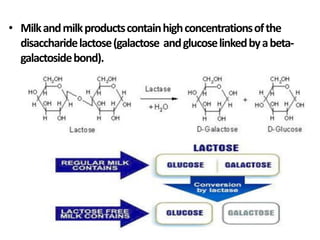
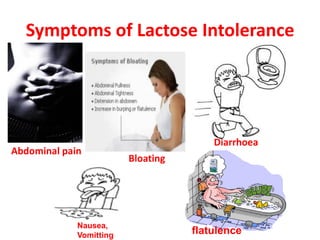
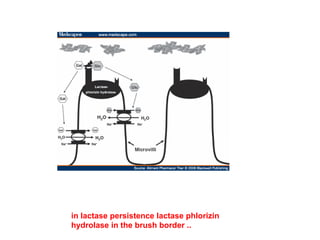
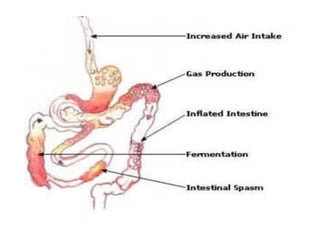
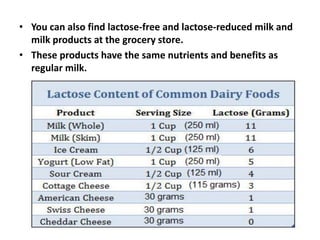
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body is unable to fully digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and milk products, due to a deficiency of the enzyme lactase. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea and flatulence. While infants produce lactase, levels typically decline after weaning in many populations worldwide. The condition can be managed by consuming smaller amounts of dairy, lactose-reduced dairy products, or supplements containing lactase enzymes. It is important for those with lactose intolerance to ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake through alternative food sources or supplements.