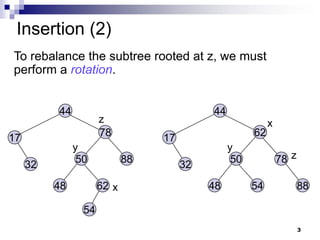
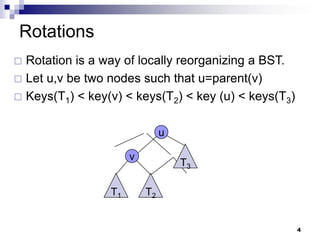
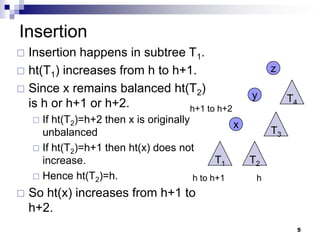
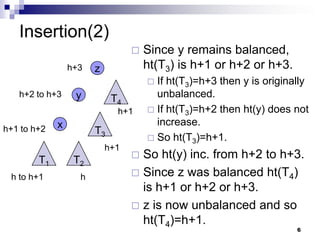
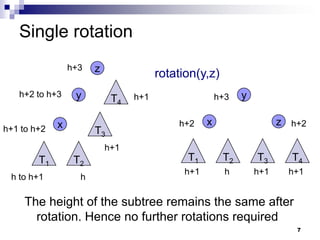
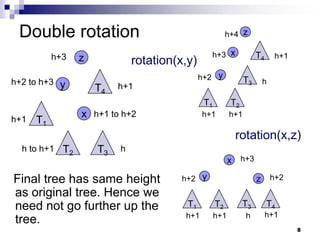
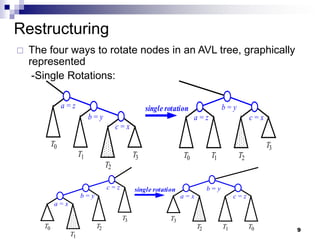
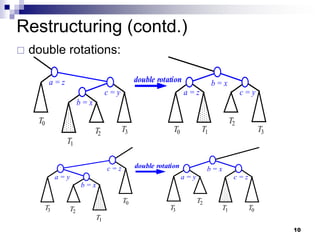
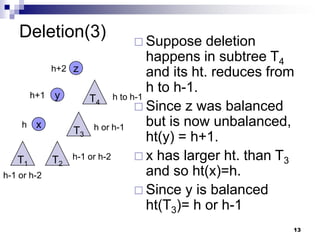
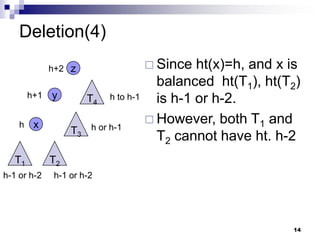
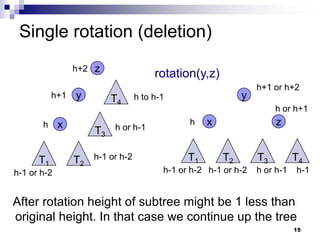
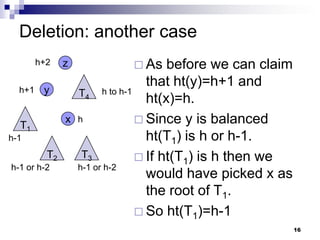
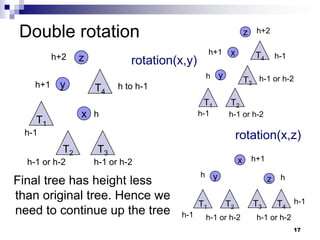
AVL trees are self-balancing binary search trees. They ensure that the height of the two subtrees of any node never differs by more than one. This balance is achieved through rotations during insertion and deletion operations. Rotations locally reorganize the tree to maintain heights differing by at most one. Both insertion and deletion in AVL trees take O(log n) time due to the potential need to traverse heights up to O(log n) during rebalancing rotations.