1. The document discusses interpolation methods, including linear interpolation and Lagrange interpolation.
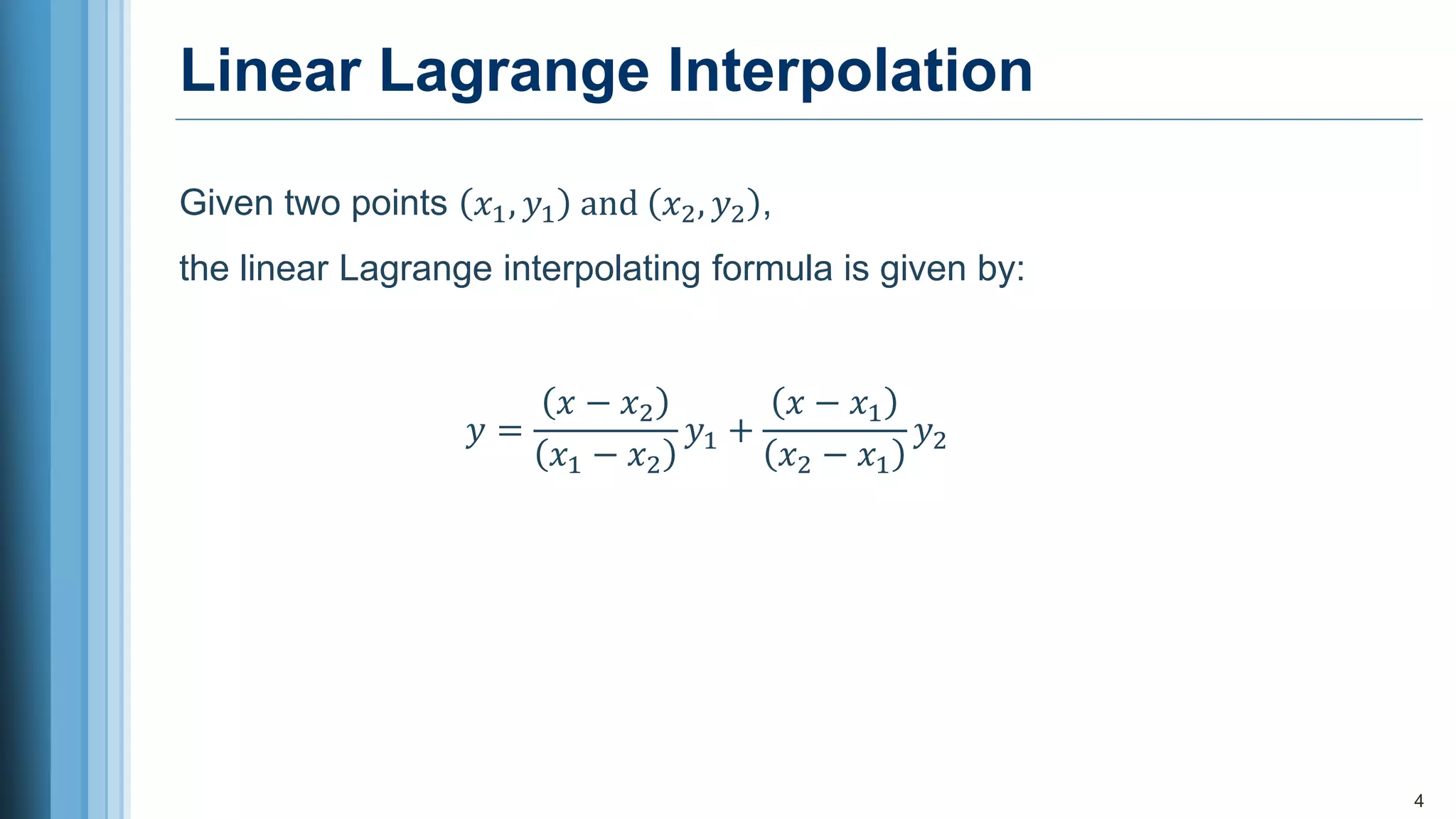
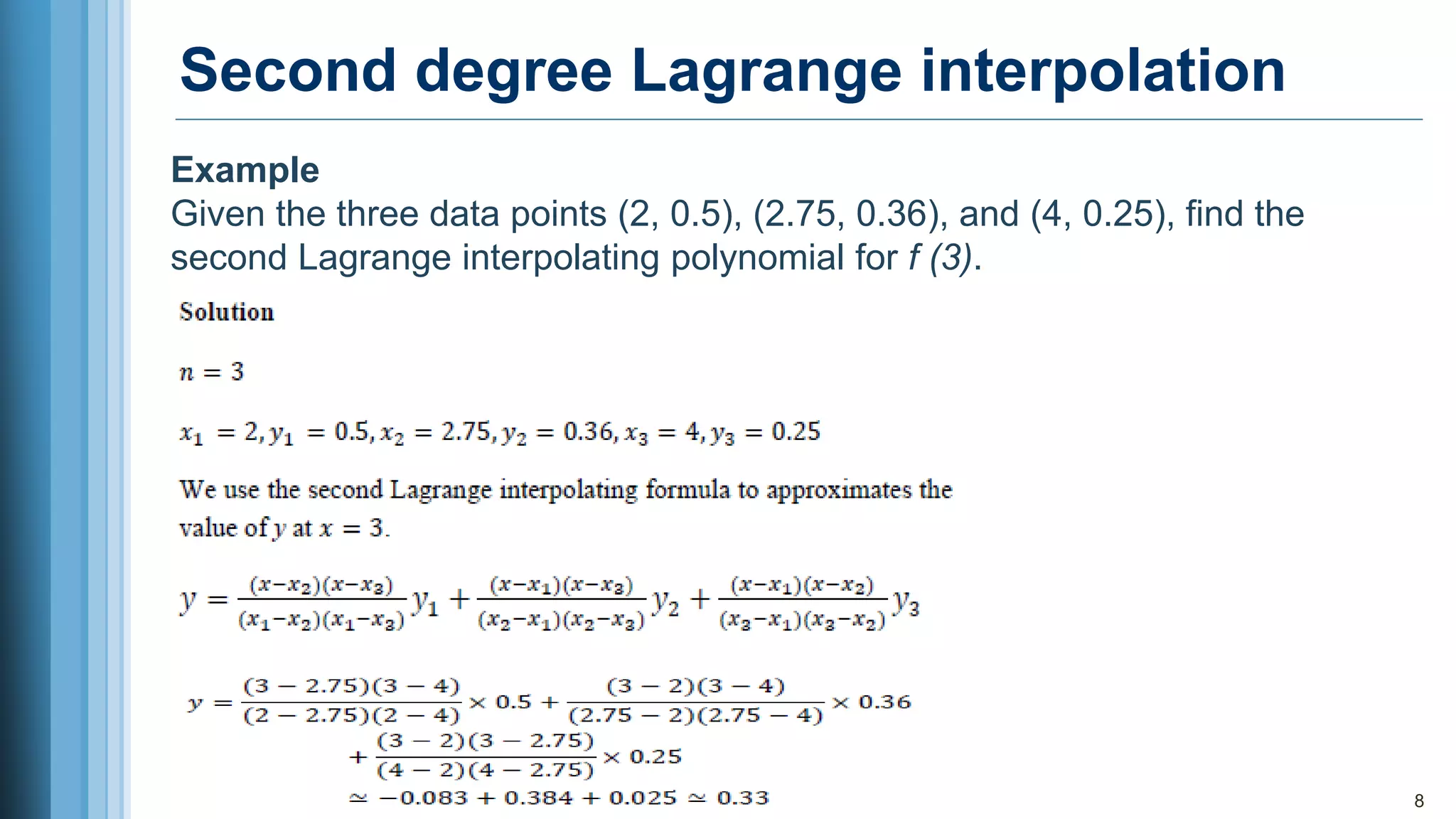
2. Lagrange interpolation approximates a function that passes through given data points, where the degree of the Lagrange polynomial equals the number of points minus one.
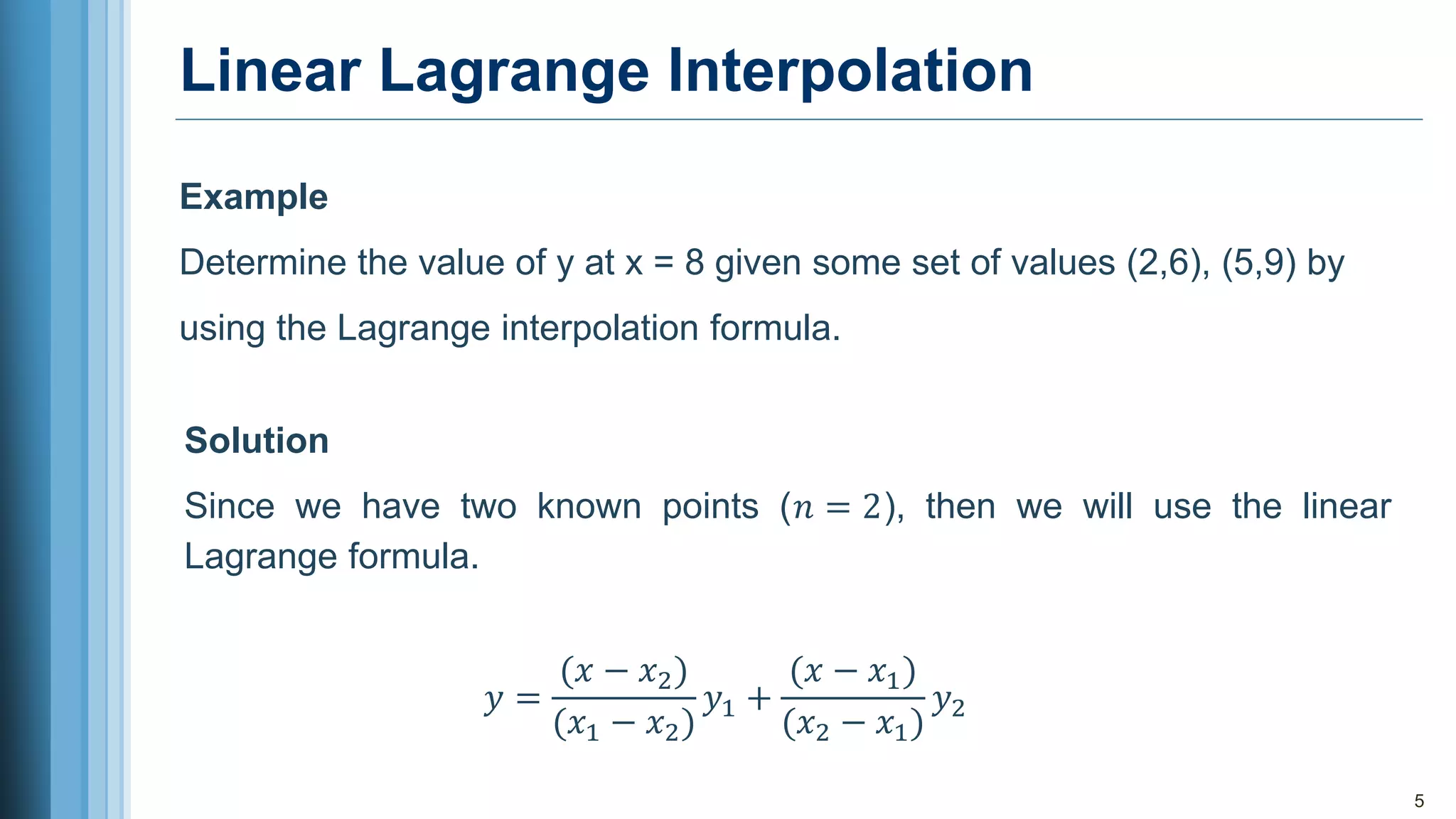
3. For two given points, the linear Lagrange interpolation formula estimates values between the points. An example calculates the y-value at x=8 using two known points.