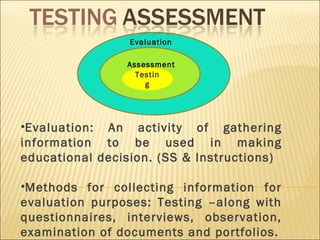
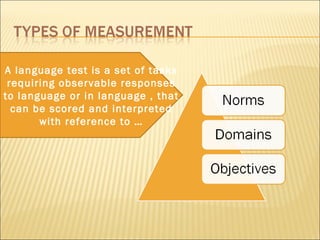
The document discusses testing and evaluation in education. It defines testing as a method to collect information to make educational decisions and notes that tests produce scores representing student attributes. The document also discusses evaluating language proficiency through testing listening comprehension, reading, dictation and other skills. It states that evaluation should use multiple methods and considers domain referencing, criterion referencing and norm referencing in interpreting test scores.