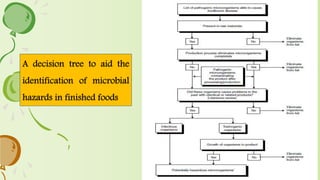
1. The document discusses various types of hazards including chemical, physical, biological, noise, and ergonomic hazards.
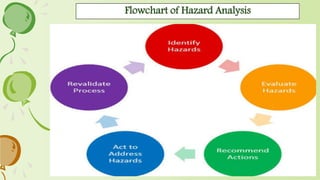
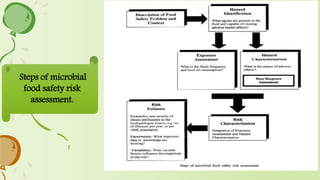
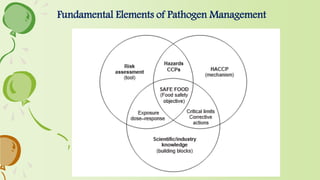
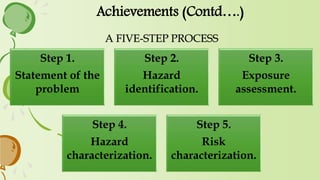
2. It also discusses key aspects of microbial risk assessment such as hazard identification, exposure assessment, hazard analysis, and risk assessment.
3. Quantitative microbial risk assessment is presented as an important discipline that uses computational techniques and data to model and predict public health outcomes from food safety hazards.