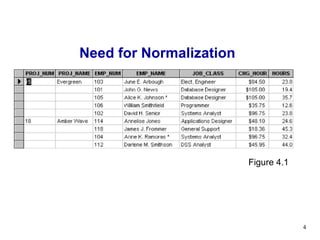
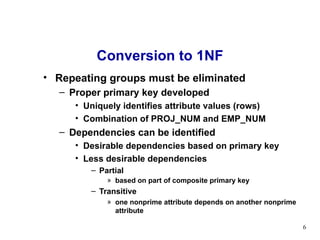
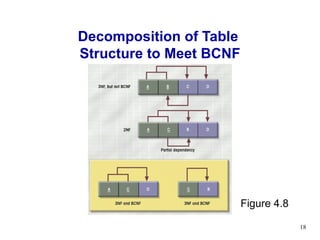
The document discusses normalization of database tables. It covers normal forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF and 4NF. The process of normalization reduces data redundancies and helps eliminate data anomalies. Normalization is done concurrently with entity-relationship modeling to produce an effective database design. In some cases, denormalization may be needed to generate information more efficiently.