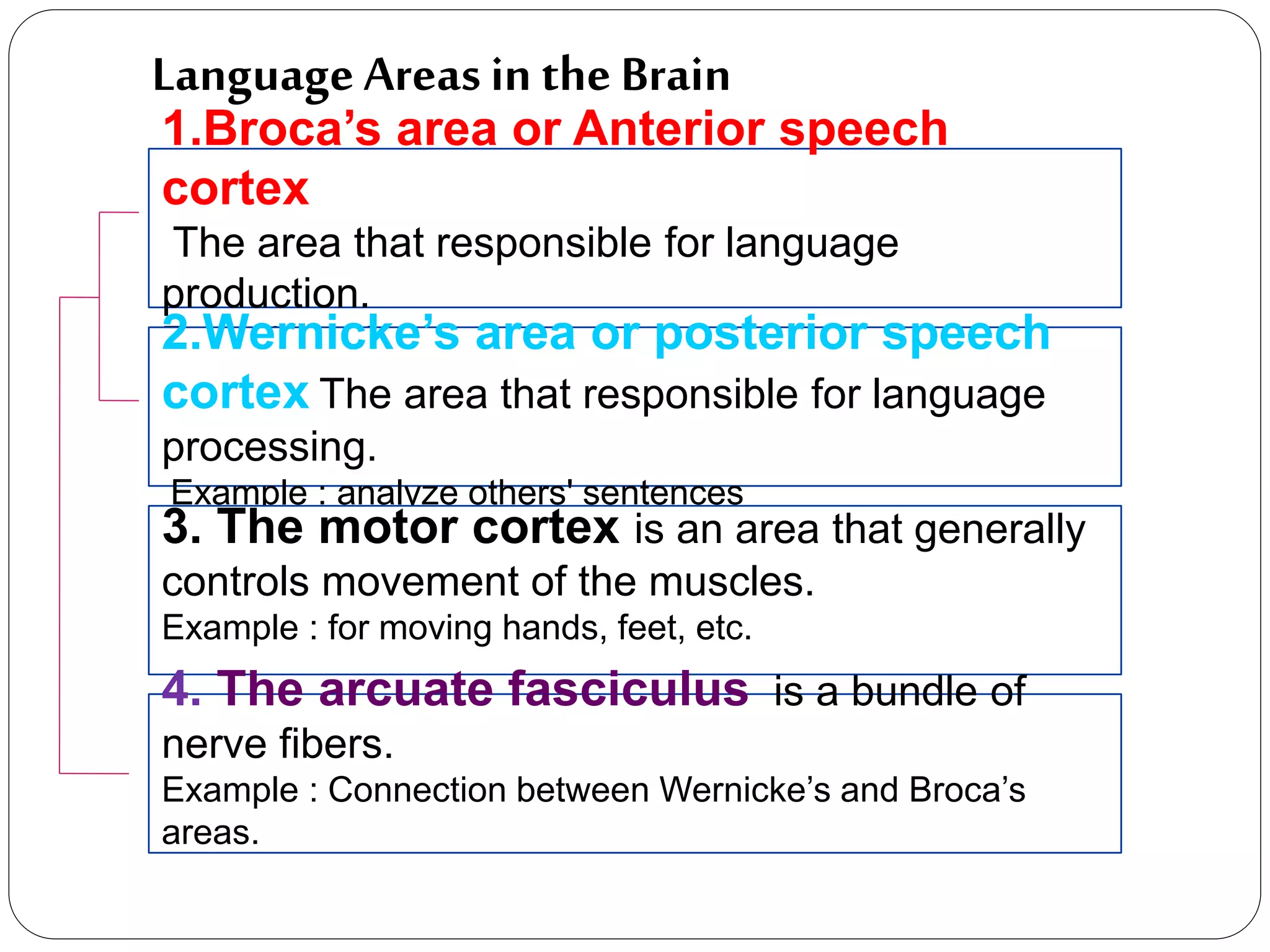
This document discusses neurolinguistics and the relationship between language and the brain. It describes several key language areas in the brain, including Broca's area, Wernicke's area, the motor cortex, and the arcuate fasciculus. It also discusses the localization view that specific language abilities can be linked to specific brain locations. The document then examines phenomena like slips of the tongue and slips of the ear. It provides definitions and examples of different types of aphasia that can result from brain damage, including Broca's aphasia and Wernicke's aphasia. The dichotic listening technique for studying brain asymmetry in auditory processing is also mentioned. Finally, the concept of