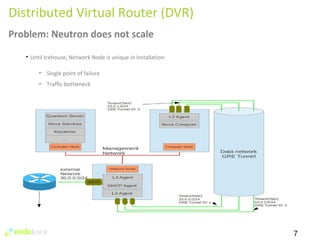
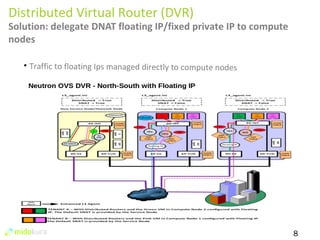
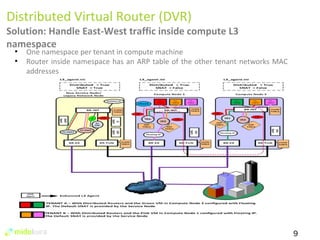
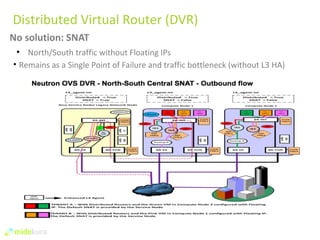
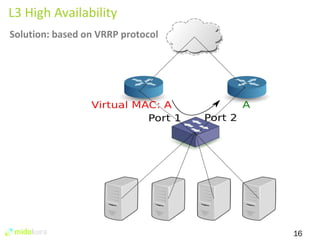
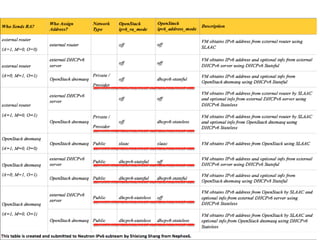
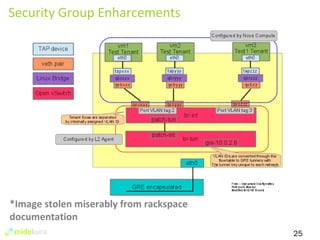
The document summarizes new features in Neutron for the Juno release, including improvements to achieve parity with Nova networking functionality, the addition of distributed virtual routing to improve scalability, L3 high availability using VRRP, full IPv6 support, and enhancements to security group implementation and communication between agents and servers.