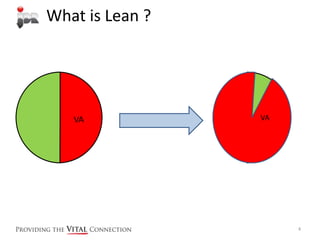
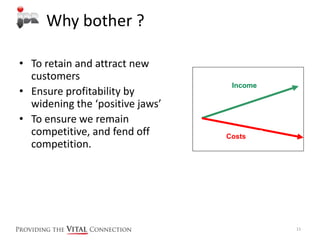
This document provides an introduction to Lean principles and tools. It explains the five key Lean principles as specify value, identify the value stream, create flow, create pull, and seek perfection. Some basic Lean tools are also introduced, including process maps to understand workflow, identifying seven types of waste, and visual management boards. The overall goal of Lean is to retain customers, ensure profitability, and increase competitiveness by removing waste from business processes to optimize workflow and productivity.