The document discusses various topics related to computer applications and history. It provides information on:
1) How computers are used in different areas of business like marketing, stock exchanges, banks, payroll, inventory etc.
2) A brief history of computing from abacuses before 1500s to the development of modern computers.
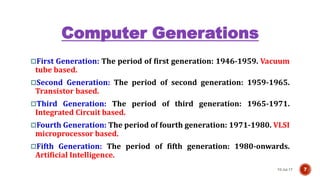
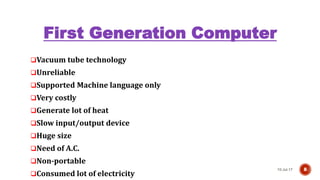
3) The five generations of computers from the first generation using vacuum tubes to the current fifth generation using artificial intelligence.
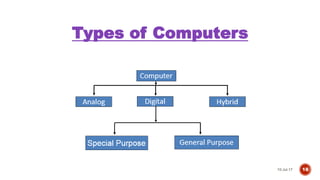
4) Types of computers like analog, digital and hybrid computers, and classifications based on size like microcomputers, minicomputers, mainframes and supercomputers.