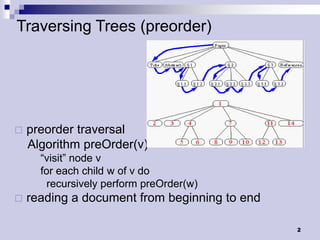
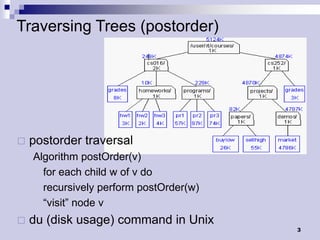
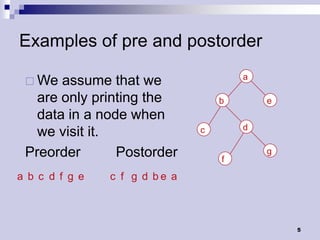
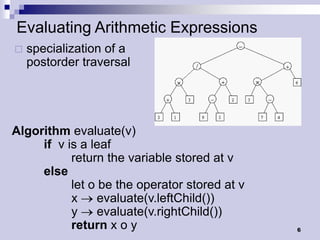
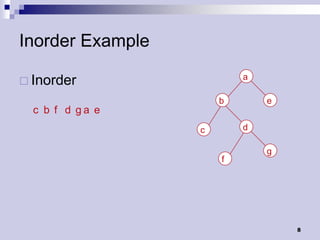
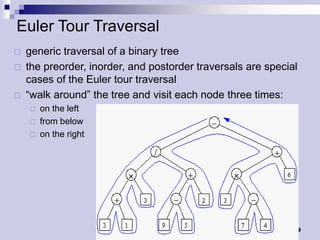
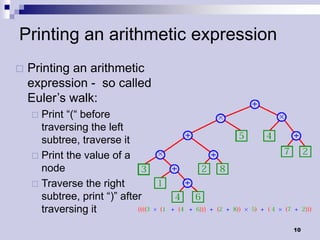
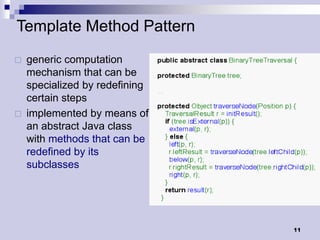
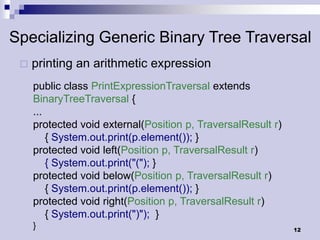
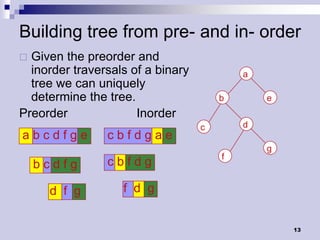
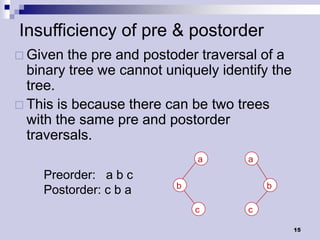
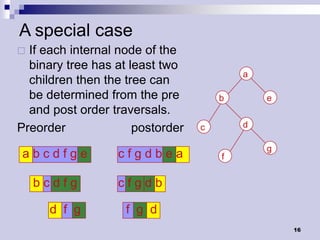
Tree traversals visit nodes in a tree in a specified order. A preorder traversal visits each node before its children, while a postorder traversal visits each node after its children. Binary trees can be traversed in preorder, postorder, or inorder. Preorder and inorder traversals can uniquely determine a binary tree, while preorder and postorder may not. Special cases like each internal node having two children can allow reconstruction from preorder and postorder.