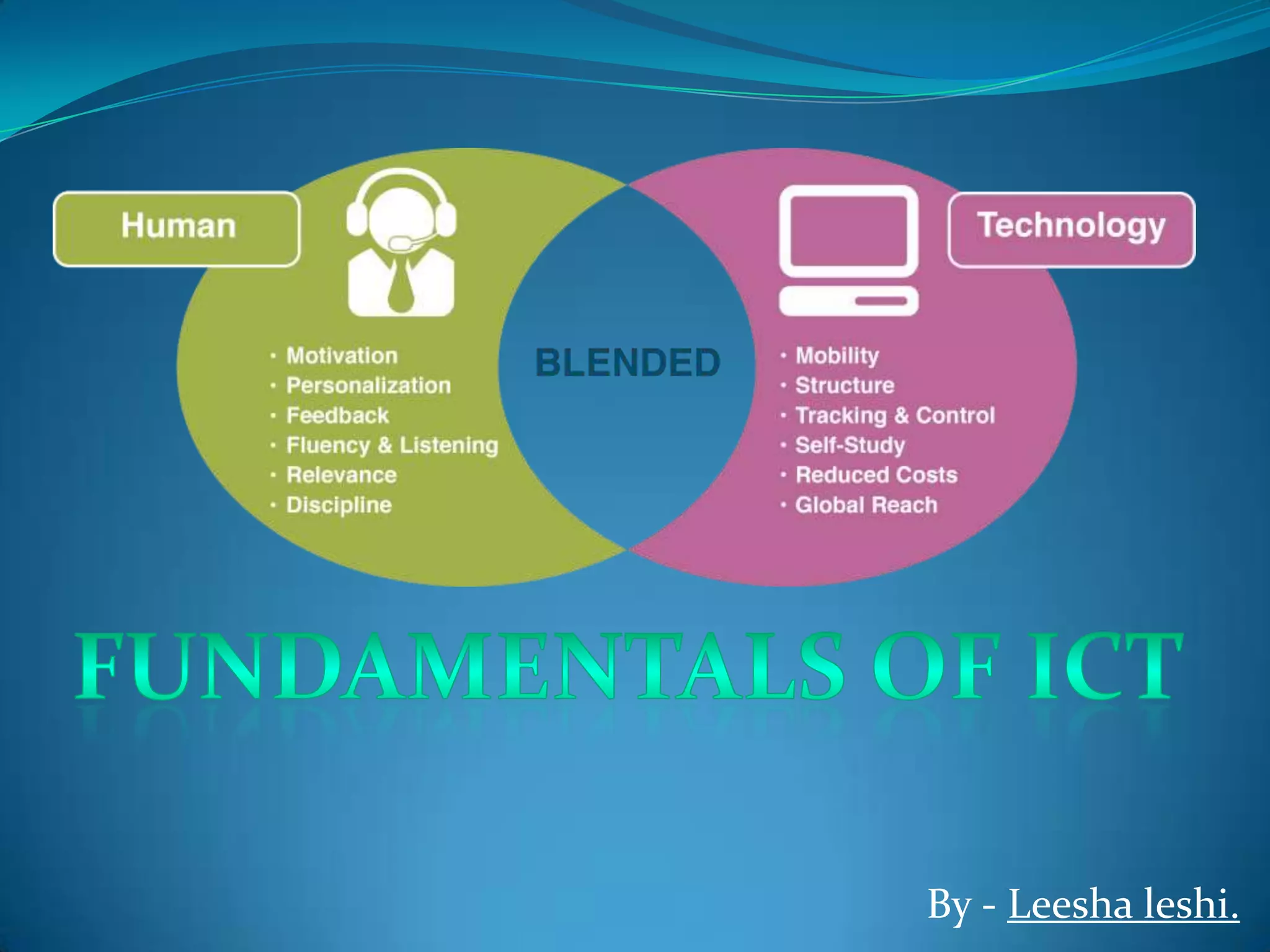
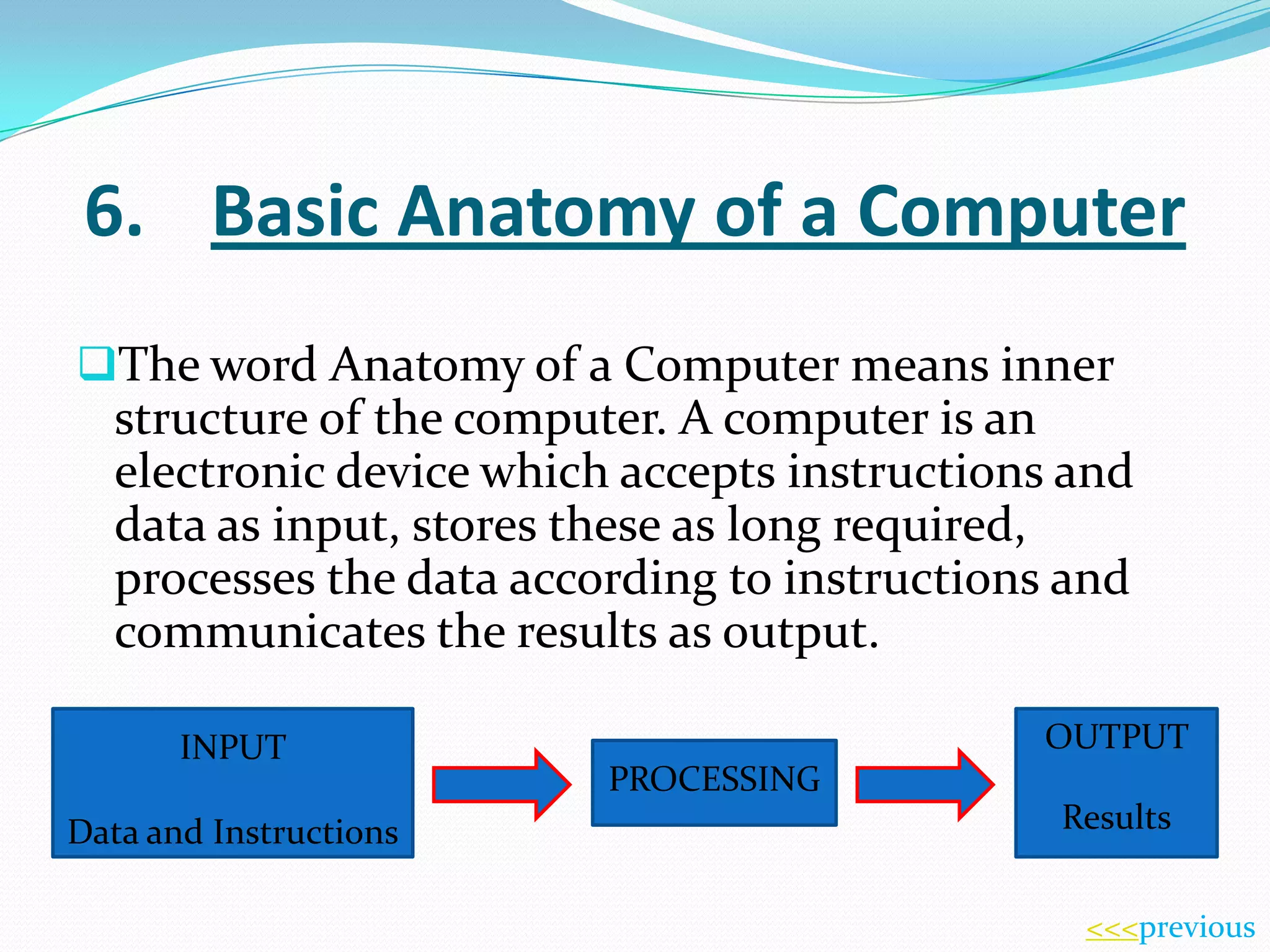
This document provides an introduction to information and communication technology (ICT). It discusses how ICT has become an important part of modern society and is used across many fields like education, banking, transportation, medicine, and engineering. It then provides an overview of computers, including their basic parts and anatomy. It describes how computers process and store data accurately and quickly. Finally, it explains that computers need instructions in the form of software and input from users to perform tasks and produce output.