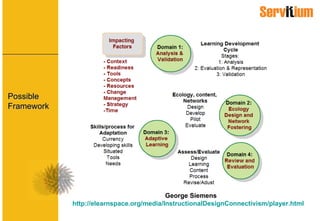
The document discusses the principles of connectivism and its impact on instructional design and learning solutions. Some of the key principles discussed include that learning is the process of forming connections, knowledge resides in connections, and learning is adaptive and non-linear. It also discusses how connectivism requires rethinking instructional design to focus on contextualization, learner networks, and continuous learning. New learning solutions need to leverage web 2.0 tools to foster collaboration and connections between learners.