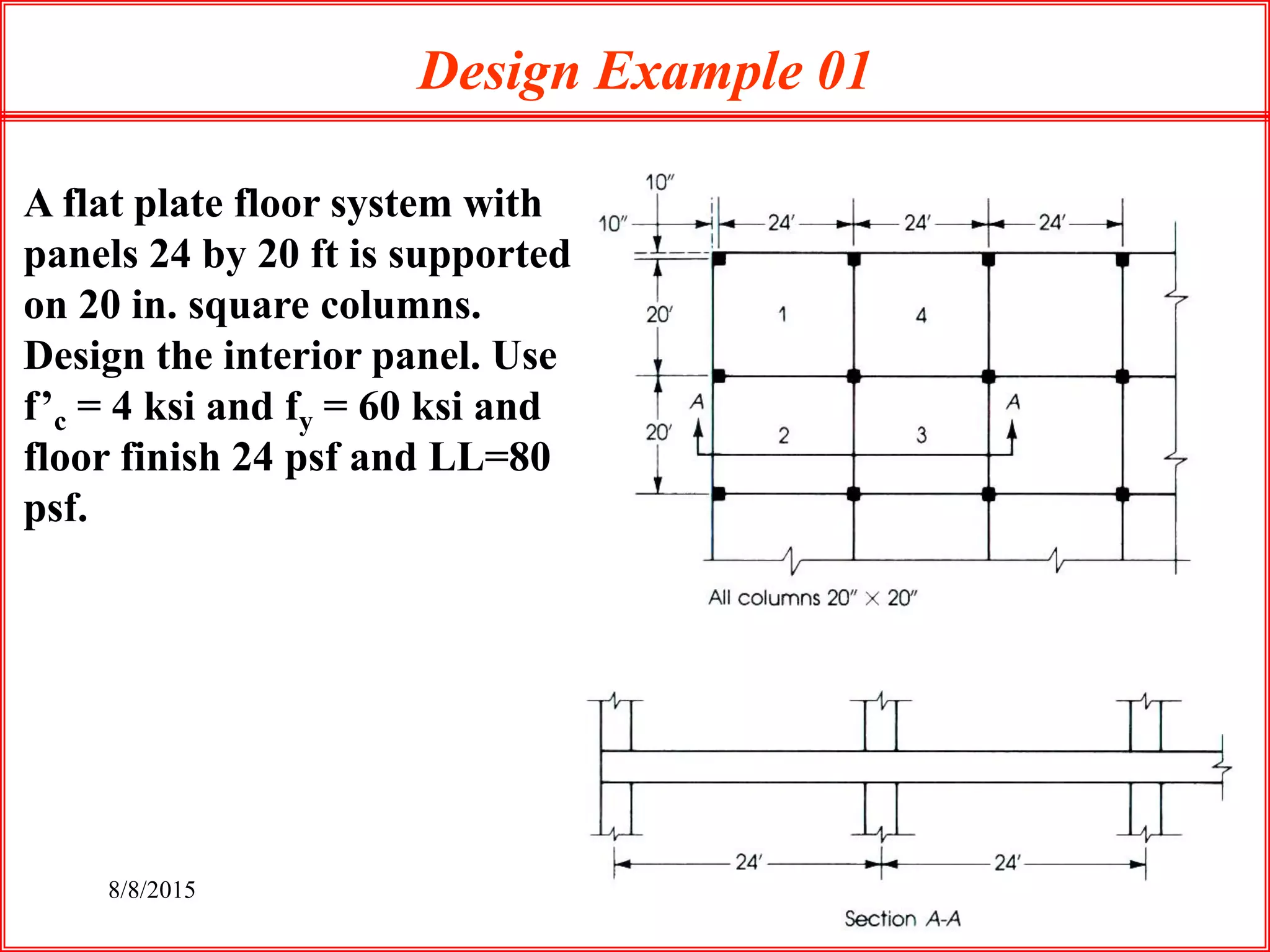
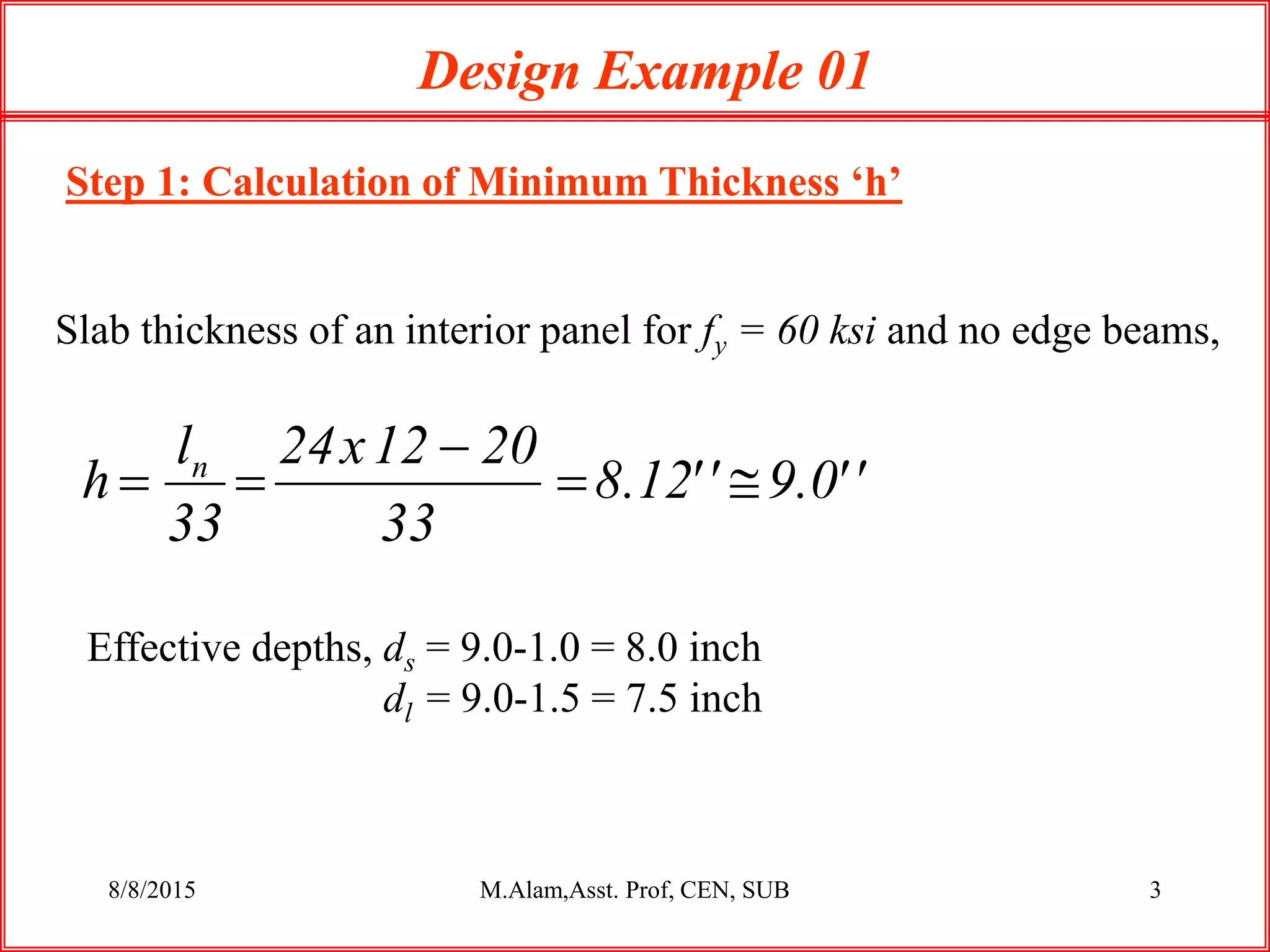
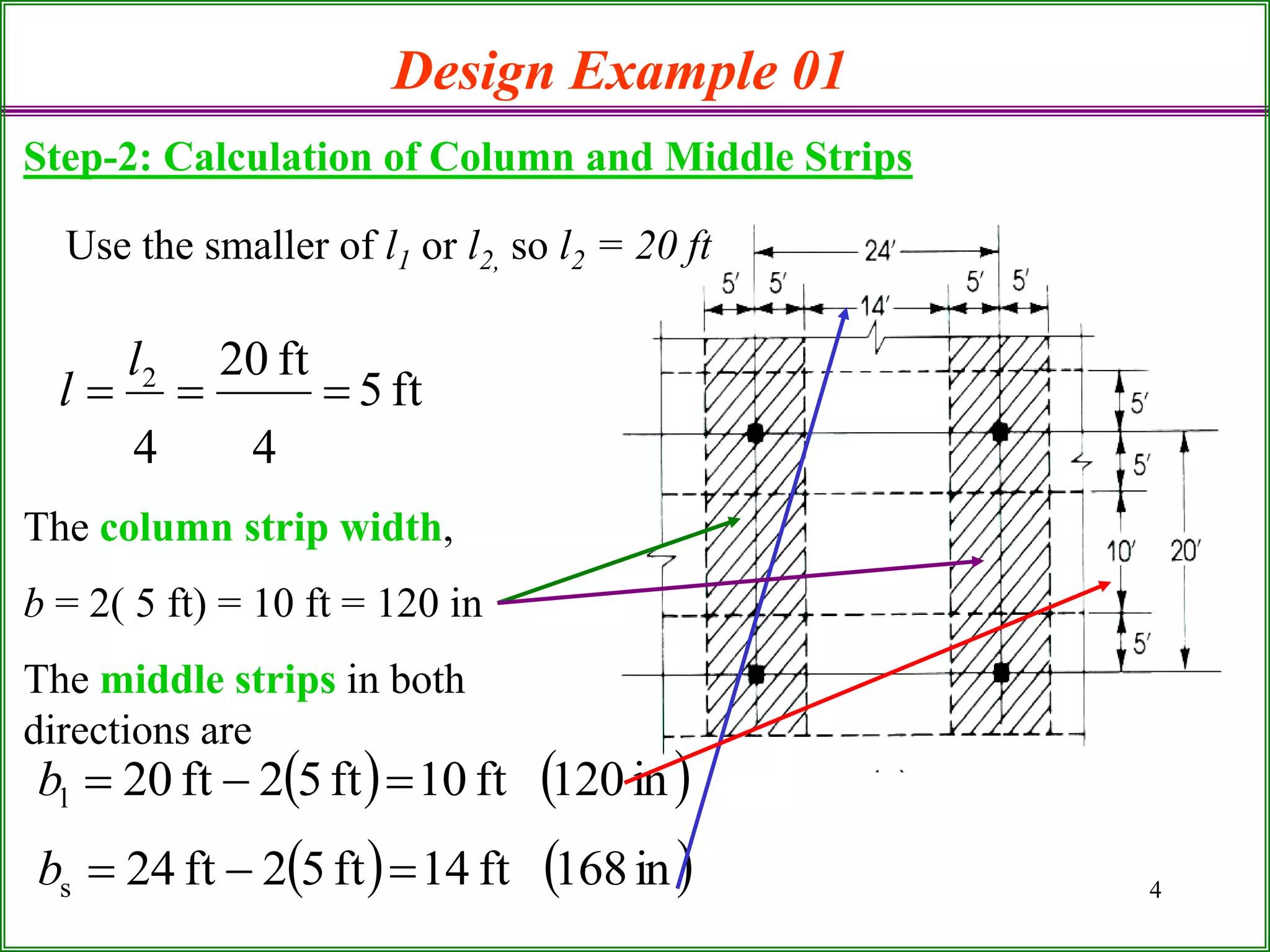
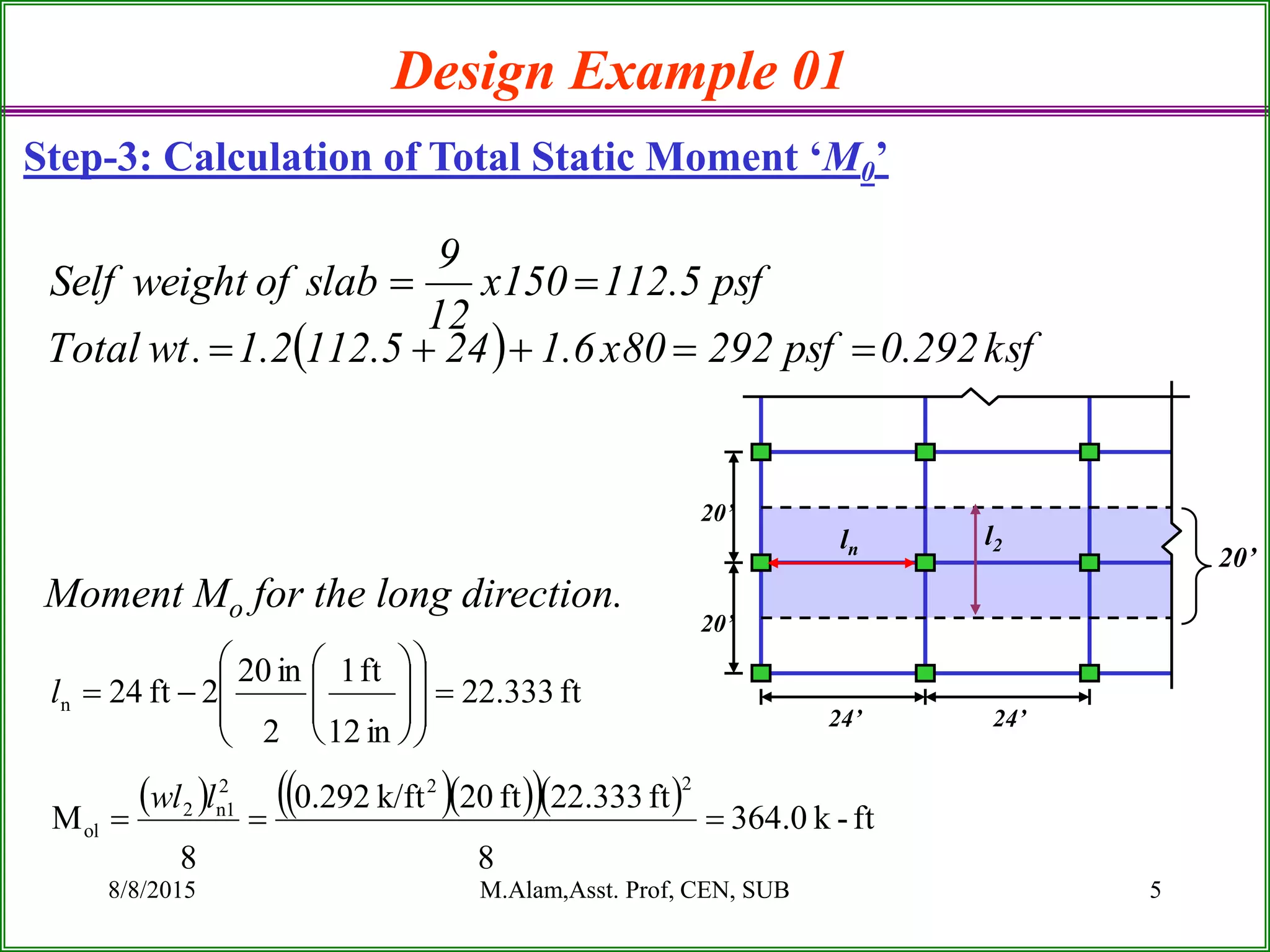
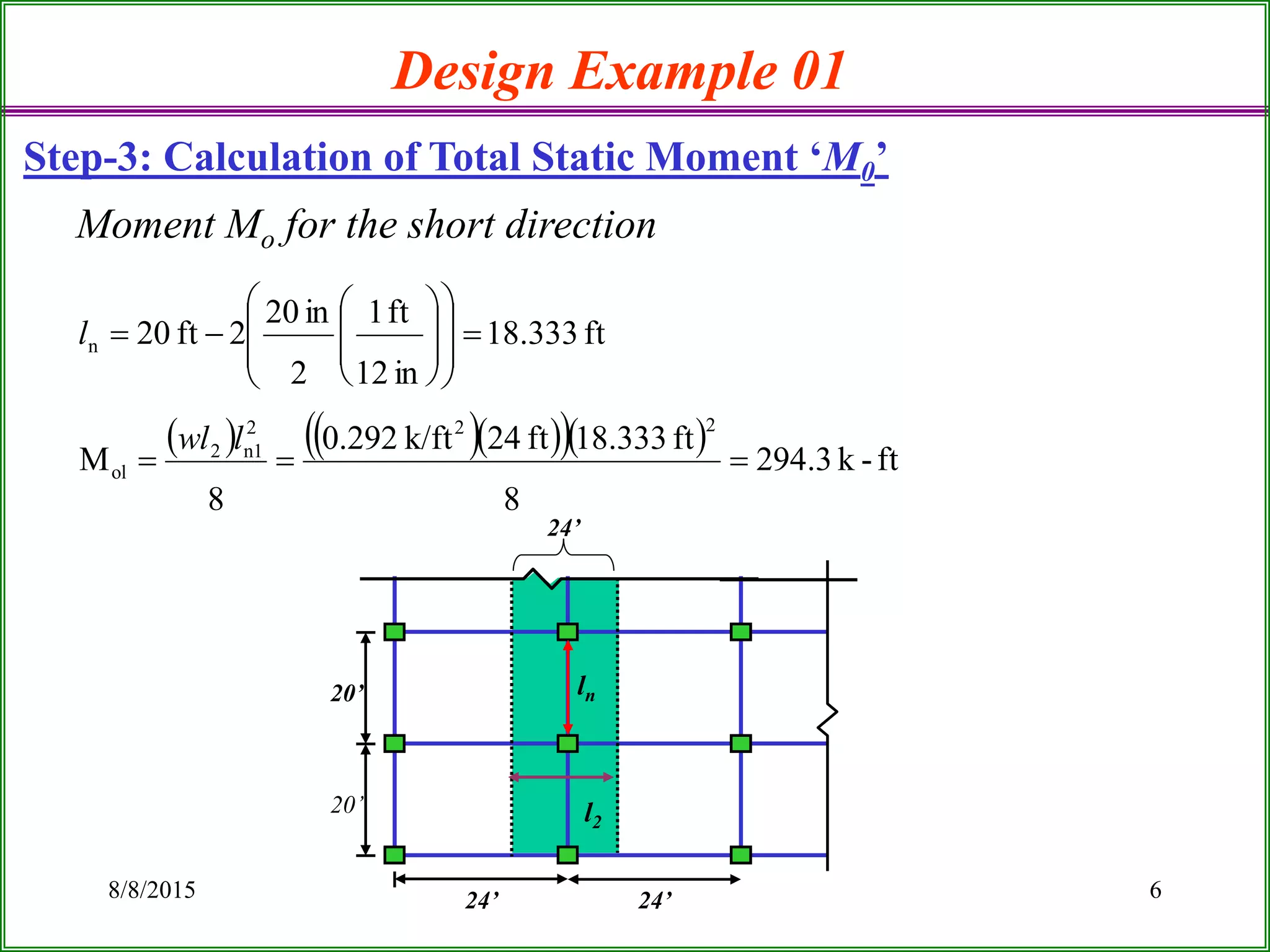
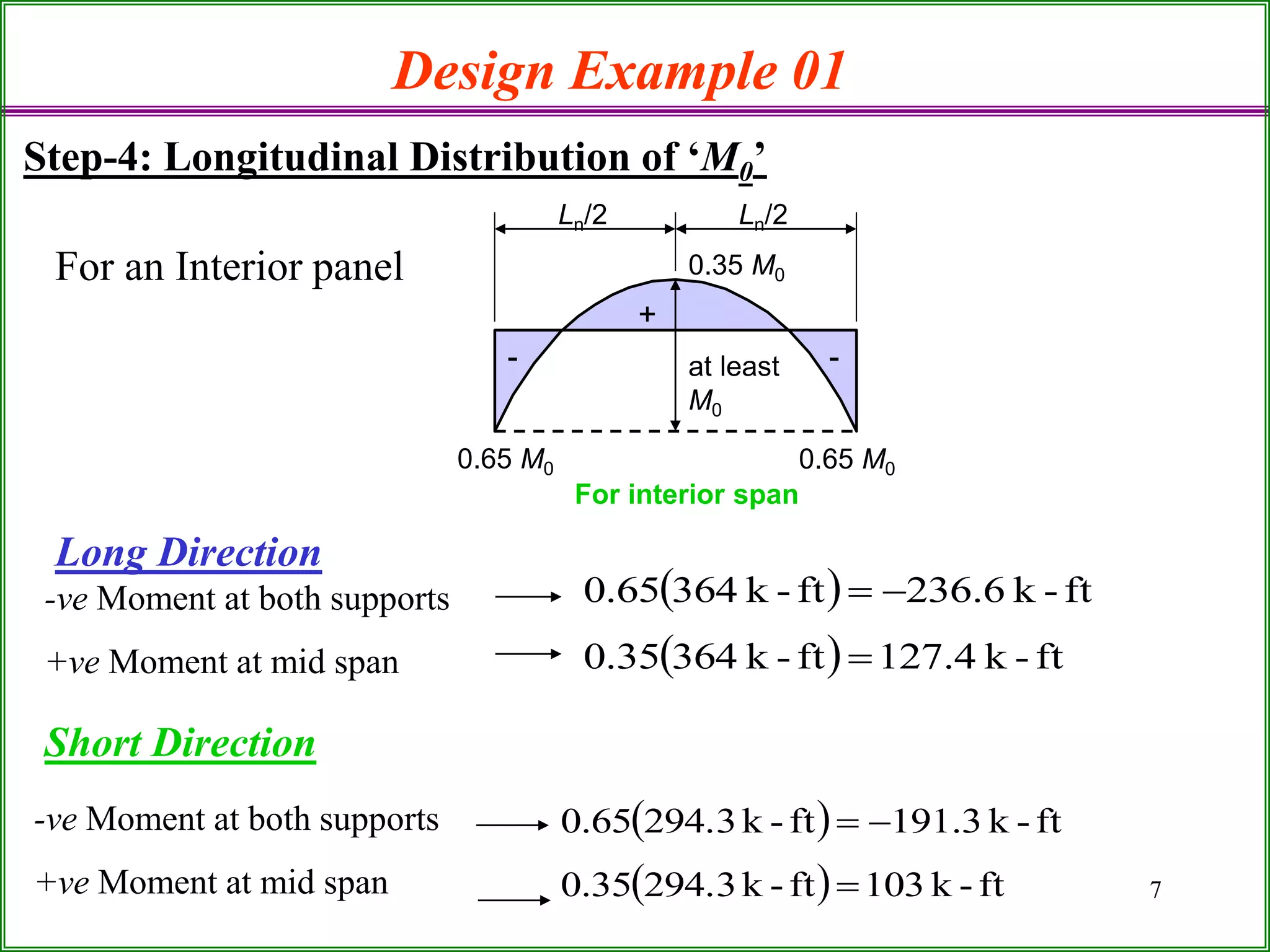
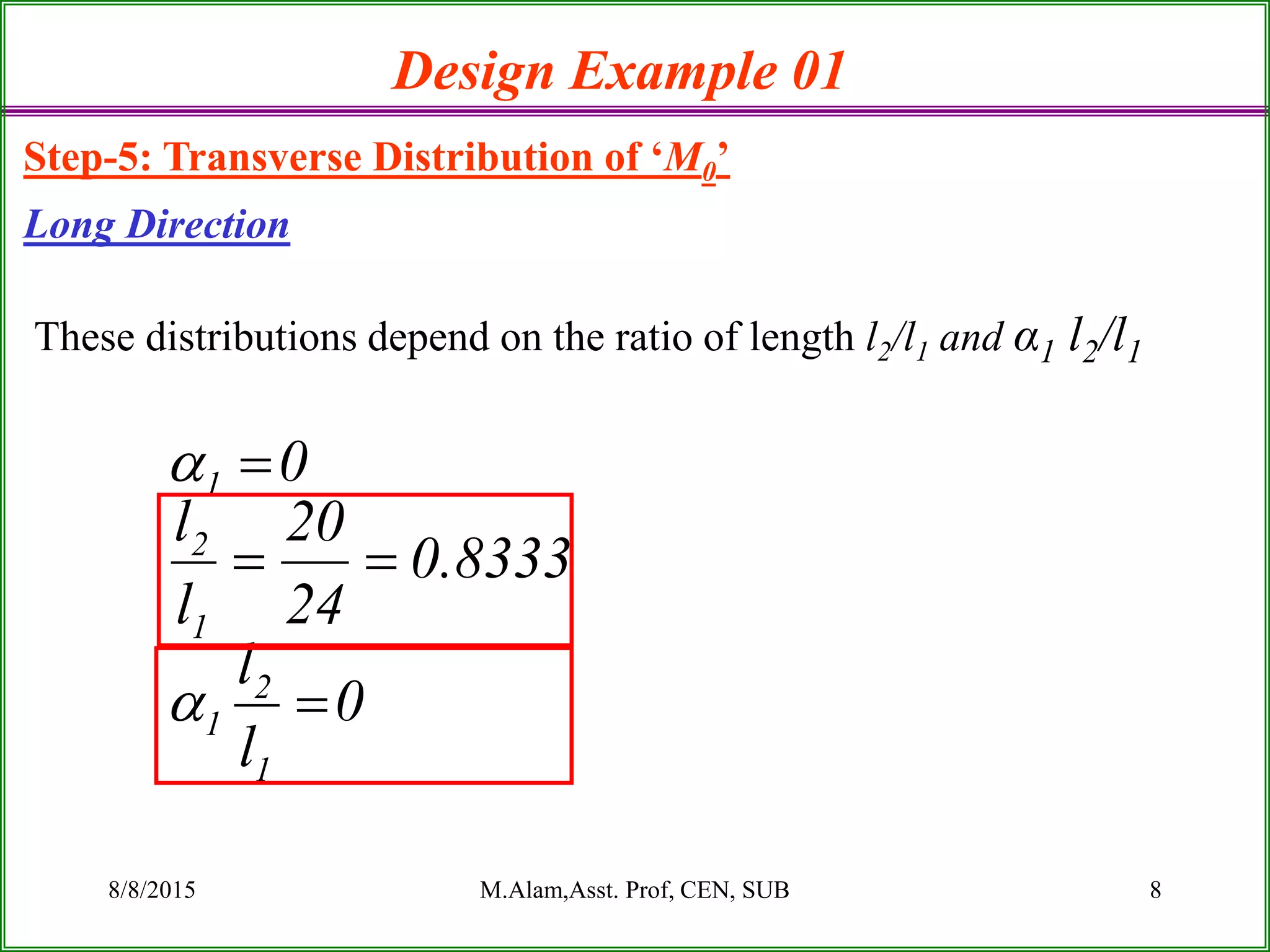
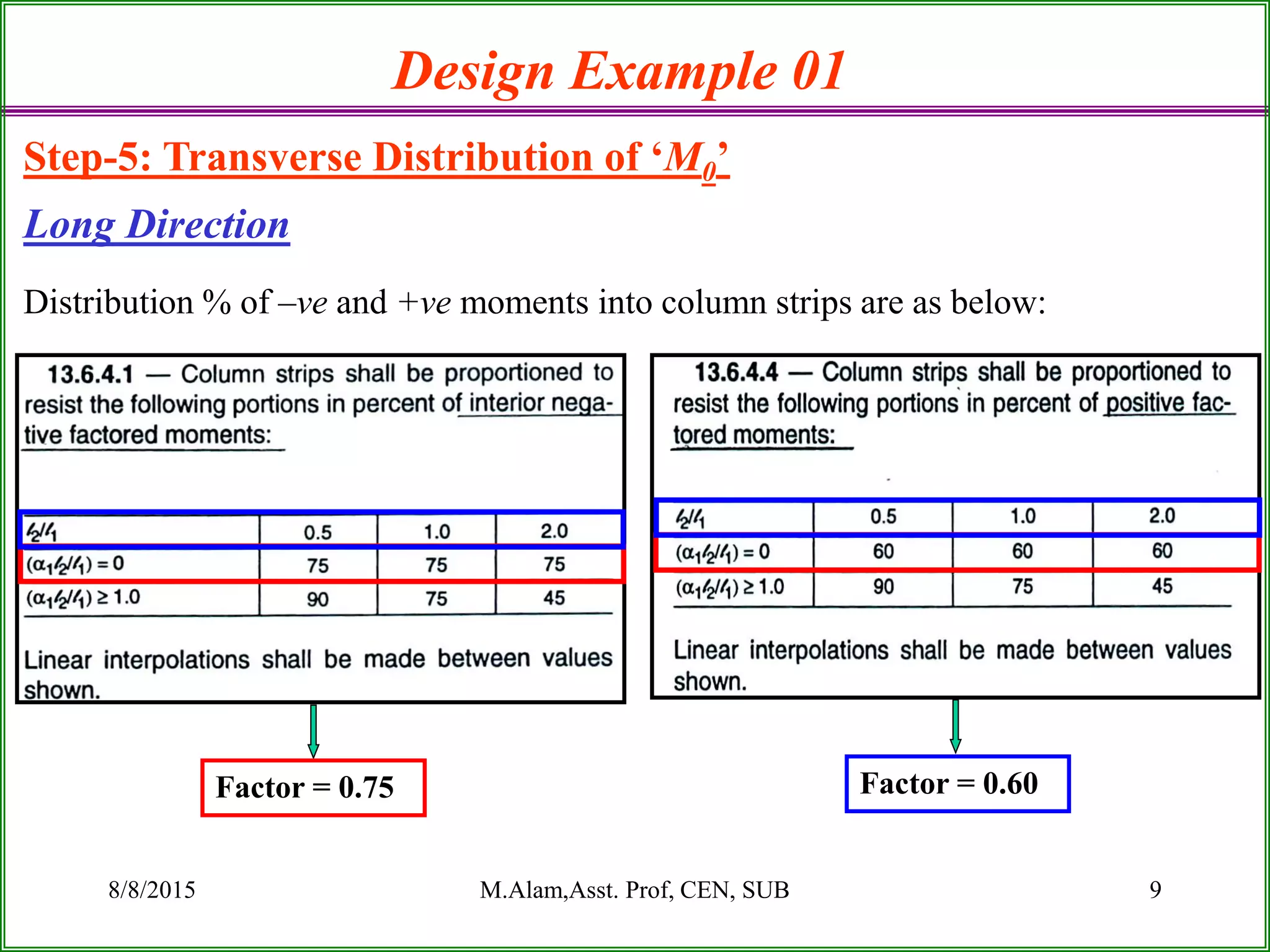
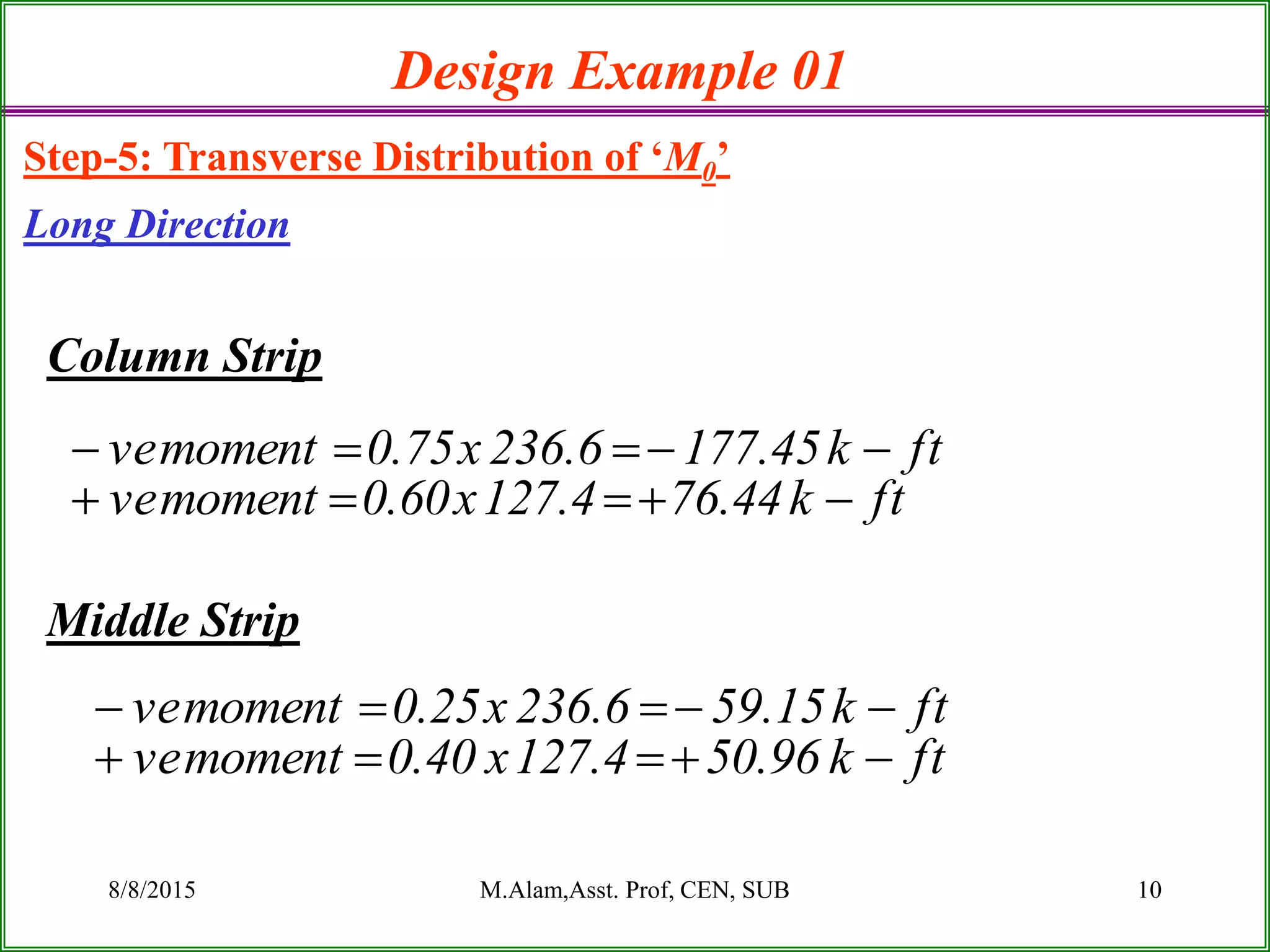
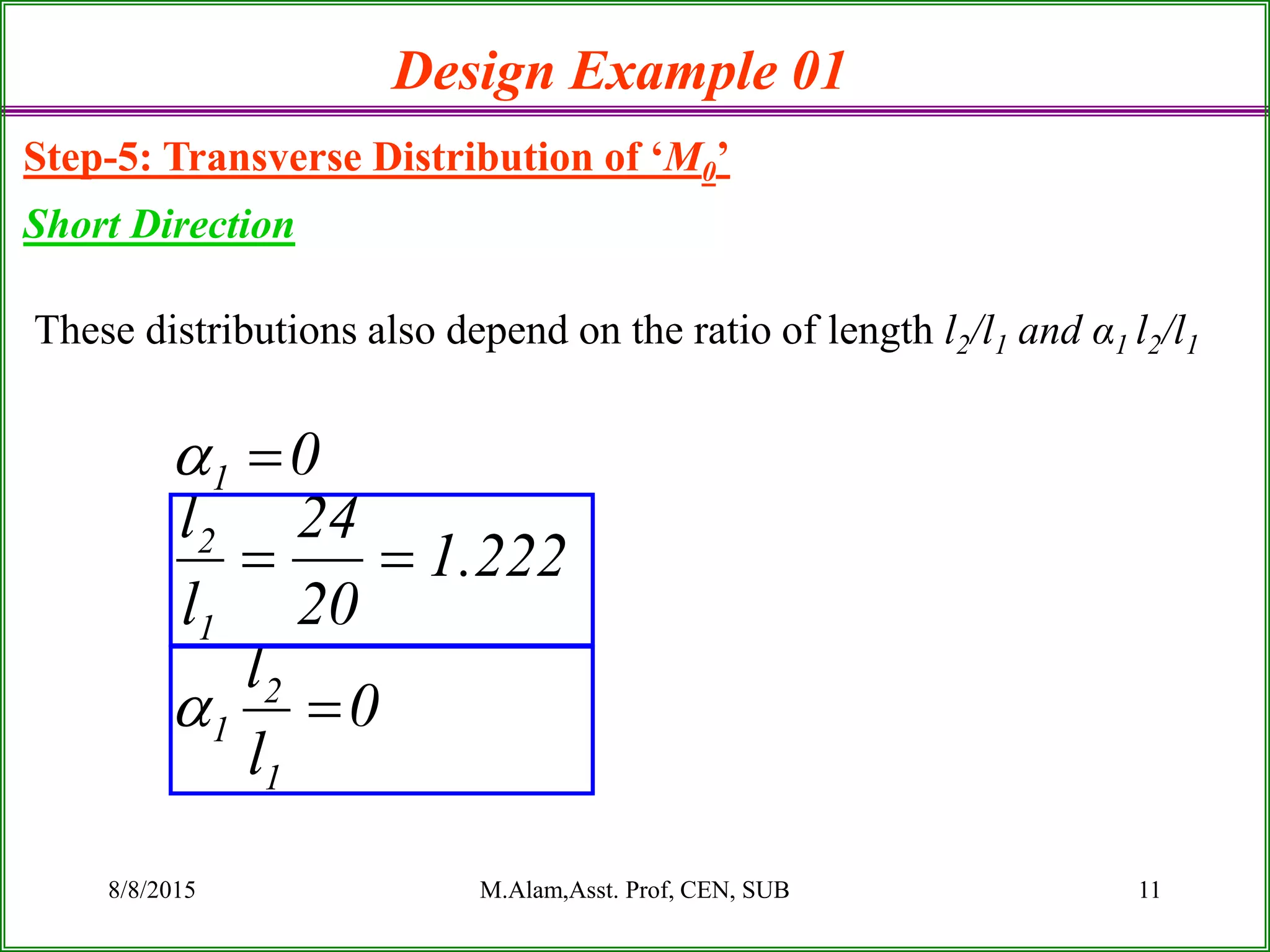
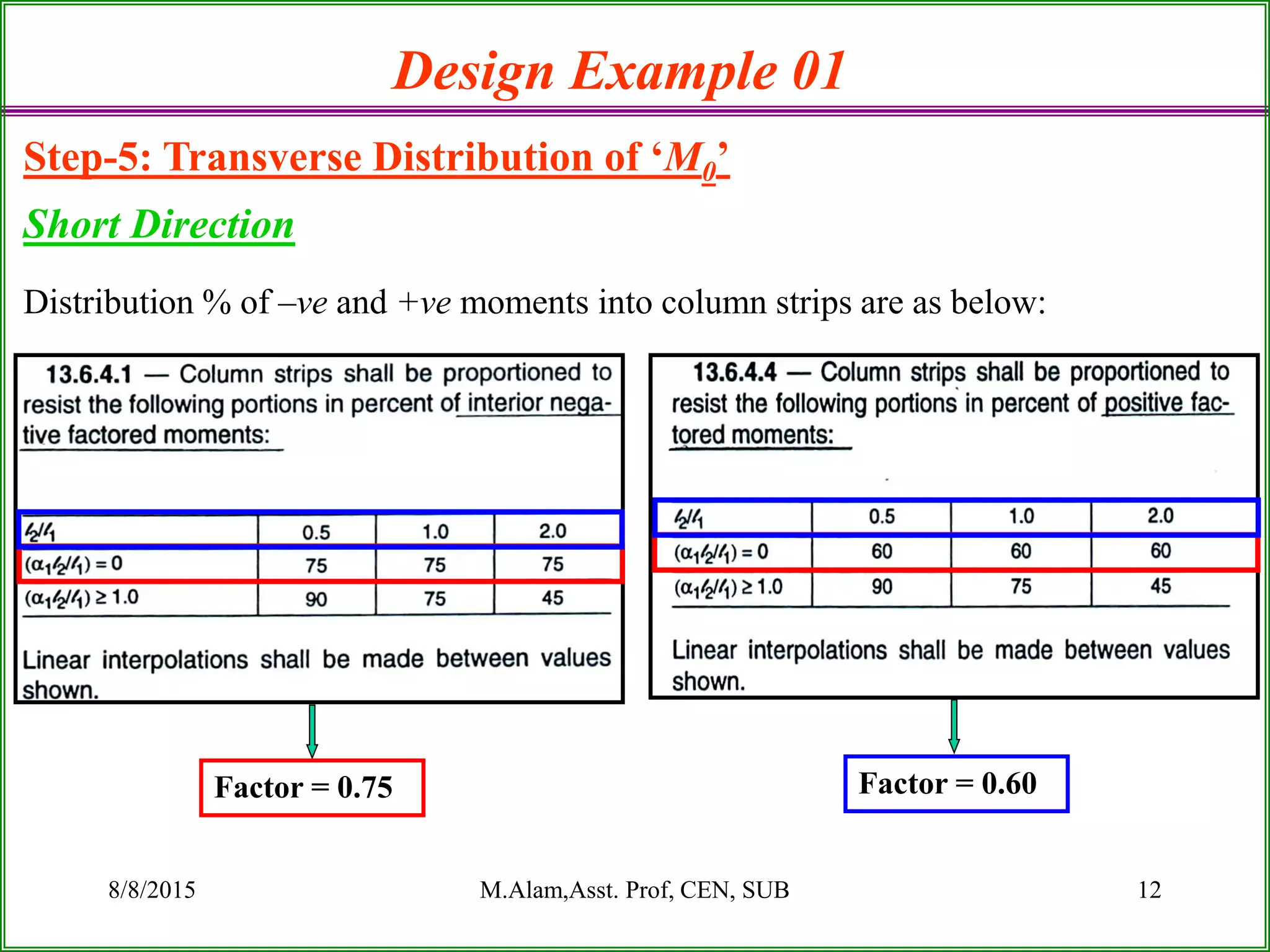
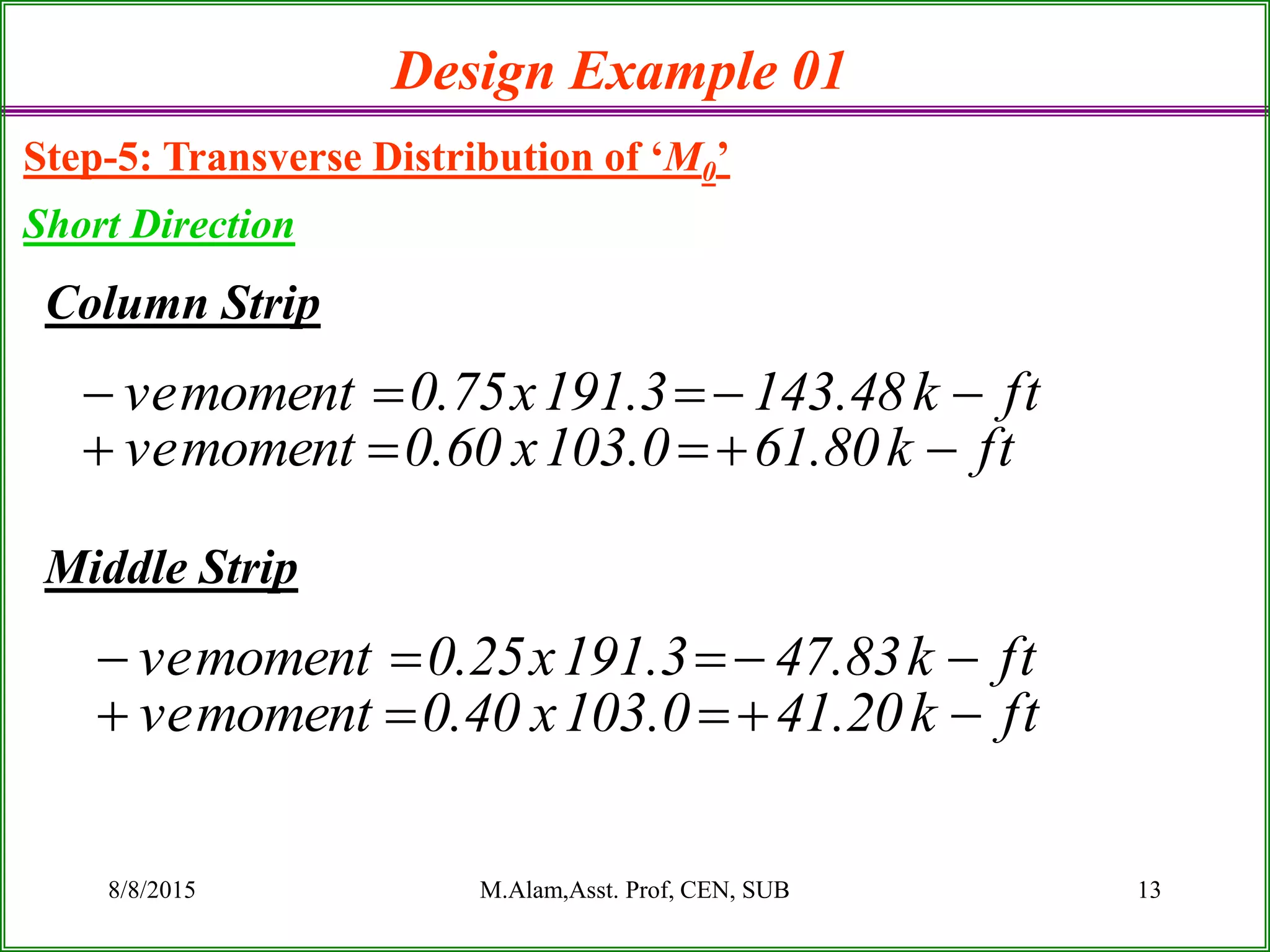
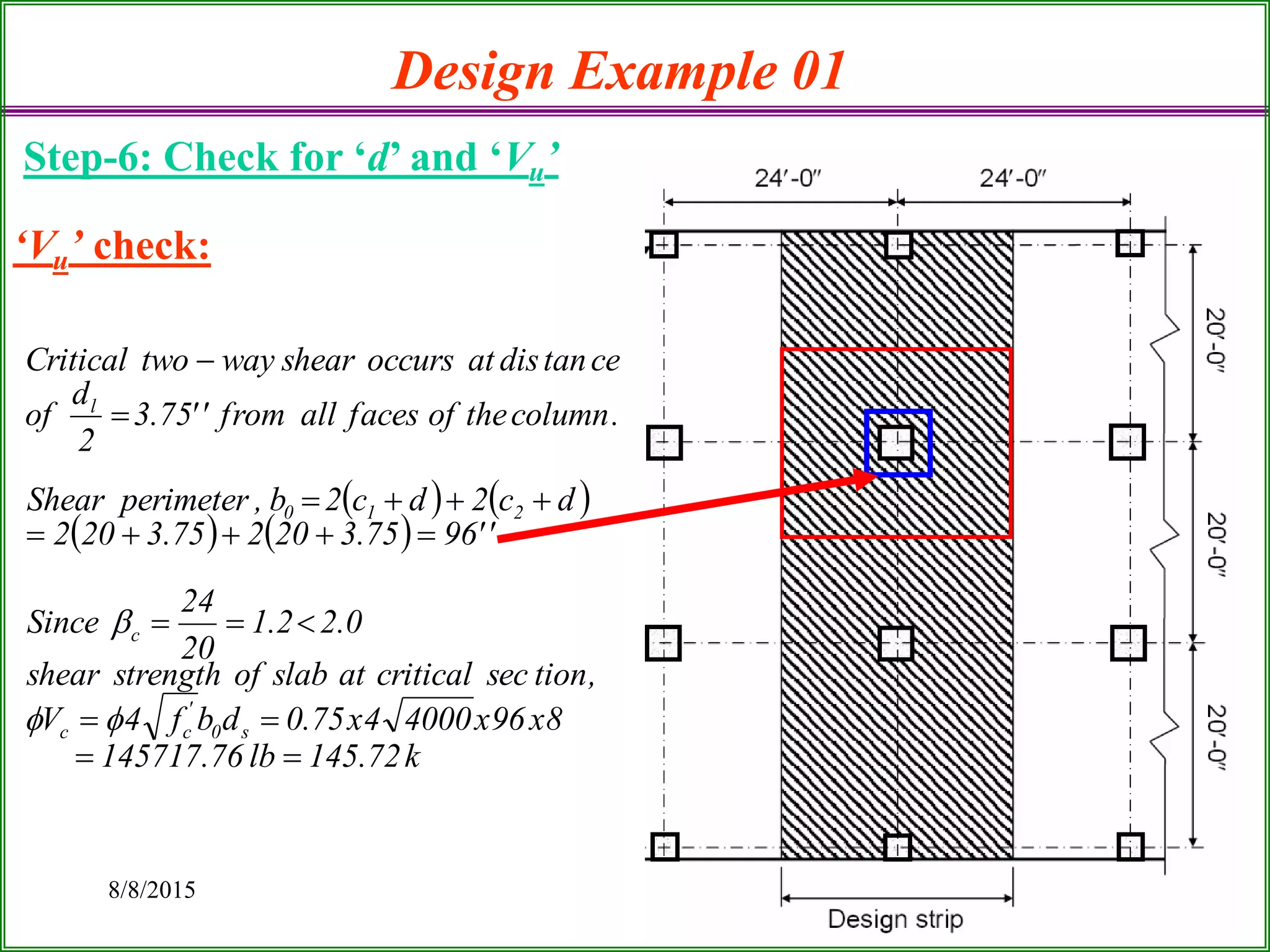
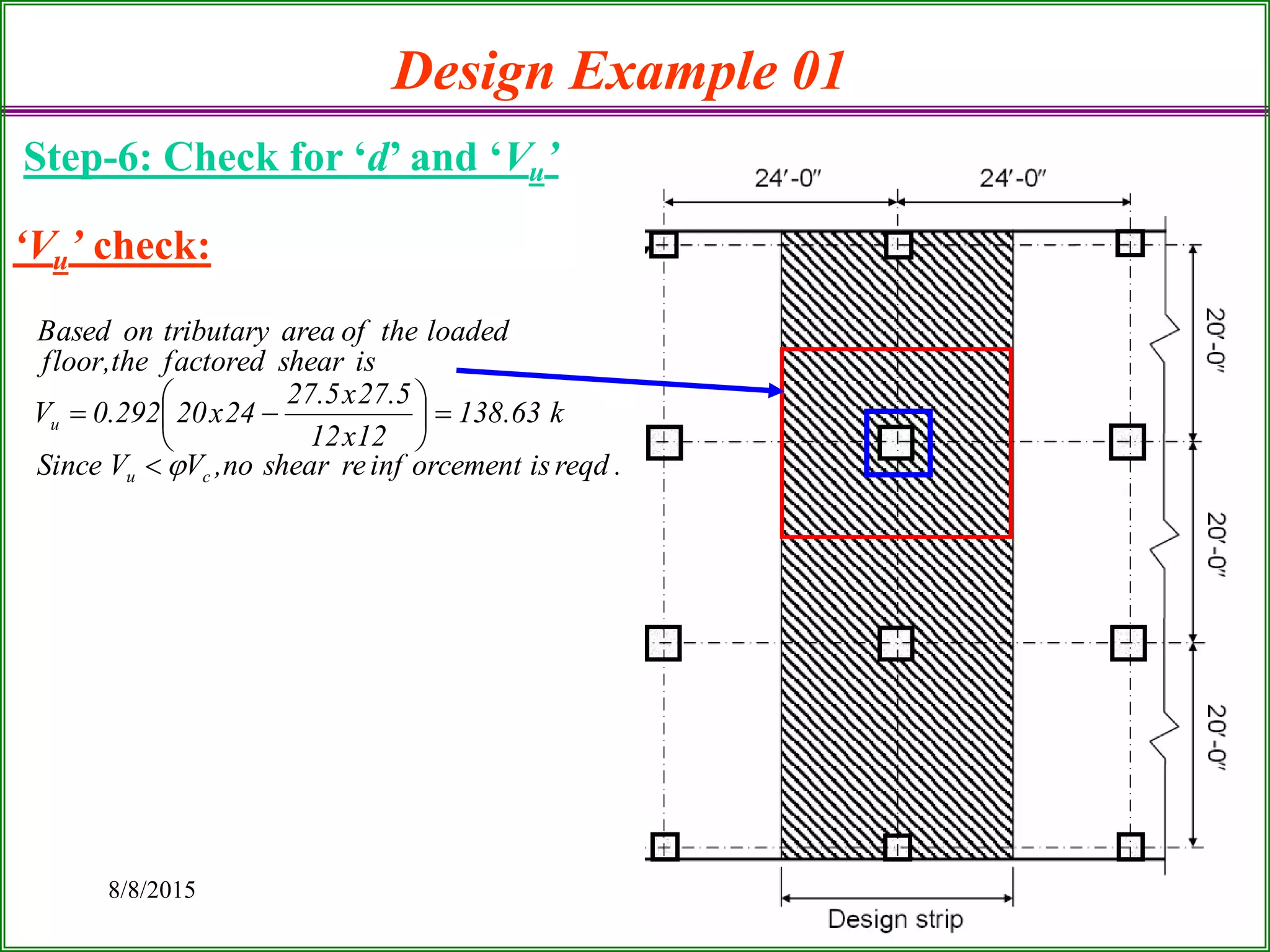
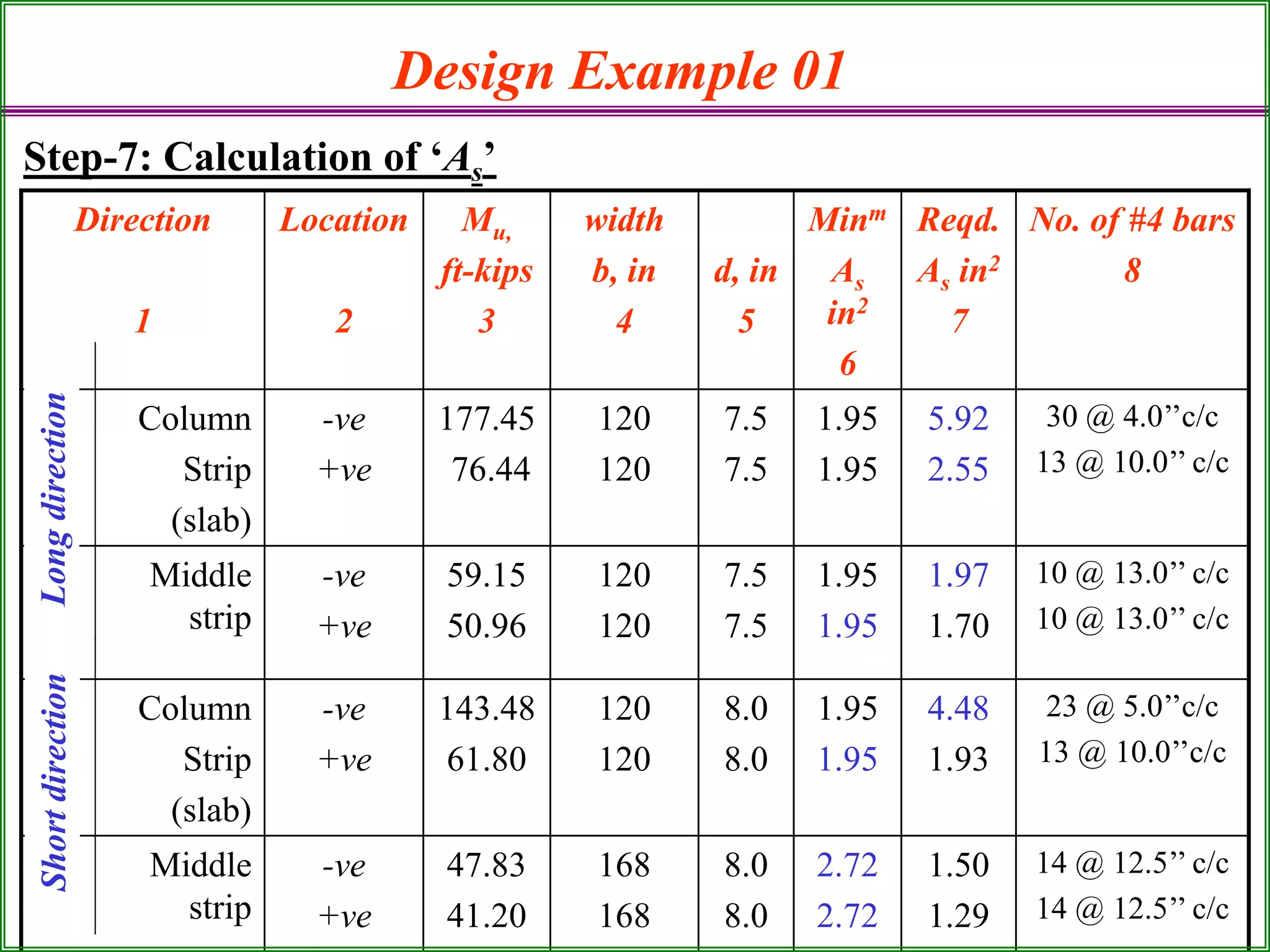
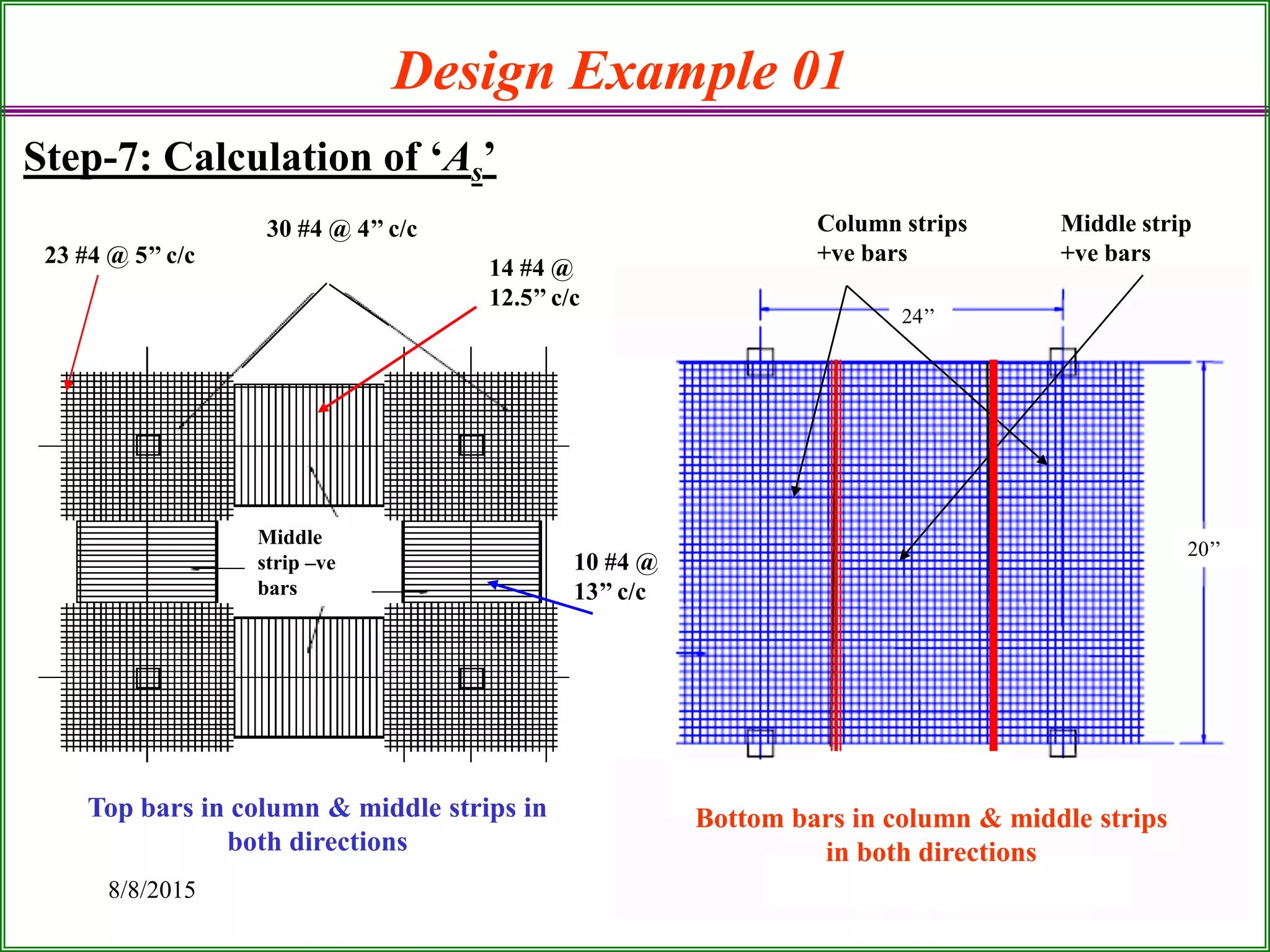
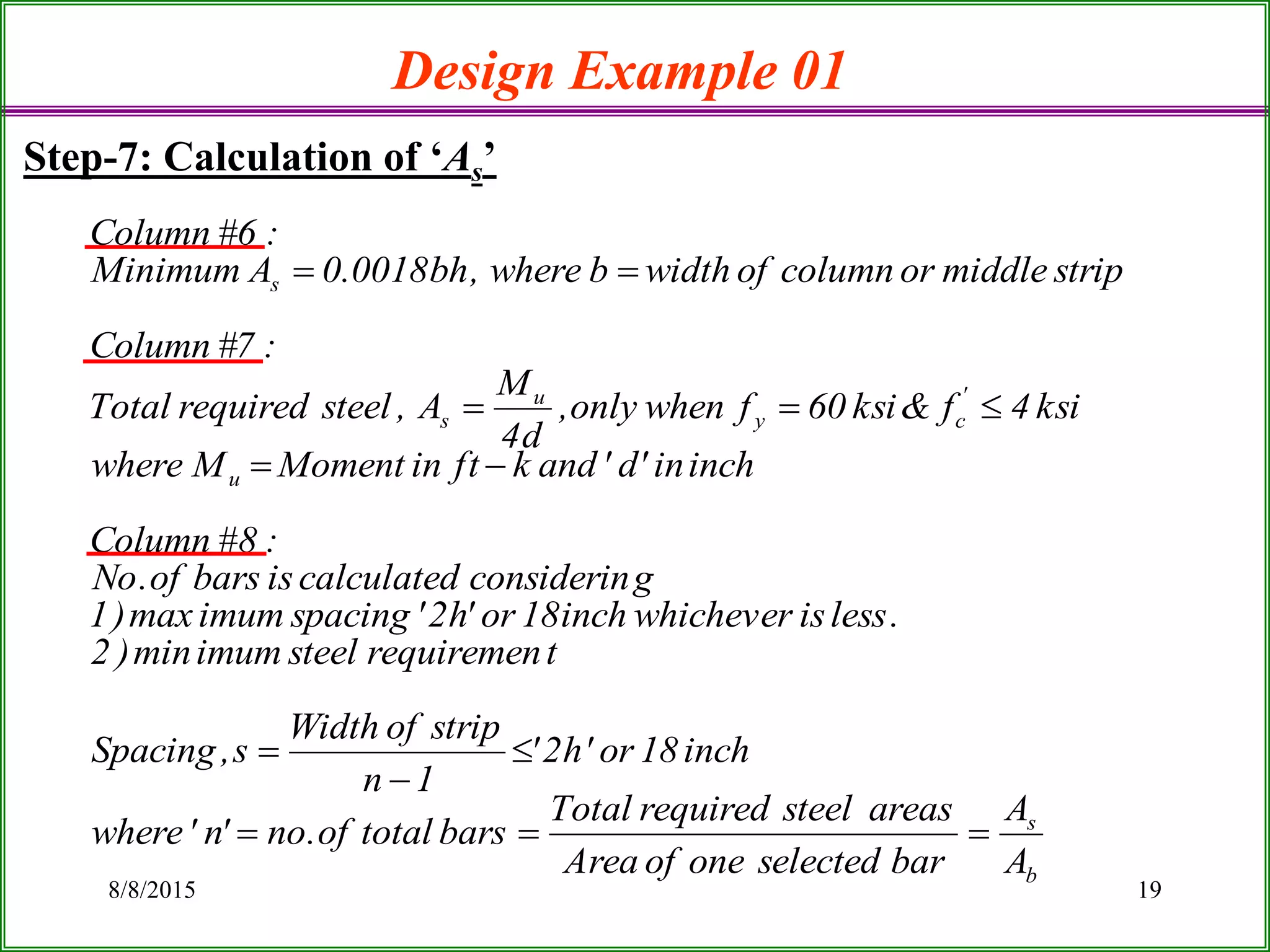
The document outlines the design process for a flat plate slab floor system supported by columns, detailing calculations for slab thickness, moment distribution, and reinforcement requirements. Key steps include determining effective slab depths, static moments for both long and short spans, and checks for shear and reinforcement areas. The design example uses specific material strengths and loads to arrive at necessary dimensions and reinforcement detailing.