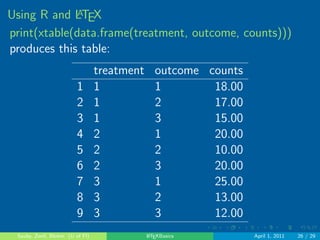
This document provides an introduction to LaTeX, covering what LaTeX is, why you would want to use it, its document structure, and how to include math, R code/objects, and references. LaTeX is a programming language used to create consistently formatted documents across different document types. It allows for fancy fonts, automatic numbering, and embedding of other objects like figures, tables, and R code/outputs. The document structure in LaTeX includes the preamble, top matter, main text, appendices, bibliography, and comments.







![. . . . . .
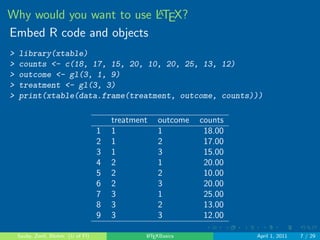
Why would you want to use LATEX?
Embed R code and objects
sample(100, 5)
[1] 85 79 82 62 73
Sauby, Zenil, Blohm (U of Fl) LATEXBasics April 1, 2011 6 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationgfforlatex-141003195207-conversion-gate02/85/LaTeX-Basics-12-320.jpg)












![. . . . . .
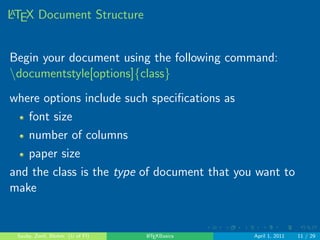
LATEX Document Structure
Begin your document using the following command:
ndocumentstyle[options]fclassg
where options include such speci](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationgfforlatex-141003195207-conversion-gate02/85/LaTeX-Basics-29-320.jpg)

![. . . . . .
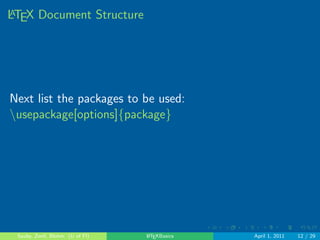
LATEX Document Structure
Next list the packages to be used:
nusepackage[options]fpackageg
Sauby, Zenil, Blohm (U of Fl) LATEXBasics April 1, 2011 12 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationgfforlatex-141003195207-conversion-gate02/85/LaTeX-Basics-31-320.jpg)