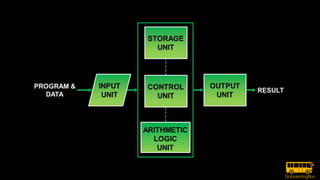
This document provides a comprehensive introduction to computer science, covering essential concepts such as computer systems, types of computation, and types of computing including personal, client/server, and cloud computing. It explains the function of computers, hardware and software distinctions, and the roles of operating systems. Additionally, it discusses various categories of cloud computing services like SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS, alongside a breakdown of computer components and the advantages of computer science.