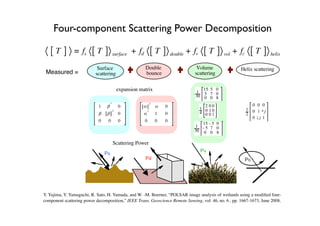
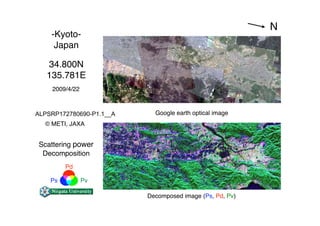
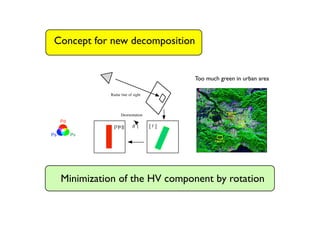
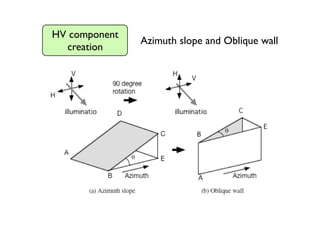
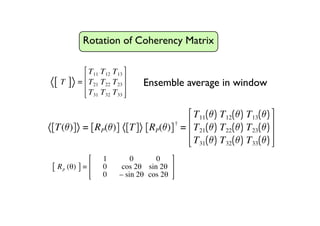
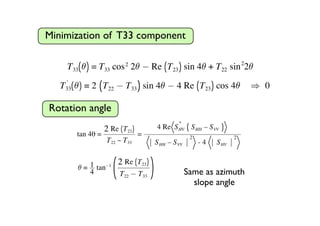
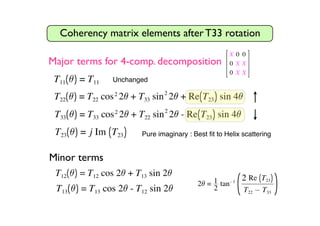
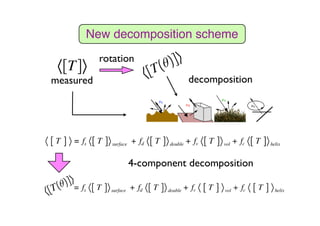
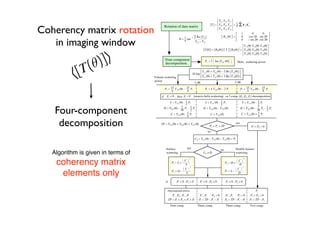
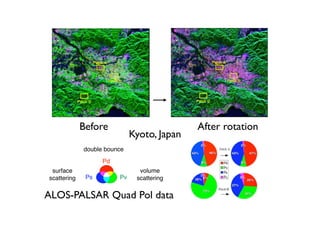
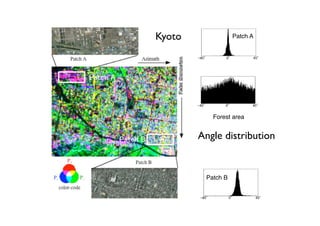
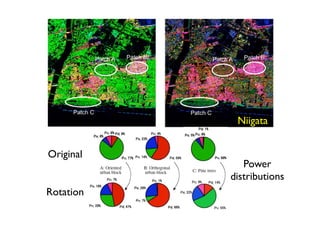
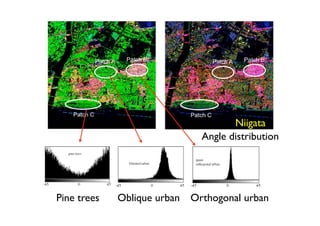
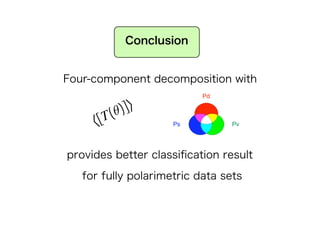
The document proposes a four-component scattering power decomposition method with rotation of the coherency matrix. This improves upon existing decomposition methods by minimizing the HV component through rotation, resulting in better separation of surface, double bounce, volume, and helix scattering mechanisms. The new method is applied to fully polarimetric SAR data sets to provide improved classification results.