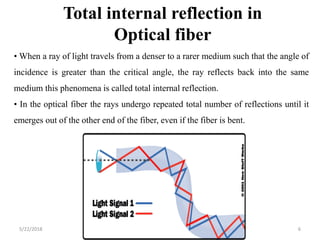
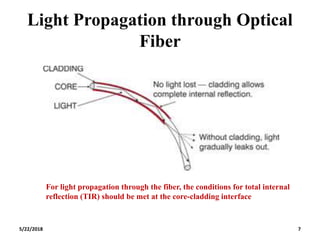
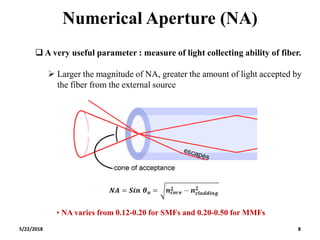
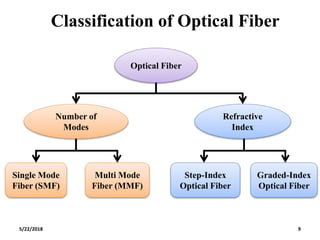
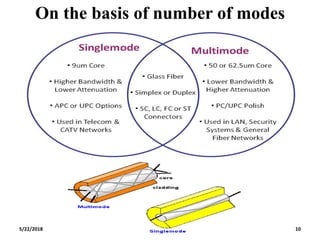
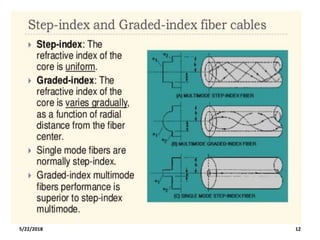
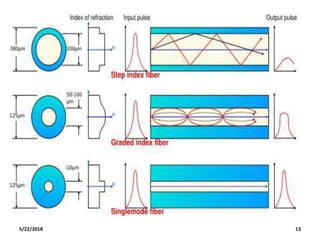
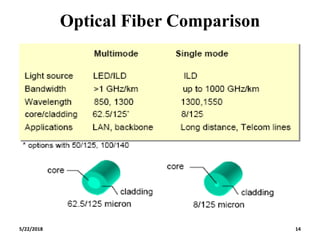
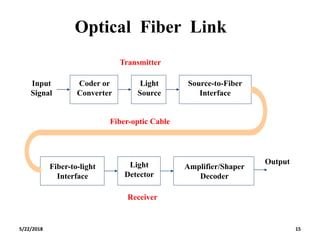
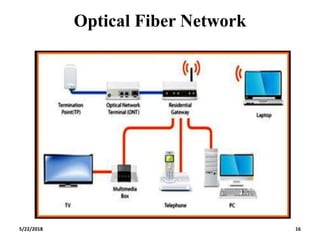
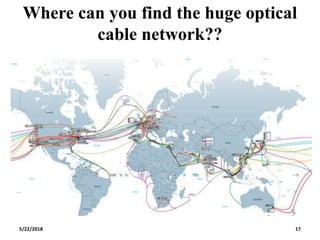
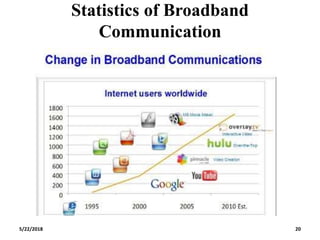
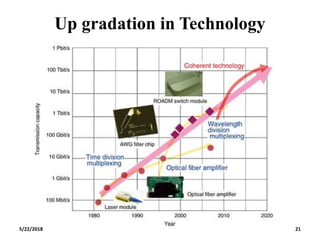
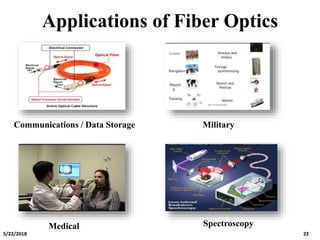
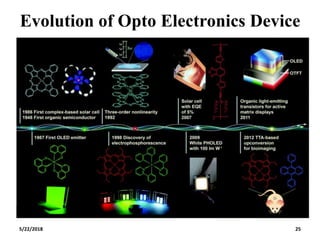
The document discusses the evolution and technology of optoelectronic devices and optical fiber communication, highlighting key historical milestones and the significance of optical fibers as a medium for guiding light. It explains the structure, classification, and propagation of light in optical fibers, including the concepts of total internal reflection and numerical aperture. The document also covers the application of fiber optics in various fields, alongside insights into the broadband communication network structure in India.