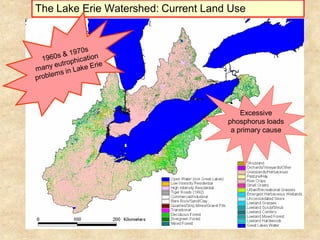
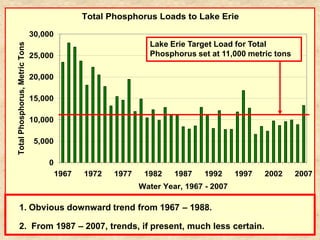
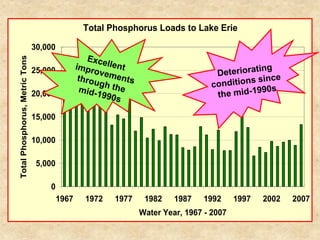
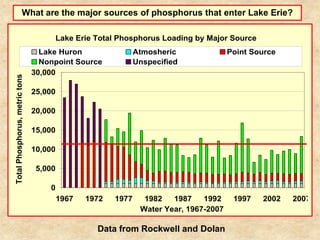
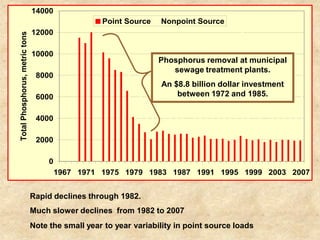
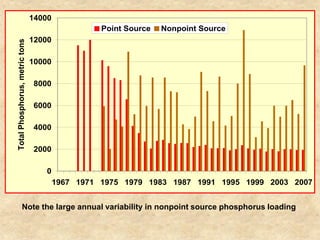
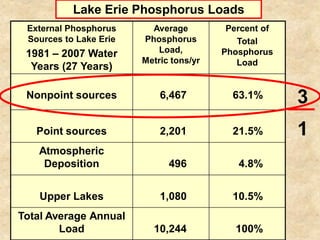
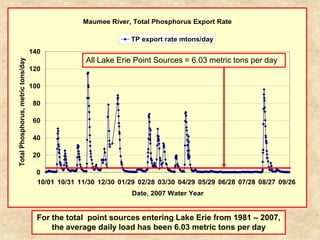
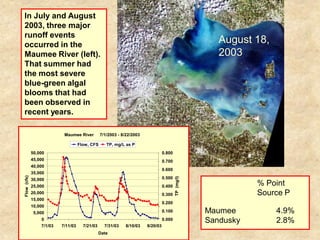
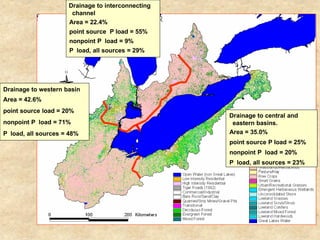
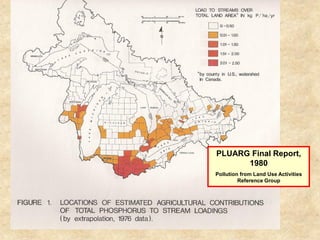
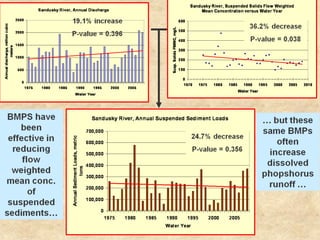
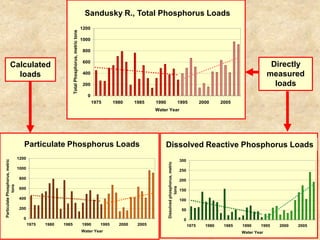
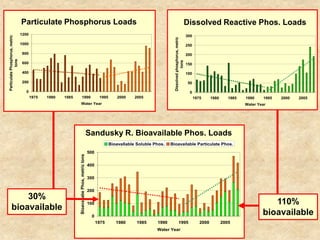
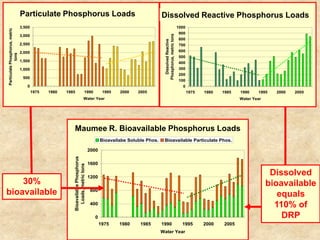
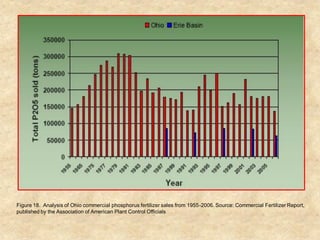
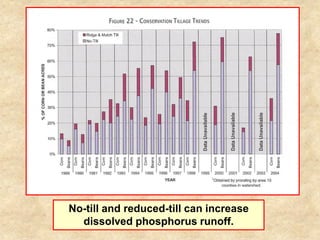
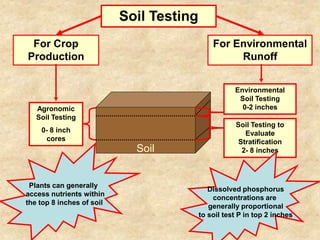
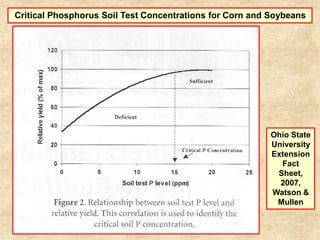
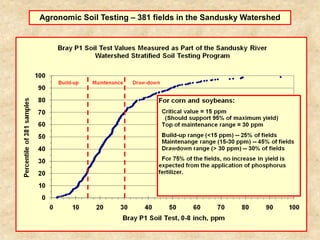
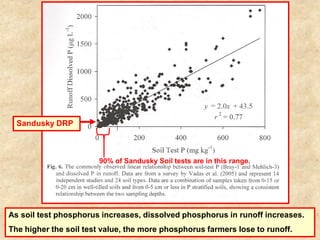
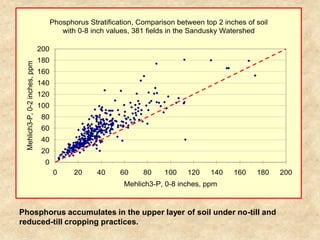
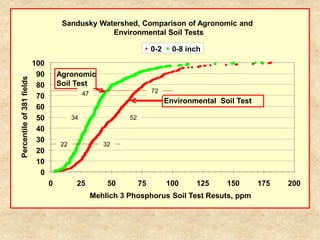
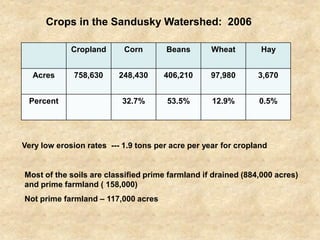
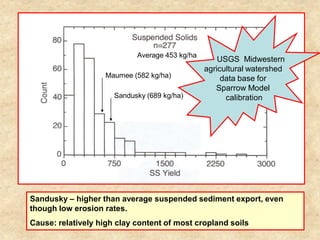
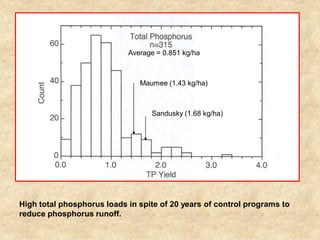
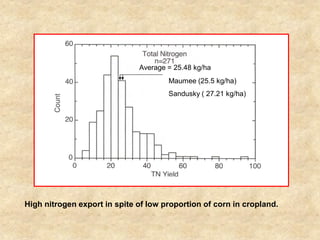
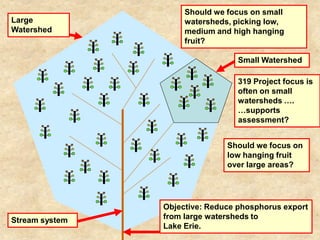
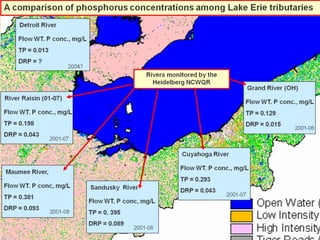
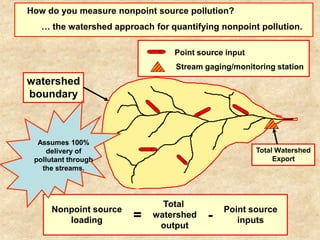
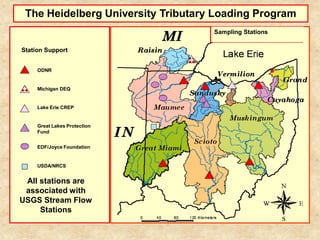
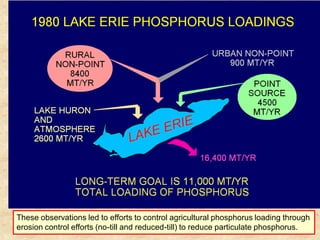
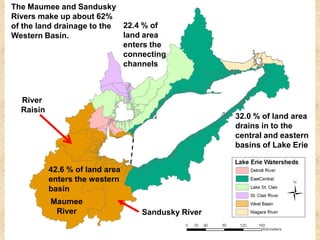
This document summarizes a presentation on phosphorus loading trends in Lake Erie. It finds that while point source phosphorus loads have significantly decreased due to sewage treatment upgrades, nonpoint source loads from agricultural runoff have not declined as sharply and show more annual variability. Specifically, the Maumee and Sandusky Rivers in Ohio export high levels of dissolved reactive phosphorus due to accumulation in surface soils under no-till practices. Reducing soil test phosphorus levels could help lower phosphorus losses to runoff.