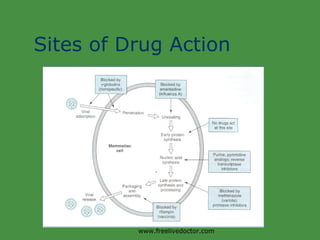
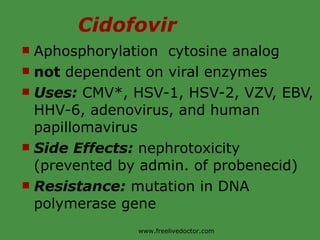
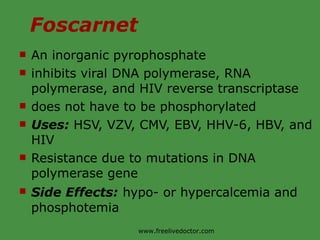
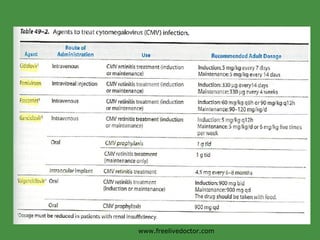
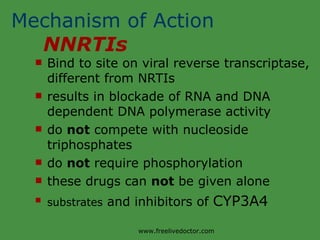
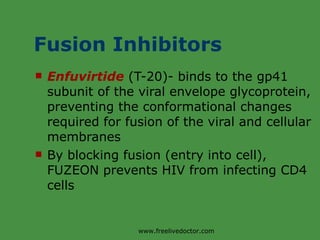
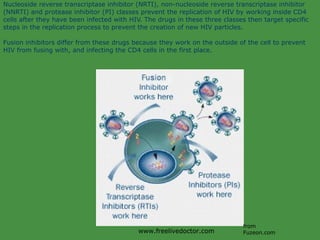
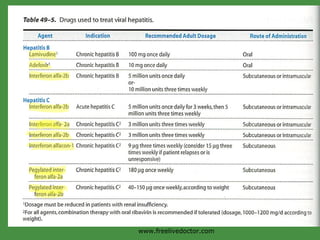
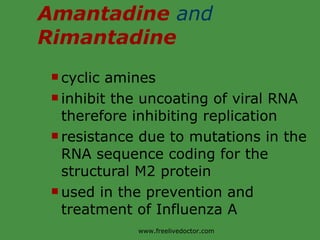
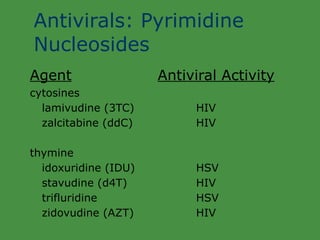
Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that rely on host cell machinery to replicate. Antiviral drugs work by blocking different stages of the viral replication cycle, either inside or outside infected cells. Common antiviral classes include nucleoside analogs, which interfere with viral DNA/RNA synthesis, and protease/reverse transcriptase inhibitors for HIV. Side effects depend on the specific agent but can include bone marrow suppression, renal toxicity, and gastrointestinal issues.