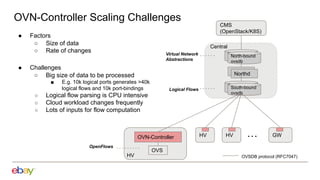
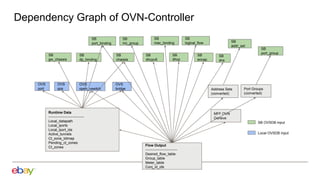
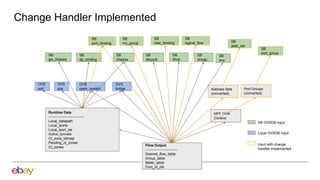
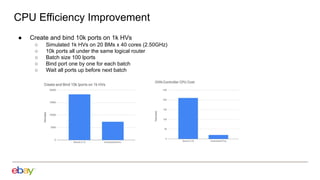
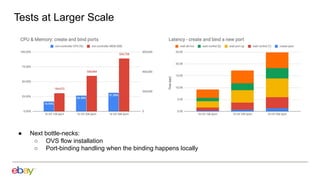
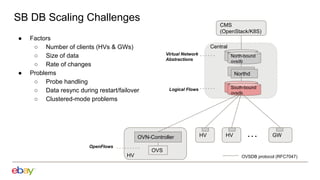
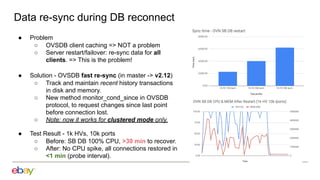
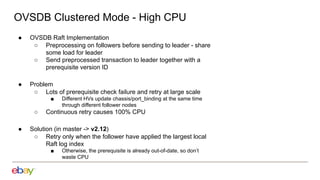
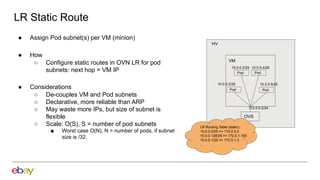
Han Zhou presents problems and solutions for scaling Open Virtual Network (OVN) components in large overlay networks. The key challenges addressed are:
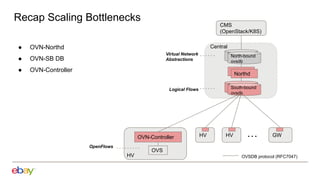
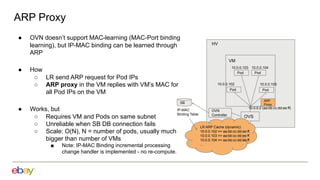
1. Scaling the OVN controller by moving from recomputing all flows to incremental processing based on changes.
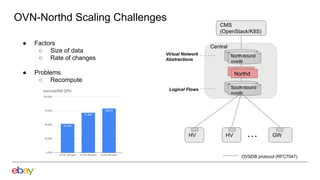
2. Scaling the southbound OVN database by increasing probe intervals, enabling fast resync on reconnect, and improving performance of the clustered mode.
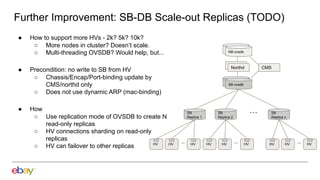
3. Further work is planned to incrementally install flows, reduce per-host data, and scale out the southbound database with replicas.