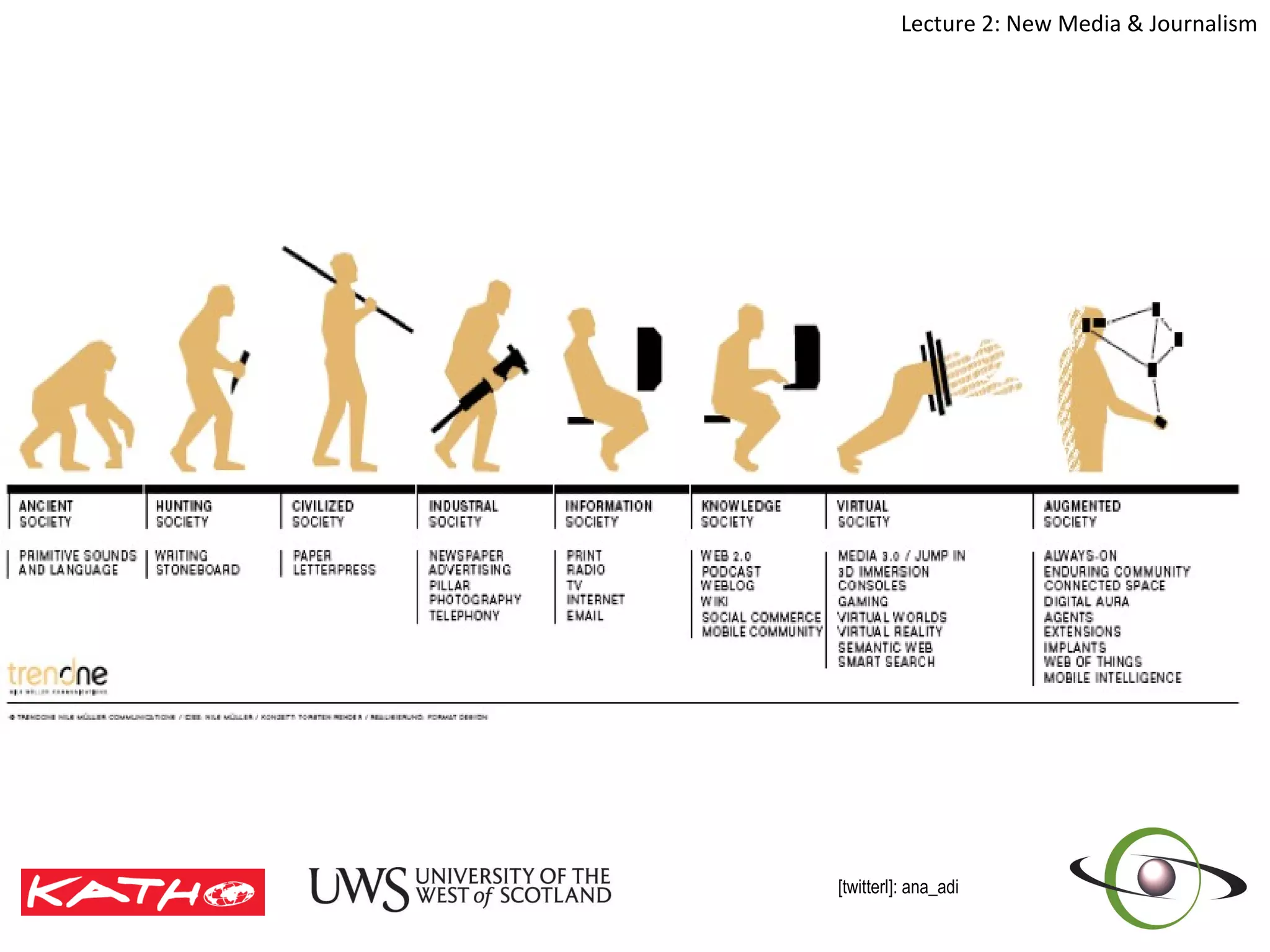
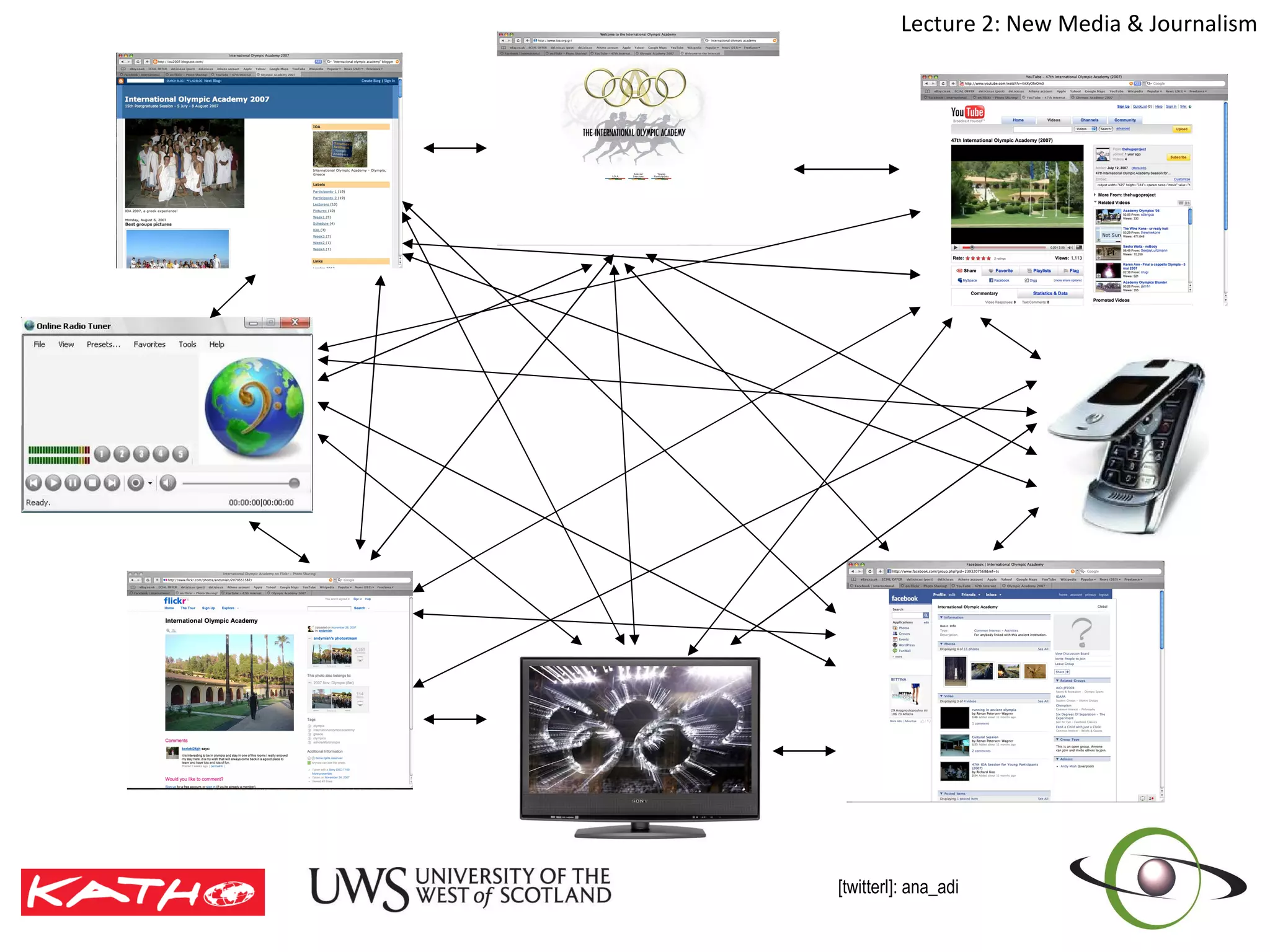
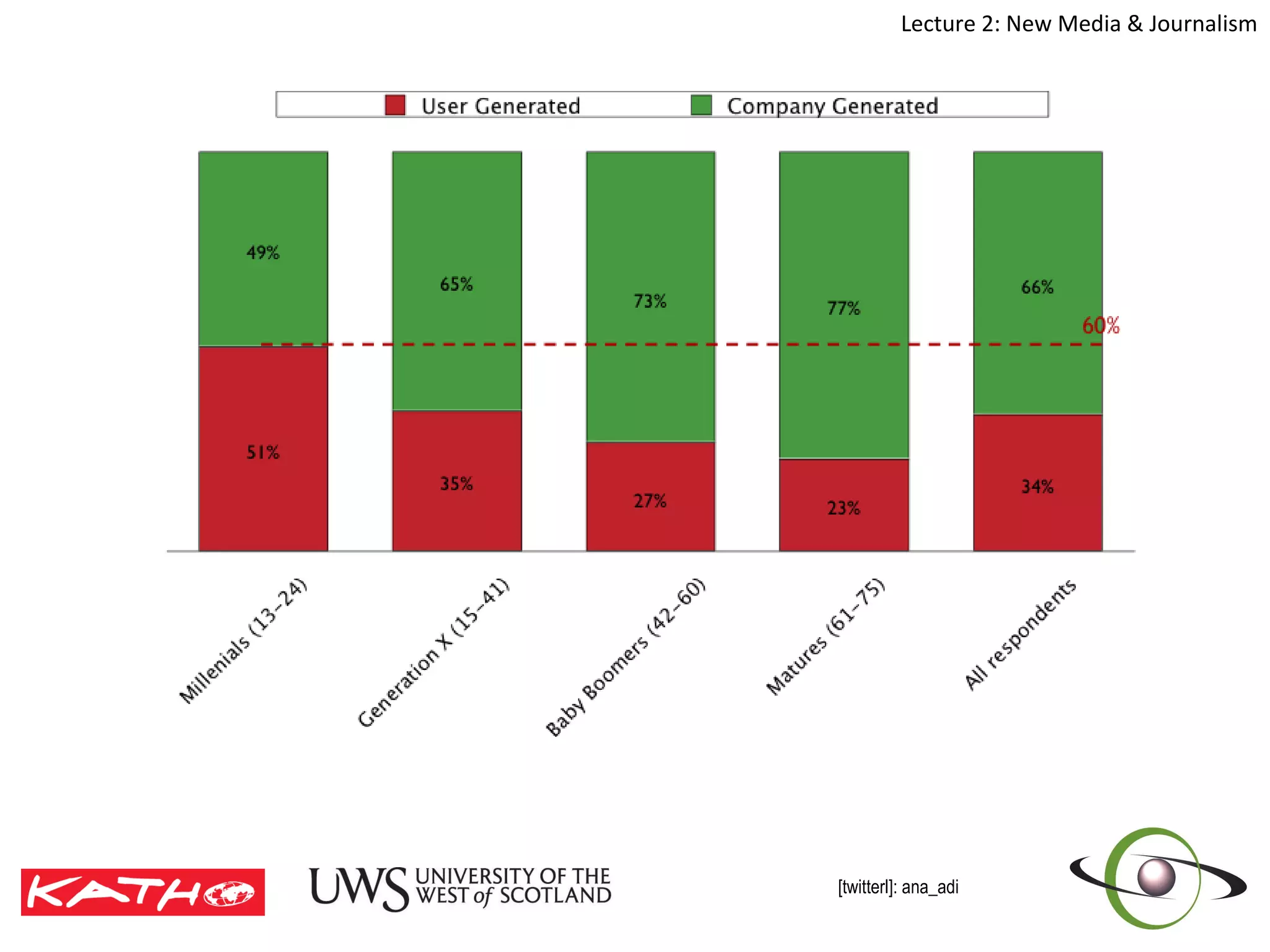
This document discusses the challenges posed to traditional media by new media in the online age. It defines media as both a technology that enables communication as well as the social and cultural practices surrounding that technology. It analyzes changes in the media landscape and their implications for journalism practice. Specifically, it notes that new media have blurred lines between producers and consumers of news and raised questions around objectivity, autonomy, and ethics for journalists. Citizen journalism is emerging as an addition to traditional forms.