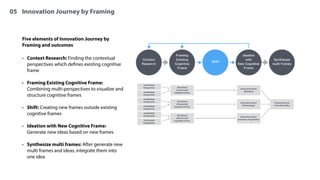
The document discusses learning processes and innovation theories, highlighting four elements—context, cognitive frame, action, and result—that shape human learning. It explores three main theories: double-loop learning, which emphasizes adapting cognitive frameworks; the SECI model, which involves knowledge transfer between tacit and explicit forms; and design thinking, a user-centered problem-solving approach. Each theory provides methods for shifting cognitive frames to foster innovation and improve outcomes.


![02 Double-Loop Learning
By Chris Argyris
[Double-Loop Learning]
Single loop learning tries to solve problems according to
already existing assumptions and action framework.
Double loop learning is to abandon the existing cognitive
frame and incorporate a new way of thinking and action
framework. In 1978, American business theorist Chris Argyris
and Donald Schon proposed in "Organizational Learning"
concept. Organizations are difficult to survive adapting to the
environment with single loop learning alone. They unlearn
stereotypes in the past successful experiences themselves,
learn new knowledge and framework from the outside by
double loop, and iterate and strengthen it by single loop
learning. It is said that only organizations that can repeat this
cycle can continue to maintain competitive advantage.
Single Loop Learning
Context Assumption Action Result
Following the assumptions
Double Loop Learning
Context Assumption Action Result
Changing the assumptions
New
Assumption
New
Action
New
Result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningprocessandinnovationtheories-170124004736/85/Learning-Process-and-Innovation-Theories-4-320.jpg)
![03 SECI Model
By Ikujiro Nonaka
[SECI Model]
SECI model is a model of knowledge creation proposed by
Ikujiro Nonaka. It represents the process of knowledge transfer
that creates the spiral of "SECI model" "tacit knowledge" and
"explicit knowledge". It tries to shift the existing cognitive
frame by unlocking tacit knowledge learned from context.
SECI model has four steps.
• “Socialization(Empathy)" (tacit to tacit)
• “Externalization(Dialogue)" (tacit to explicit)
• “Combination(Linking)" (explicit to explicit)
• “Internalization(Action)" (Explicit to Tacit)
It is created while spirally moving the knowledge transfer
process, returning to the initial "Socialization", and constantly
repeating this cycle.
Knowledge Spiral
Context
Cognitive
Frame
Action Result
Interaction between tacit and explicit knowledge
Socialization
Empathy
Externalization
Dialogue
Combination
Linking
Socialization
Empathy
Result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningprocessandinnovationtheories-170124004736/85/Learning-Process-and-Innovation-Theories-5-320.jpg)
![04 Design Thinking
by Stanford University
[Design Thinking / Human Centered Design]
Design thinking is said to be the word that IDEO 's David Kelley
and Tim Brown created with Roger Martin in the 1990' s. It is
said that working on problem solving with a practical user-
centered approach leads to innovation.
Although there are various kinds of design thinking recently, it
tries to shift the existing cognitive frame by“User Insight”from
empathizing people. In design thinking advocated by Stanford
University, there are five processes.
• Empathize: Work to fully understand the experience of the
user for whom you are designing.
• Define: Process and synthesize the findings from your
empathy work in order to form a user point of view that you
will address with your design.
• Ideate: Explore a wide variety of possible solutions through
generating a large quantity of diverse possible solutions.
• Prototype: Transform your ideas into a physical form.
• Test: Try out high-resolution products and use observations
and feedback.
Design Thinking by Stanford University
Context
Cognitive
Frame
Action Result
Human Centered Design
Empathize
Define Ideate Prototype Test
New
Assumption
from
User Insight](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningprocessandinnovationtheories-170124004736/85/Learning-Process-and-Innovation-Theories-6-320.jpg)