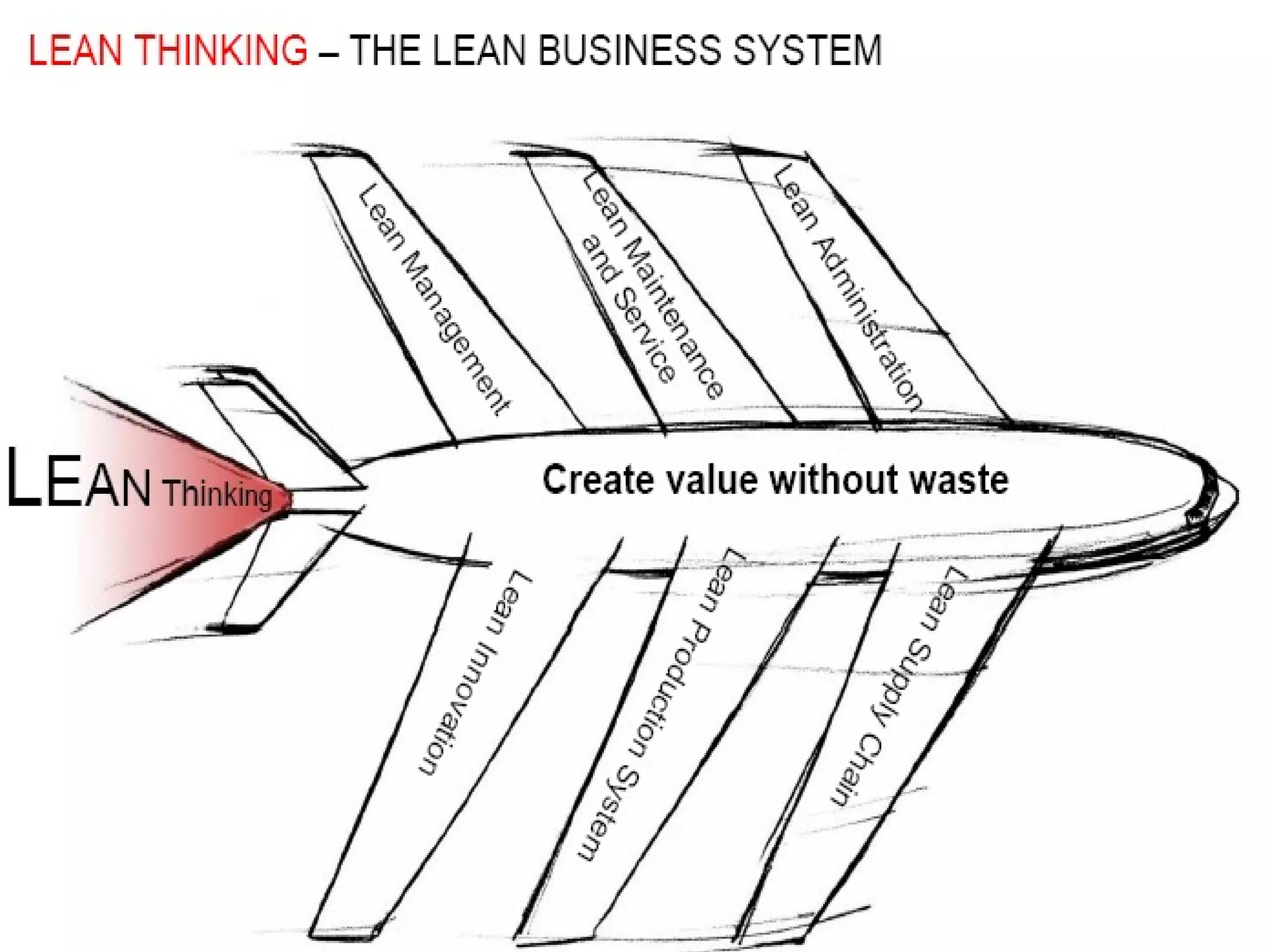
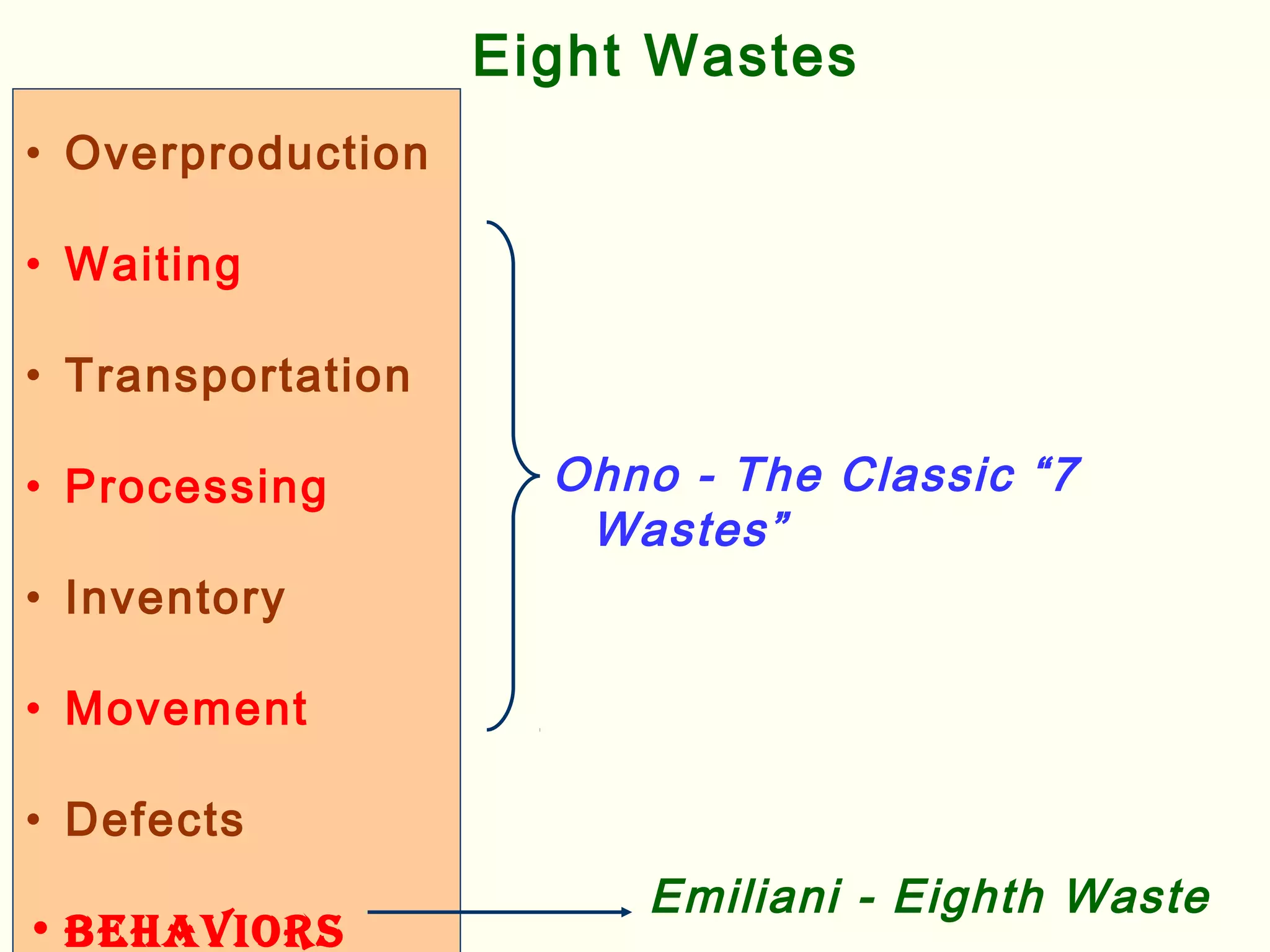
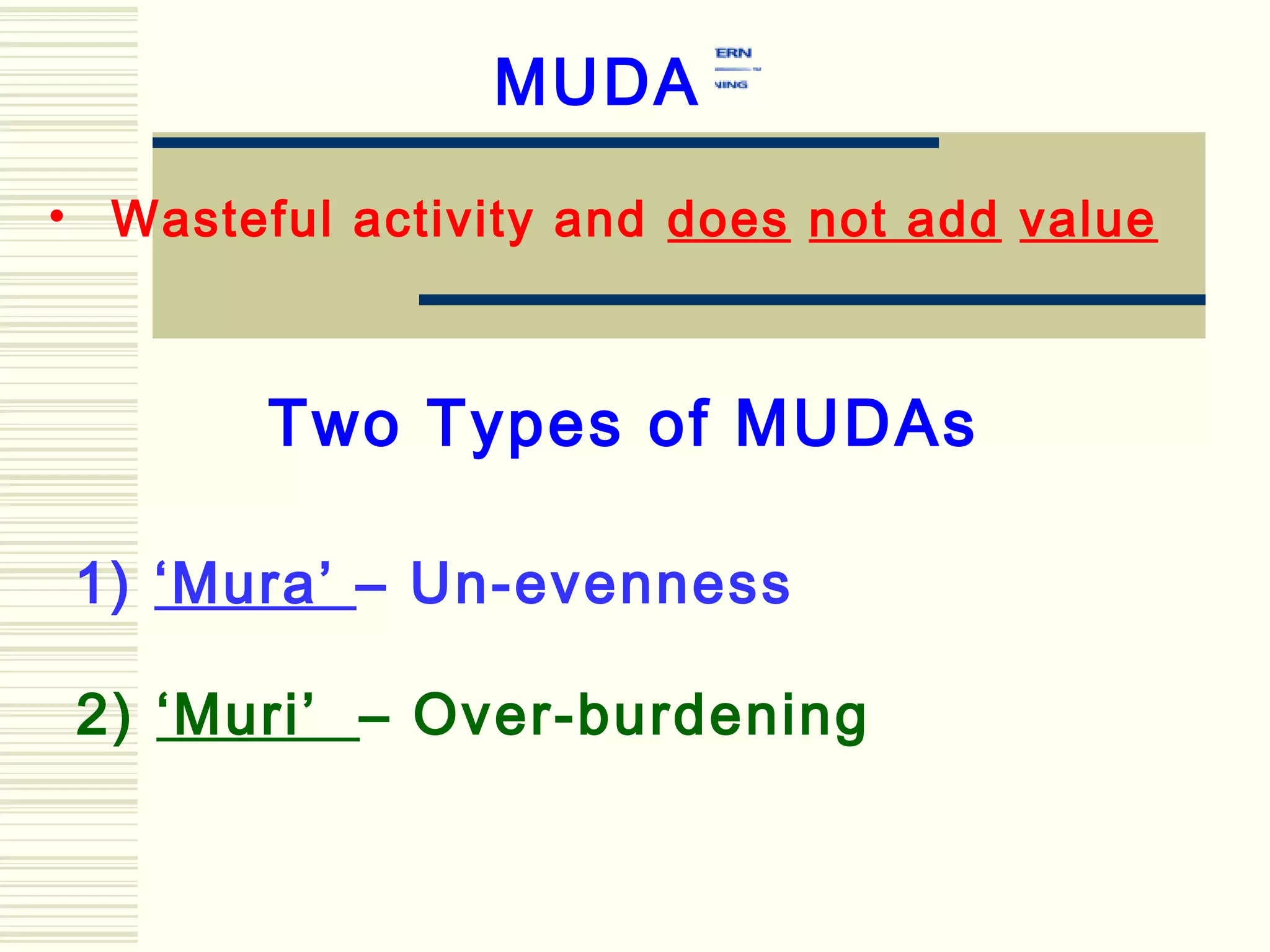
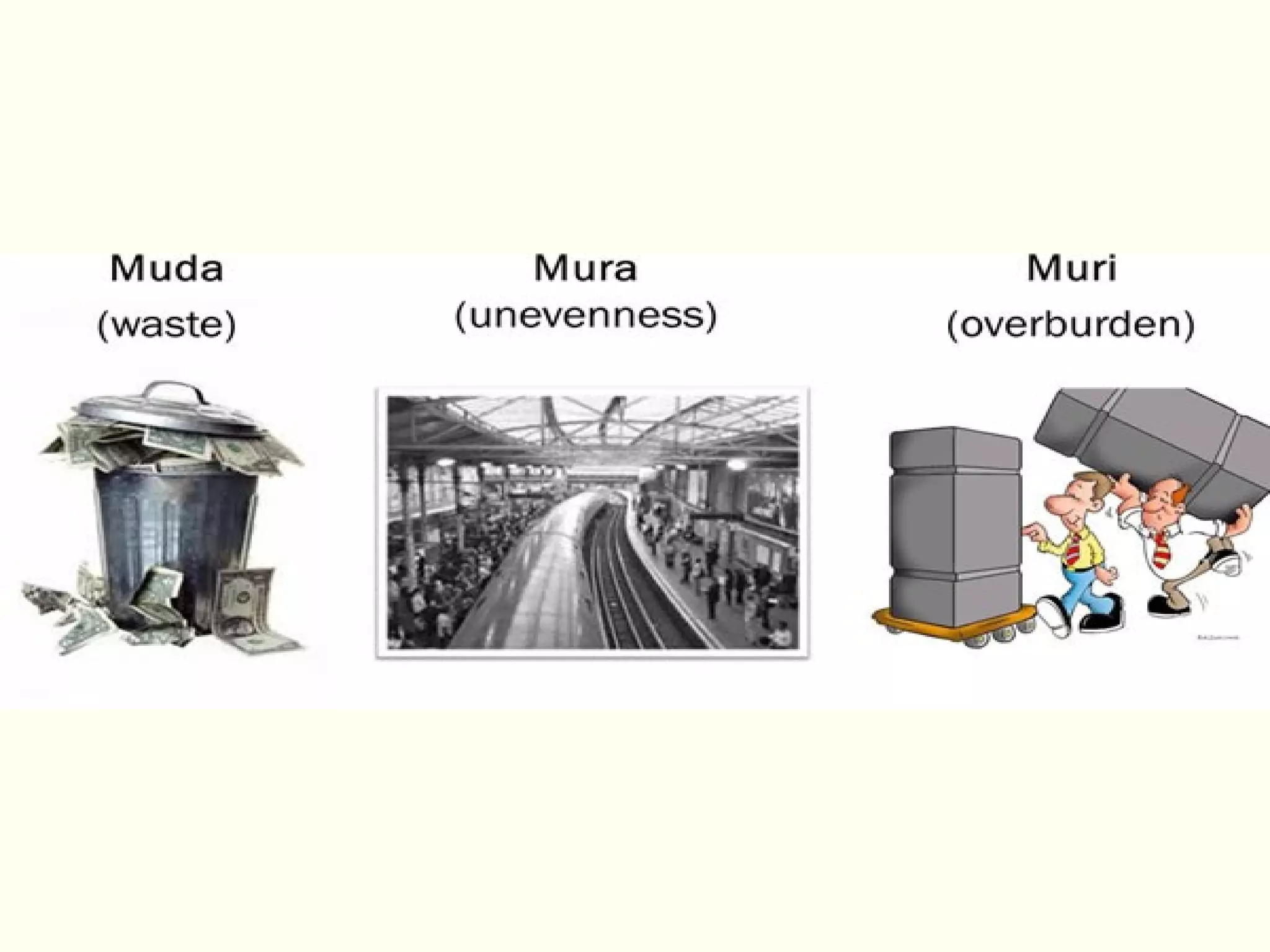
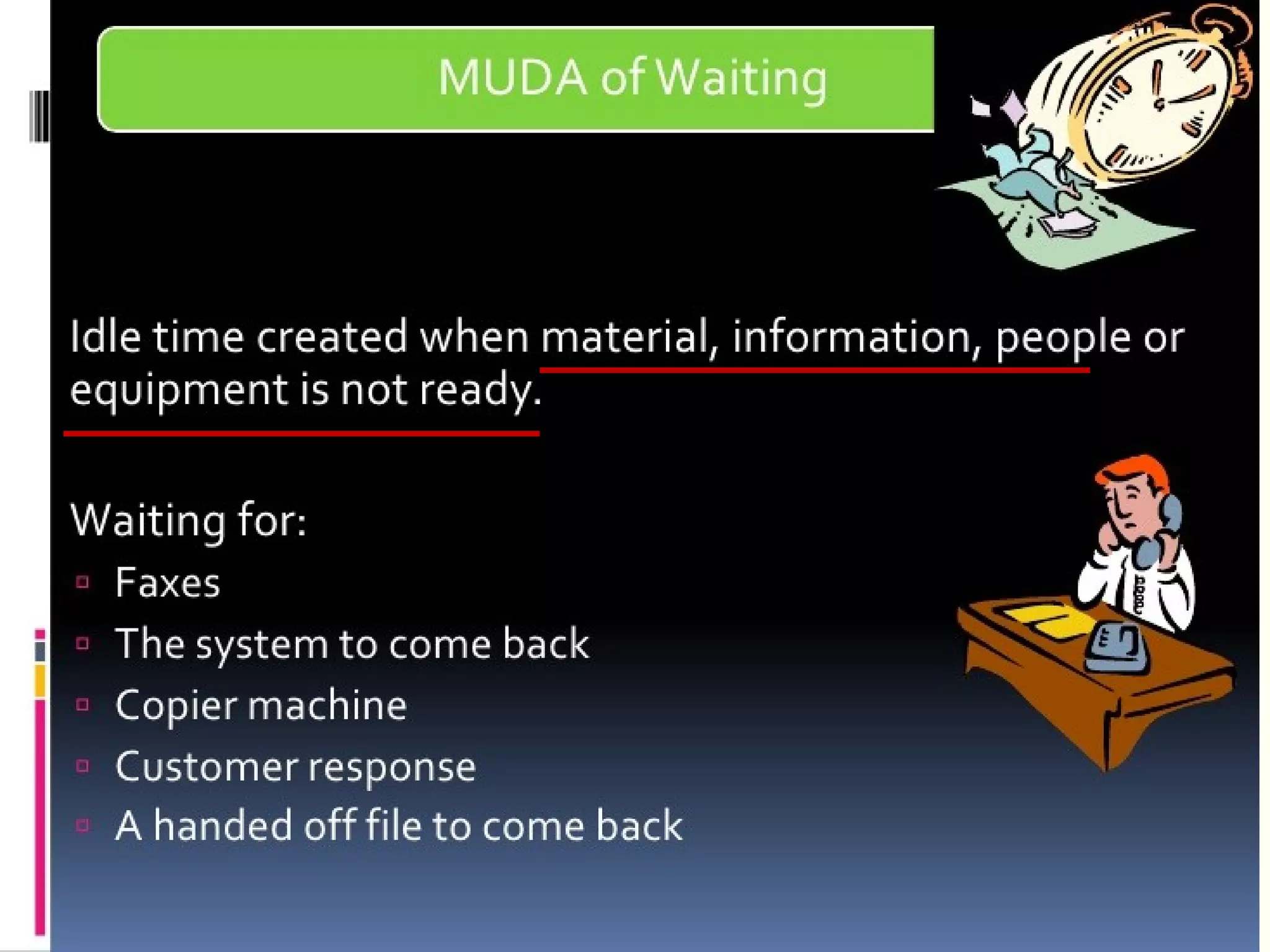
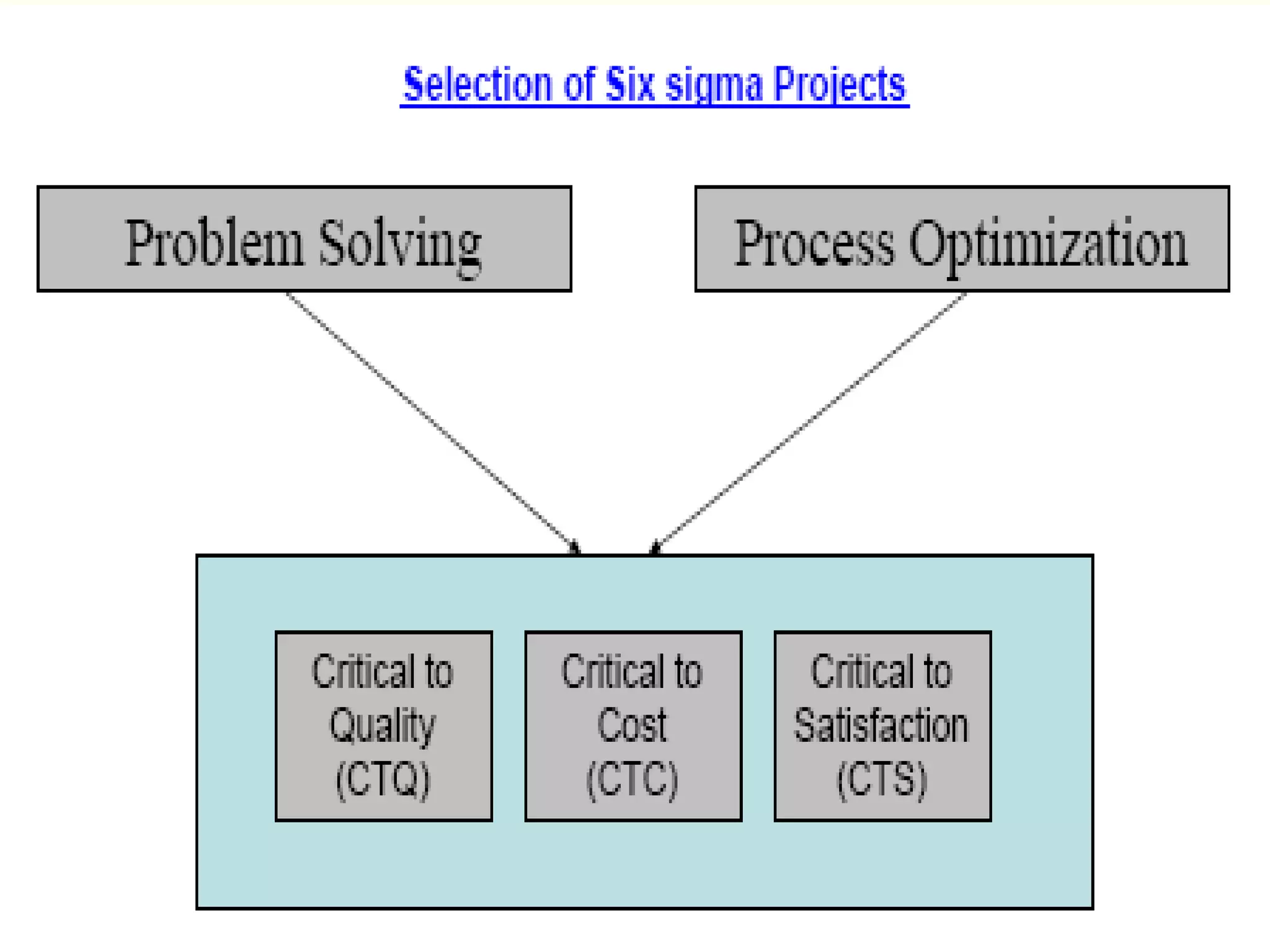
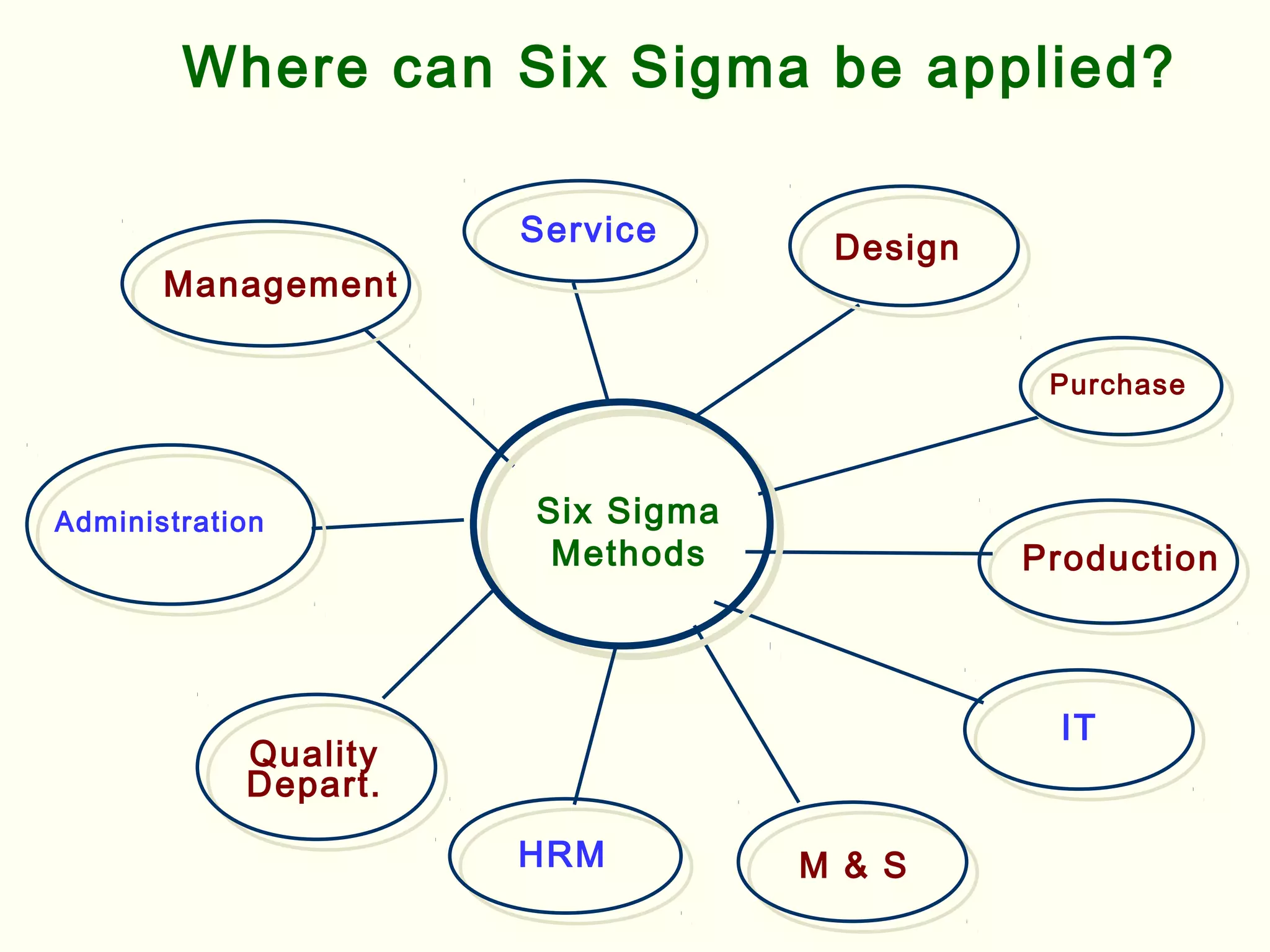
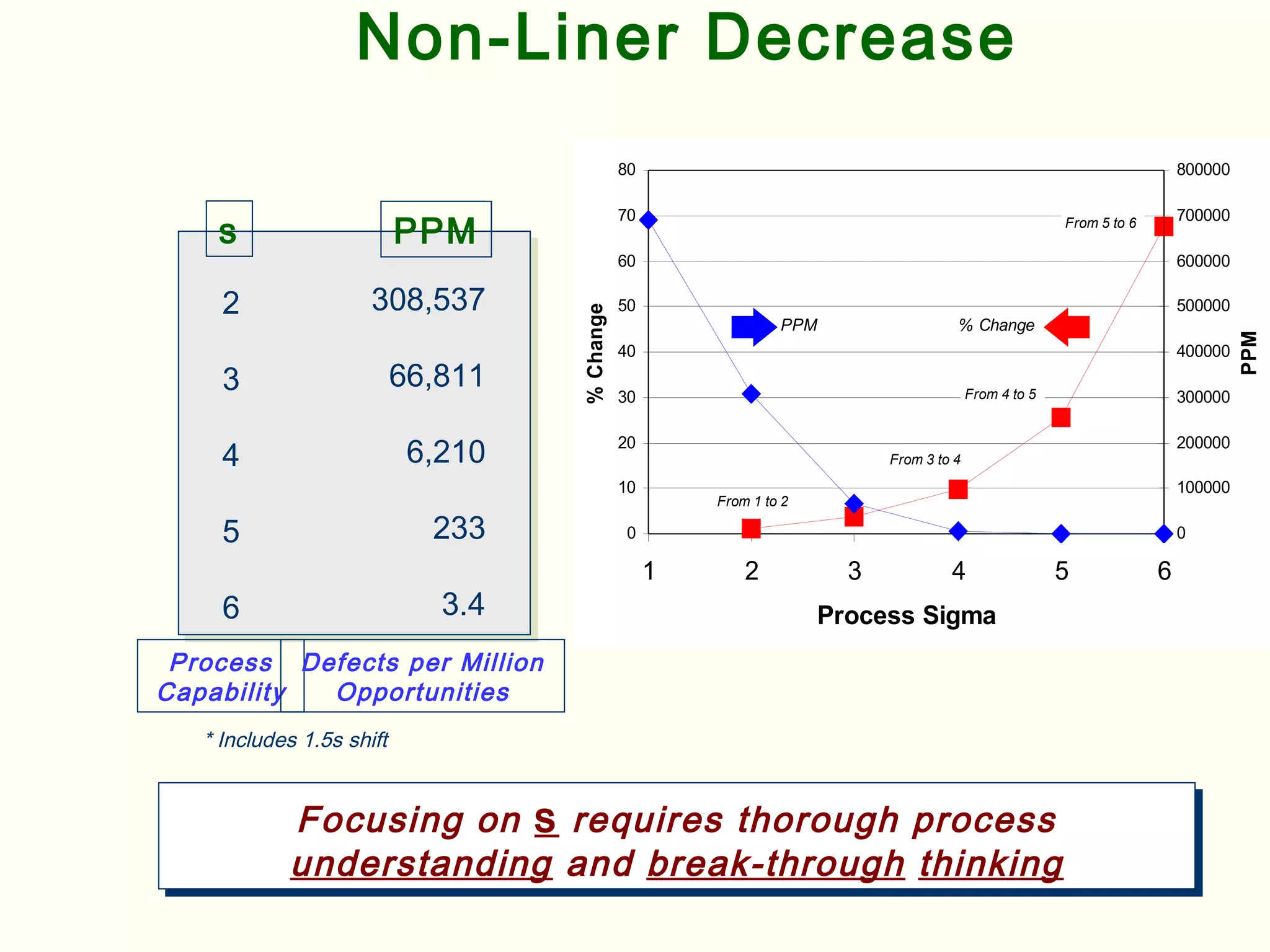
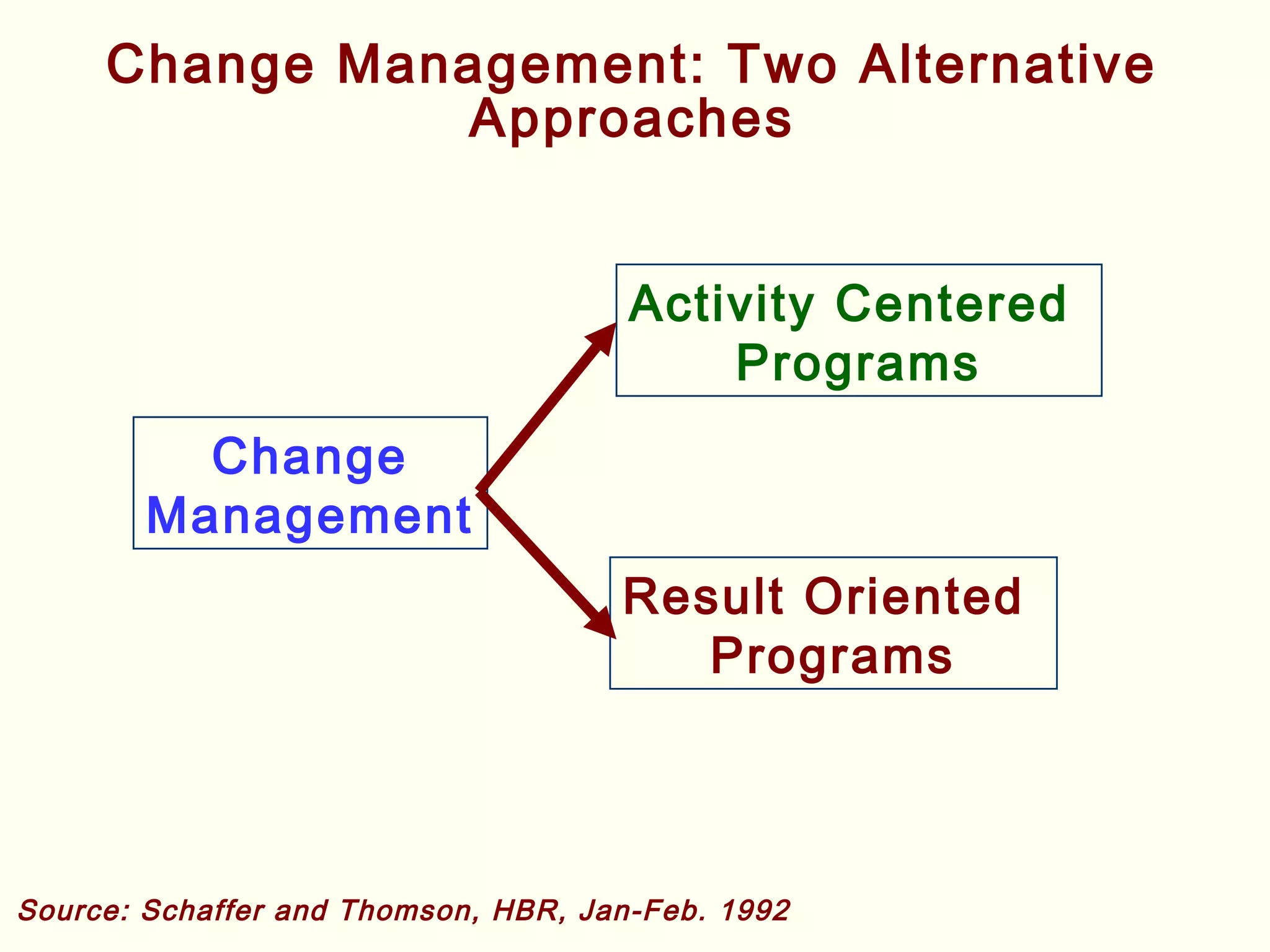
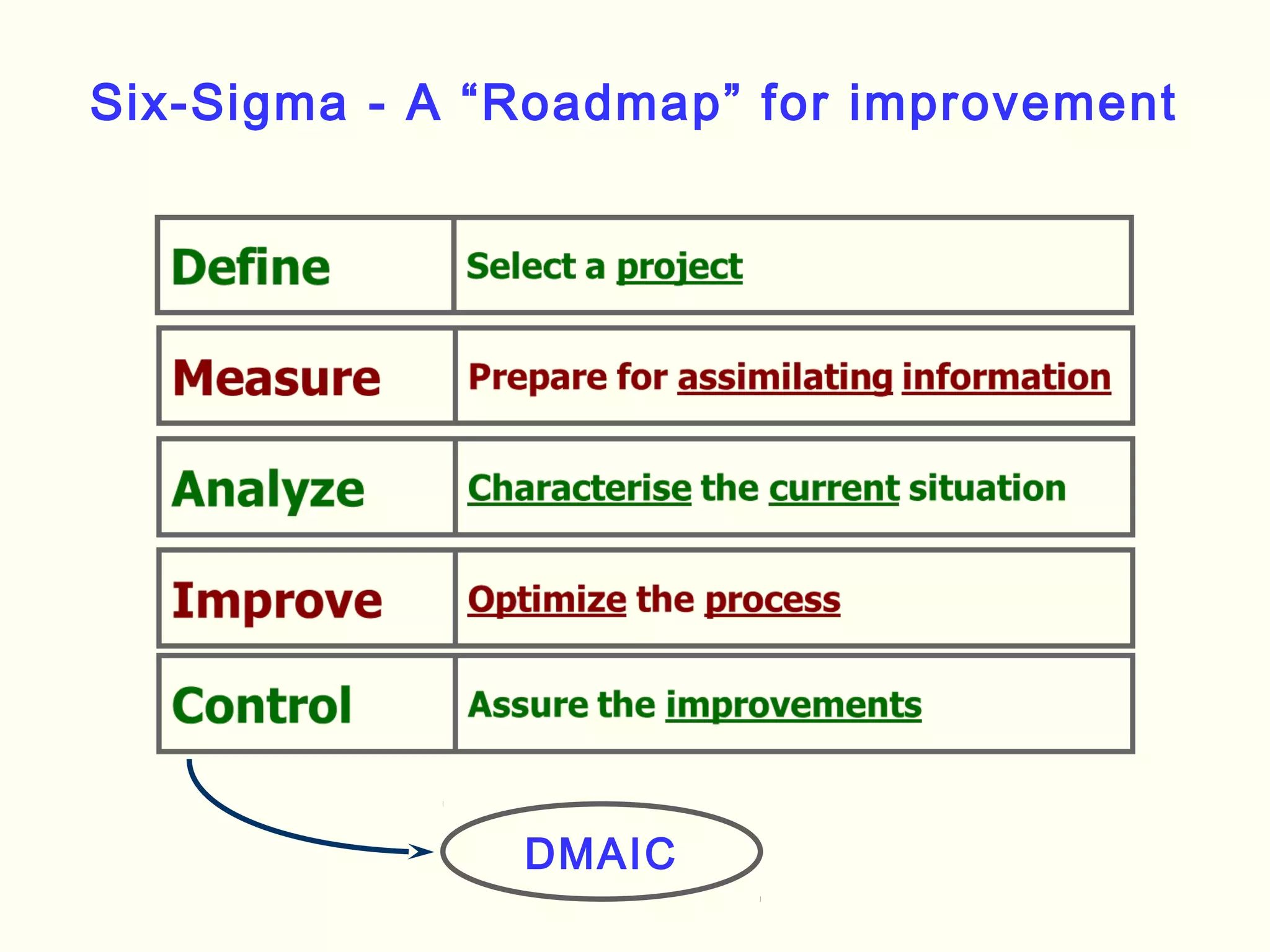
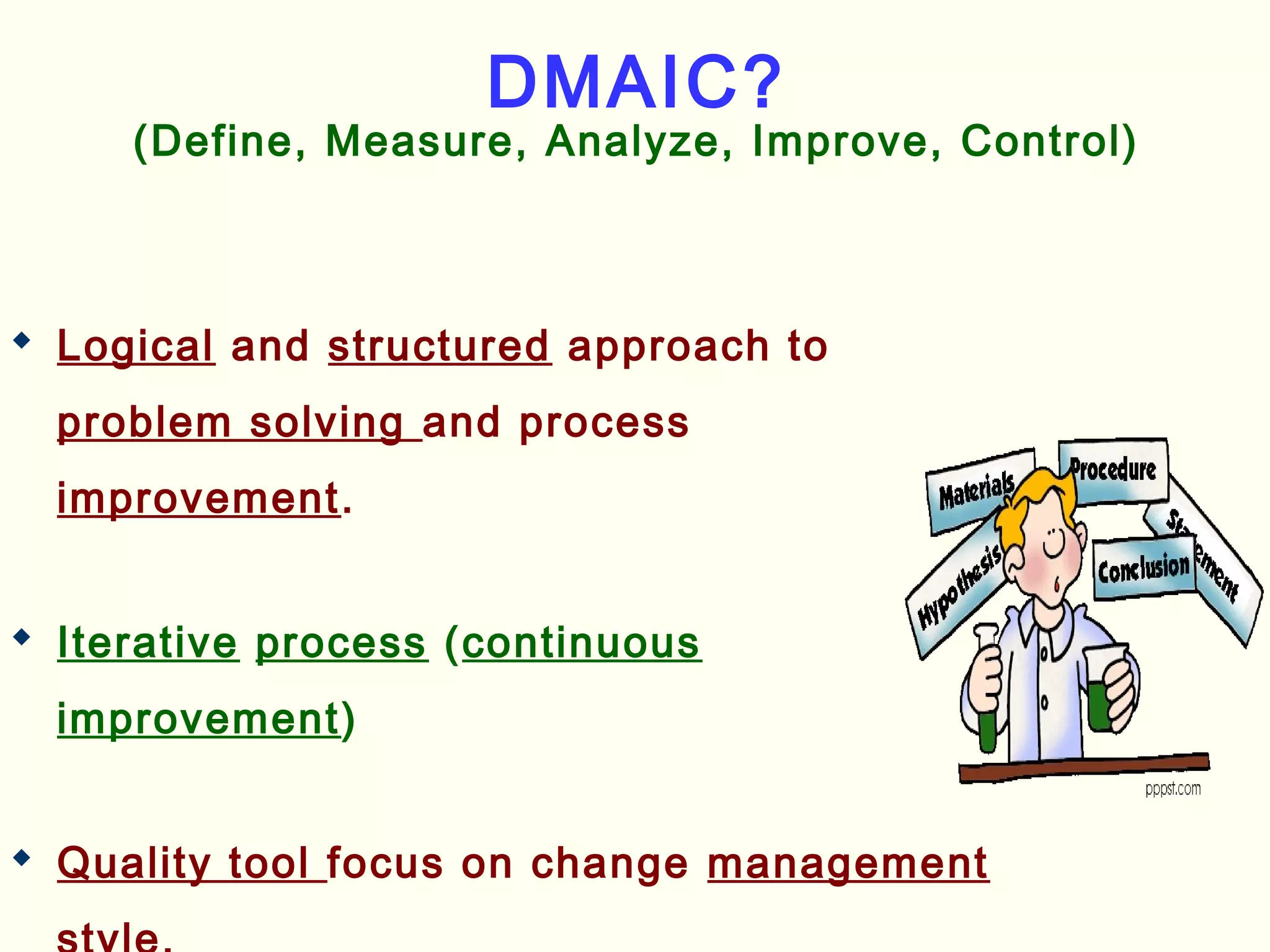
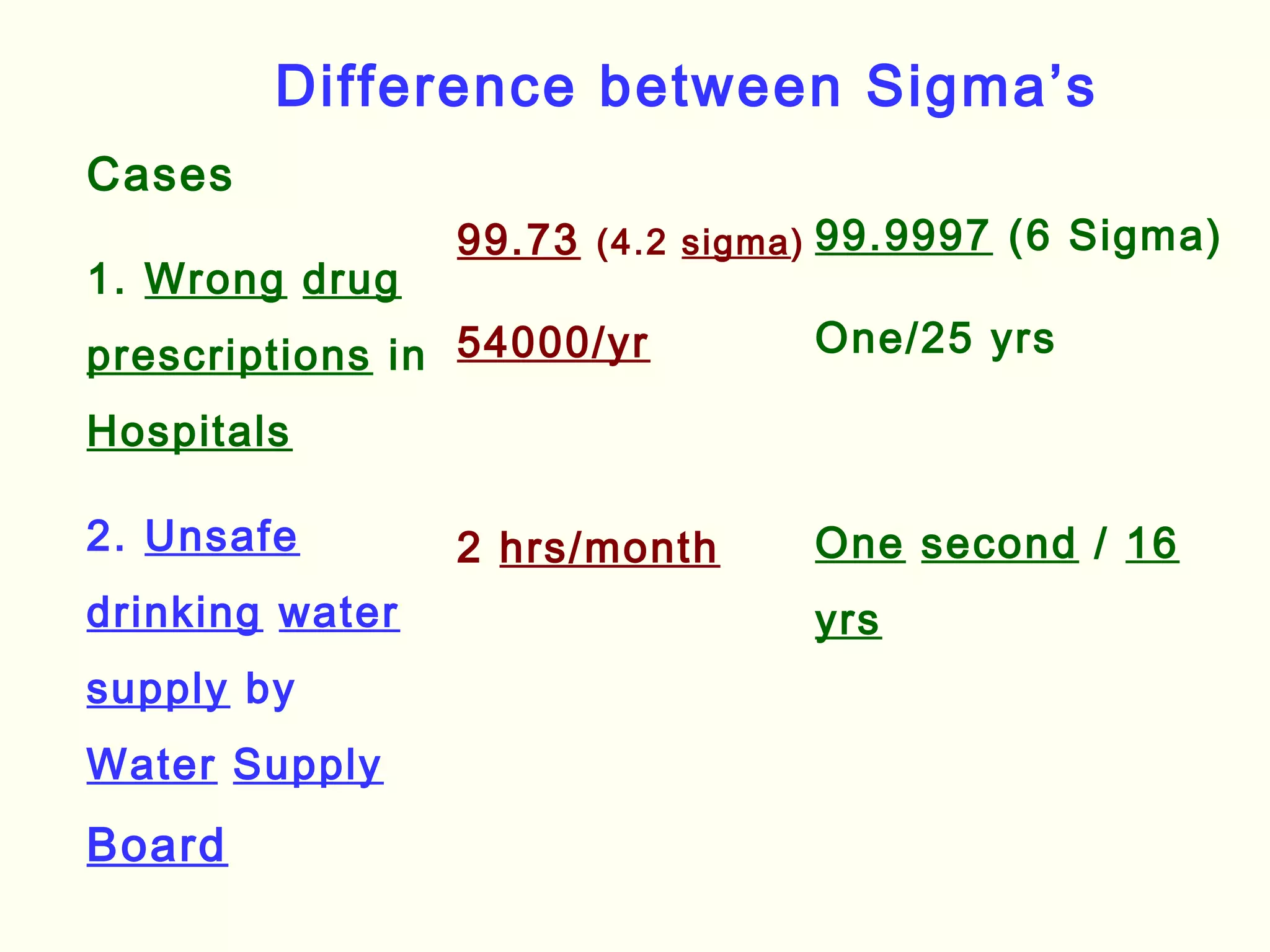
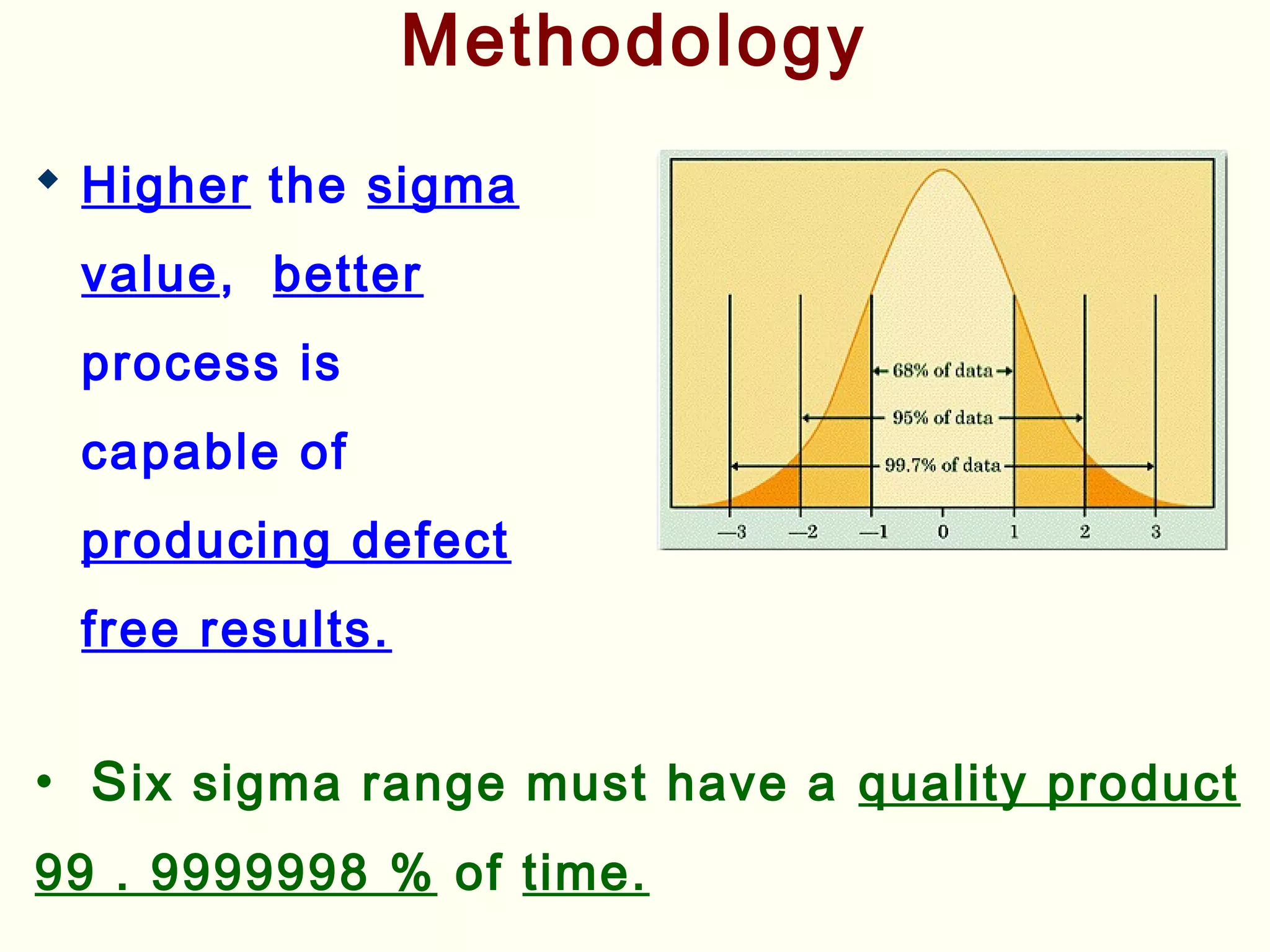
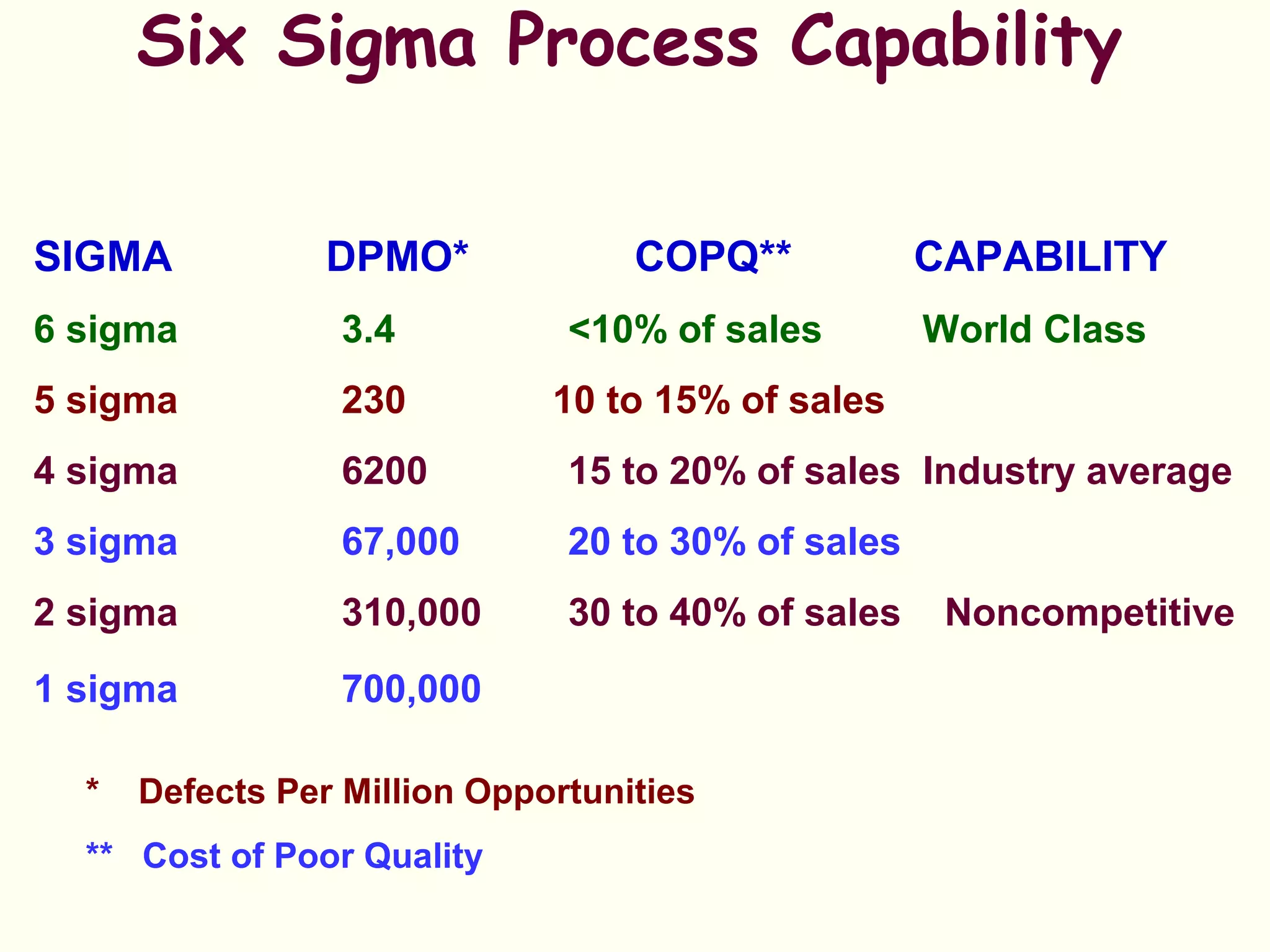
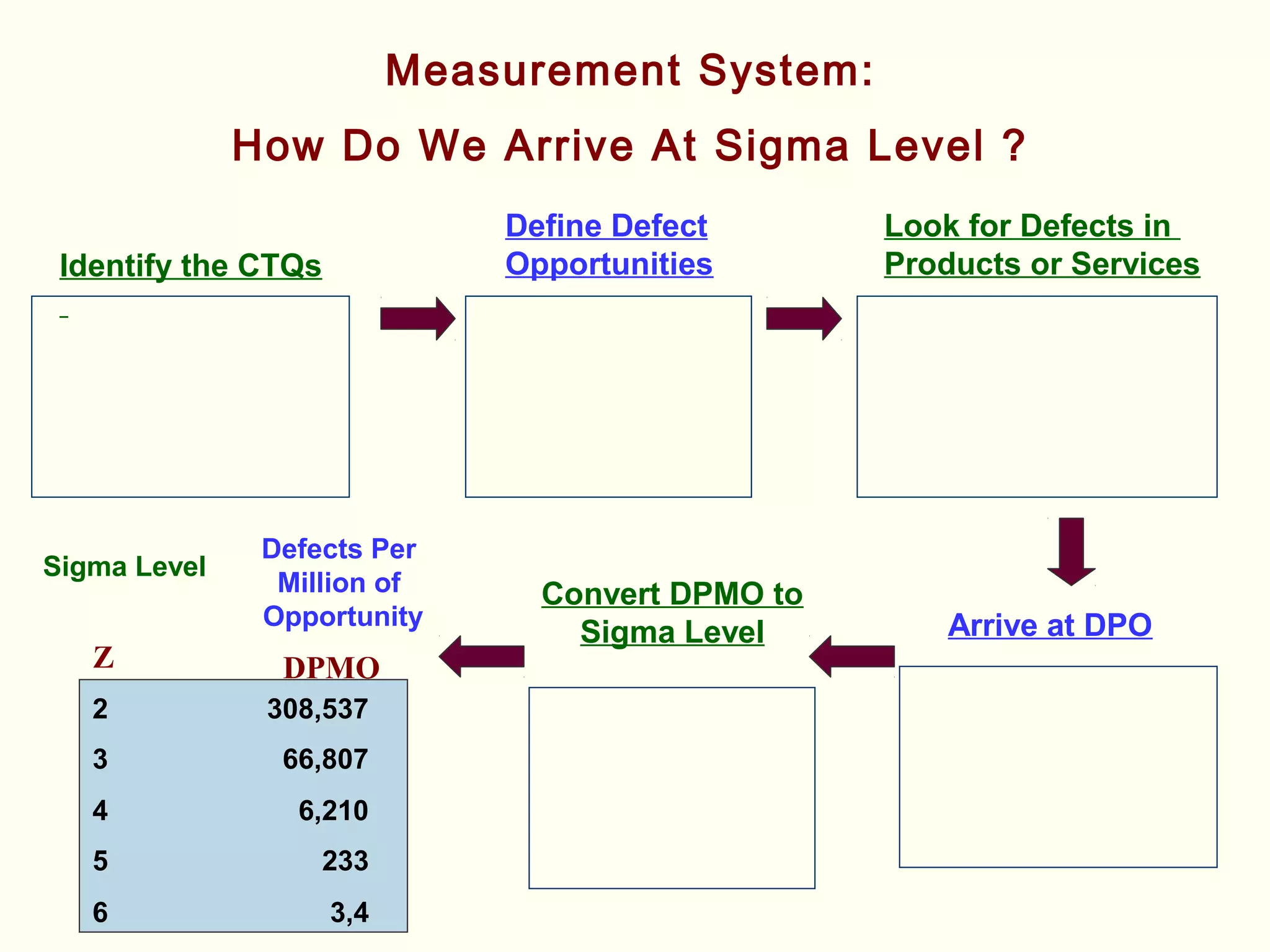
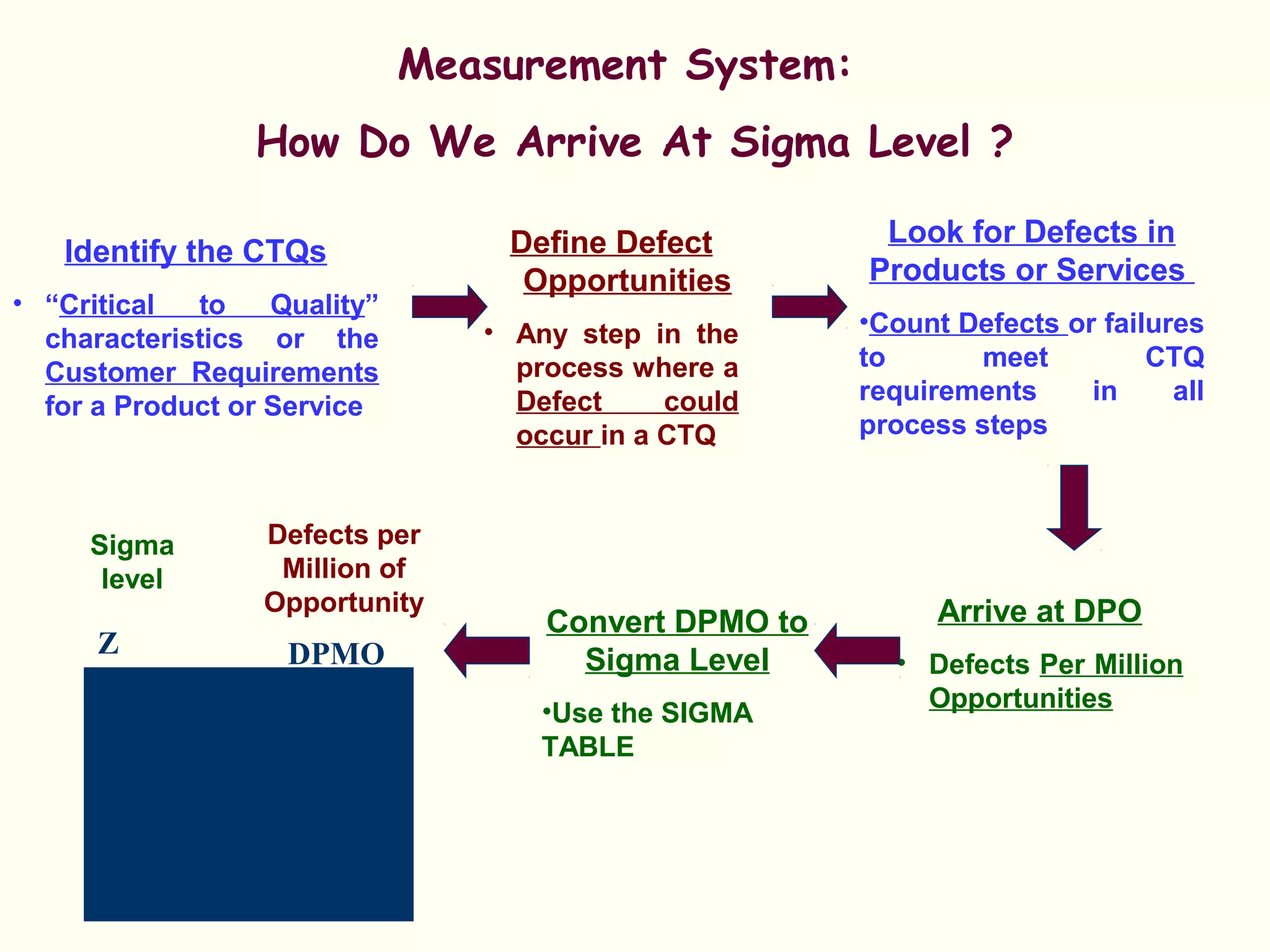
Lean management focuses on eliminating waste and increasing customer value. The seven types of waste are overproduction, waiting, transportation, inappropriate processing, unnecessary inventory, defects, and unnecessary motion. Lean uses less of everything through techniques like just-in-time production to half human effort, space, tools, and new product development time. Six Sigma aims to reduce variation and defects through statistical analysis and defines quality as 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It uses the DMAIC methodology of define, measure, analyze, improve, and control to solve problems and drive process improvement. Various standards like ISO, OHSAS, SA8000, ISO 14000 and ISO 26000 provide frameworks for quality, health and safety, social accountability, and