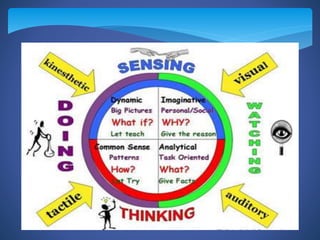
This document provides information on differentiated instruction strategies for teachers. It discusses learning styles, including mastery, understanding, self-expressive, and interpersonal learners. Several differentiated strategies are then described in detail, including admit slips, window panes, mnemonics, think-pair-share, jigsaw, task rotation, graffiti, and exit slips. Examples are provided for many of the strategies. The document aims to educate teachers on incorporating various learning styles and differentiated strategies into their instruction.