The document provides an overview of database normalization through 6 levels:
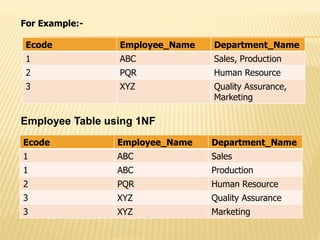
1) First normal form (1NF) removes repeating groups from tables.
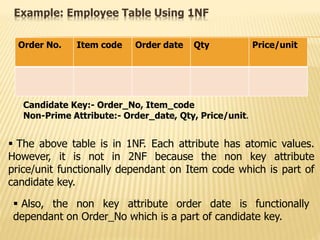
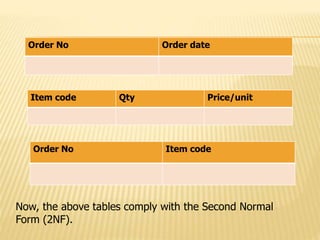
2) Second normal form (2NF) removes partial dependencies from tables that are in 1NF.
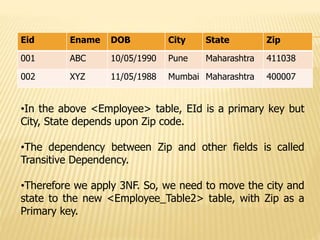
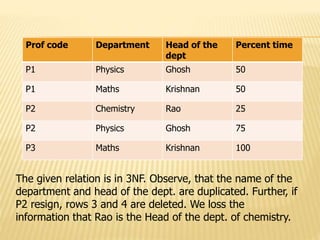
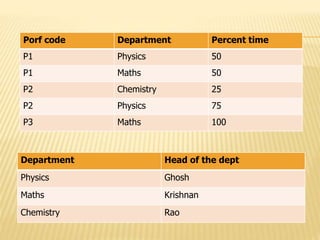
3) Third normal form (3NF) removes transitive dependencies from tables that are in 2NF.
4) Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF) deals with certain types of anomalies not handled by 3NF.
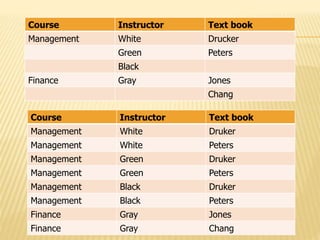
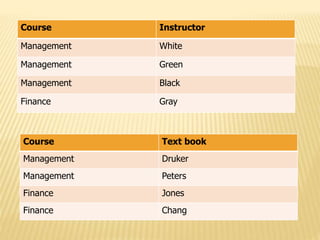
5) Fourth normal form (4NF) removes multivalued dependencies from tables in BCNF.
6) Fifth normal form (5NF) relates to join dependencies that cannot be decomposed losslessly into two tables.