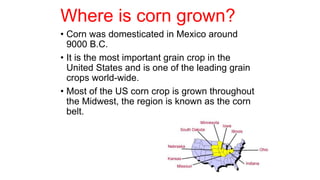
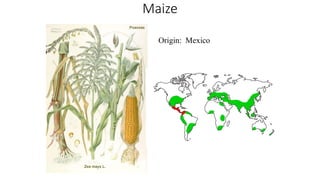
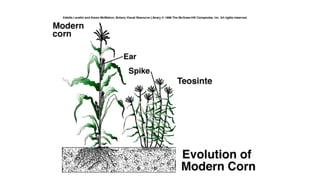
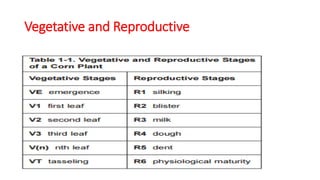
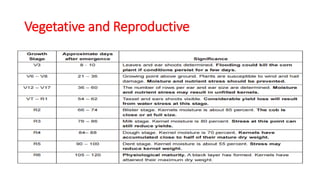
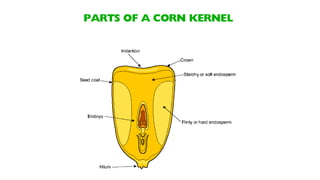
1) The document provides an overview of maize (corn) production, including what it is, where it's grown, different types, and cultural practices for growing it.
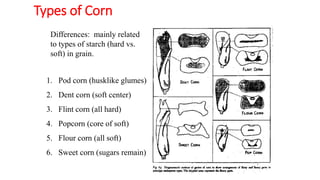
2) There are six main types of corn classified based on kernel characteristics, with the most common being dent corn, flint corn, and sweet corn.
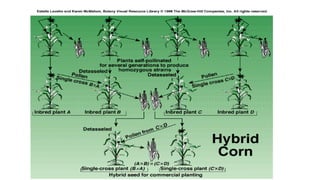
3) Hybrid corn varieties produce higher yields than open-pollinated varieties and have greater resistance to diseases, insects, and drought.