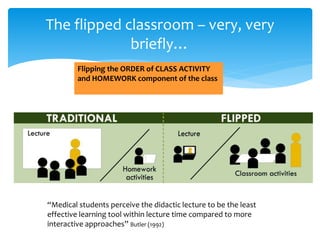
The document discusses the implementation of an integrated flipped classroom model at Monash Malaysia for medical students, aiming to enhance learning by combining traditional teaching with technology. Feedback from students indicated a preference for this approach over traditional lectures, highlighting its effectiveness in teaching complex concepts through virtual mini-vodcasts and interactive face-to-face sessions. The initiative also encourages collaboration among different disciplines within the medical curriculum, fostering a holistic educational experience.