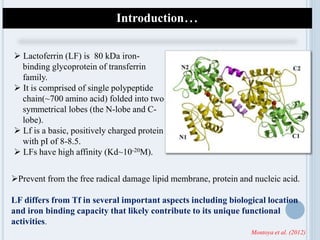
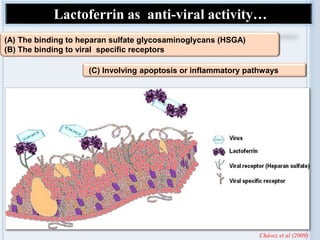
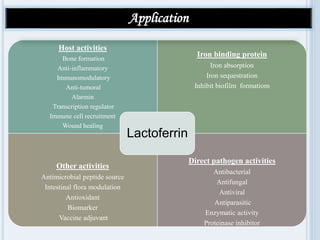
Lactoferrin is an 80 kDa iron-binding glycoprotein known for its multifunctionality, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. It plays a crucial role in inhibiting bacterial growth by sequestering iron and blocking pathogen adhesion, while also showing potential in neuroprotection and as a therapeutic agent against various viruses. Current research emphasizes the need for advancements in its application across food, feed, and pharmaceutical sectors to enhance efficacy and consumer acceptance.