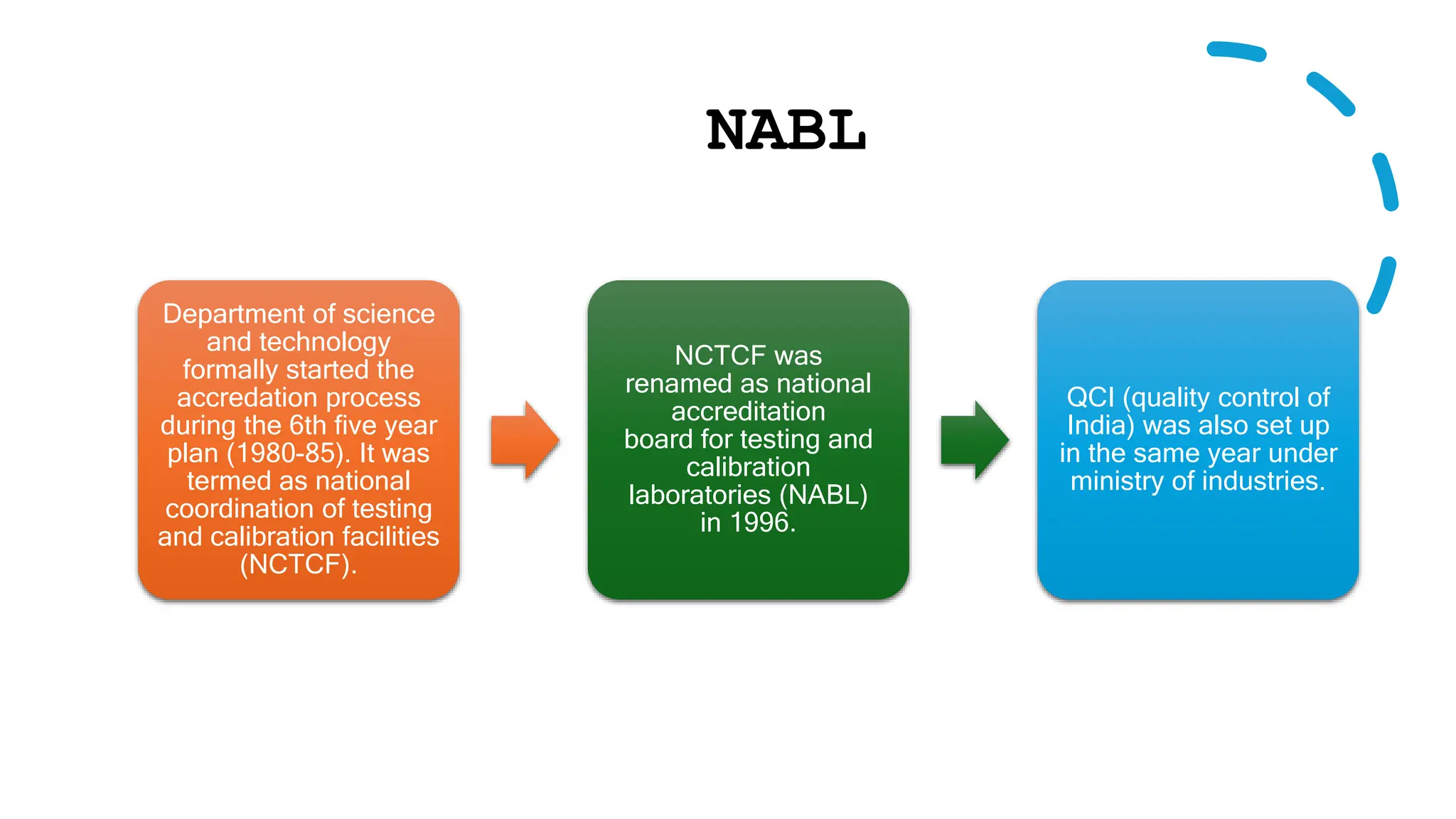
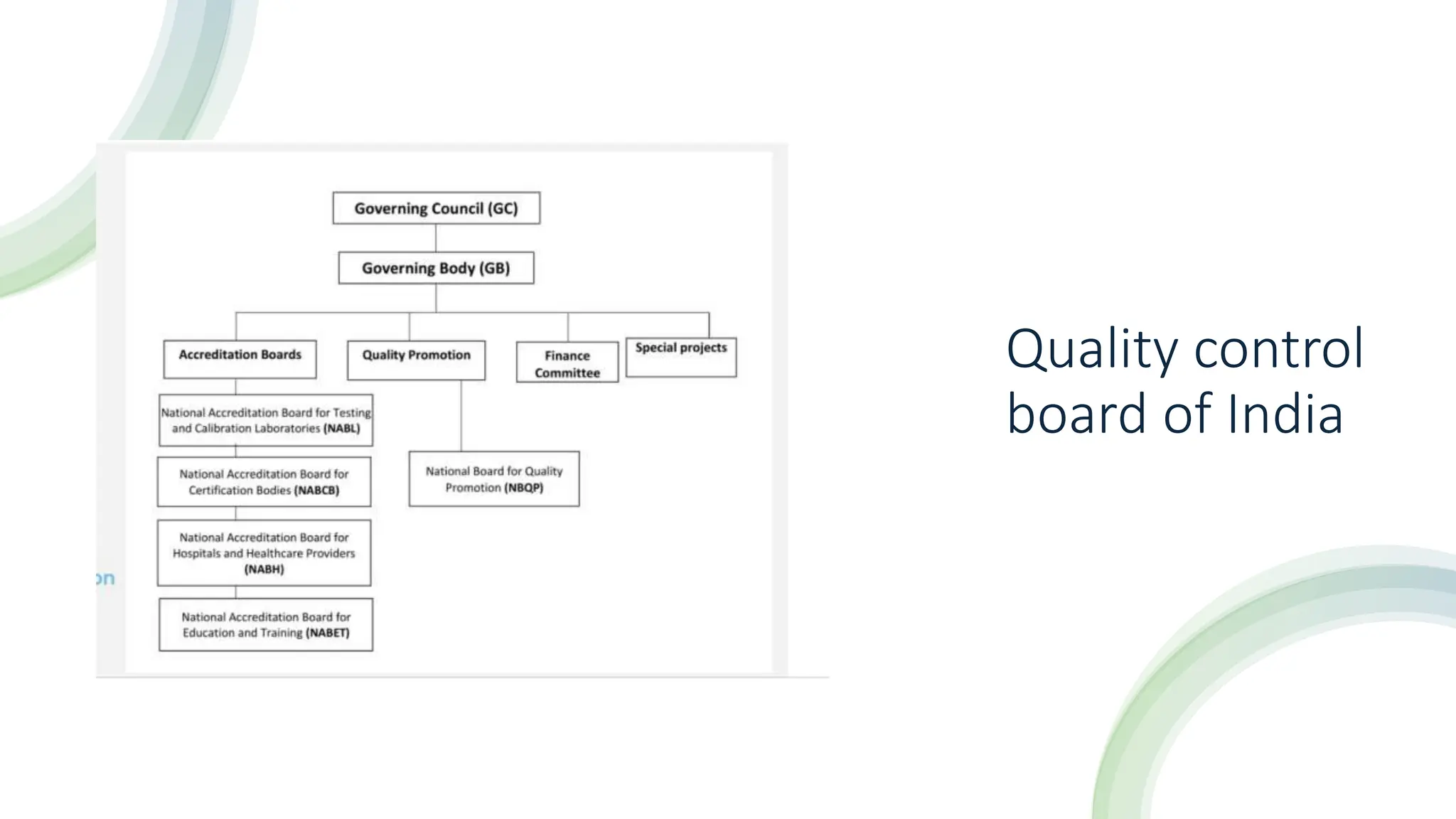
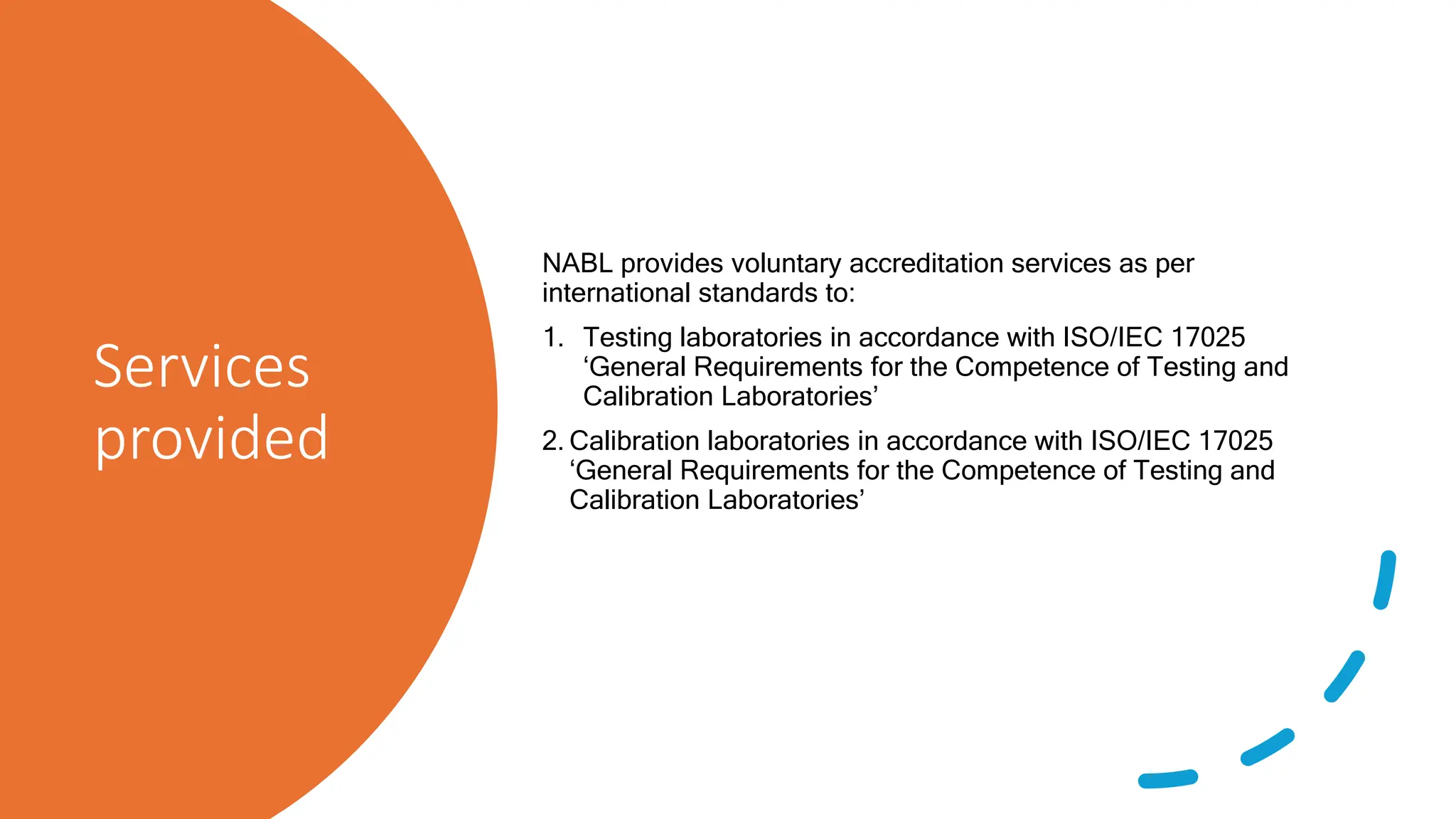
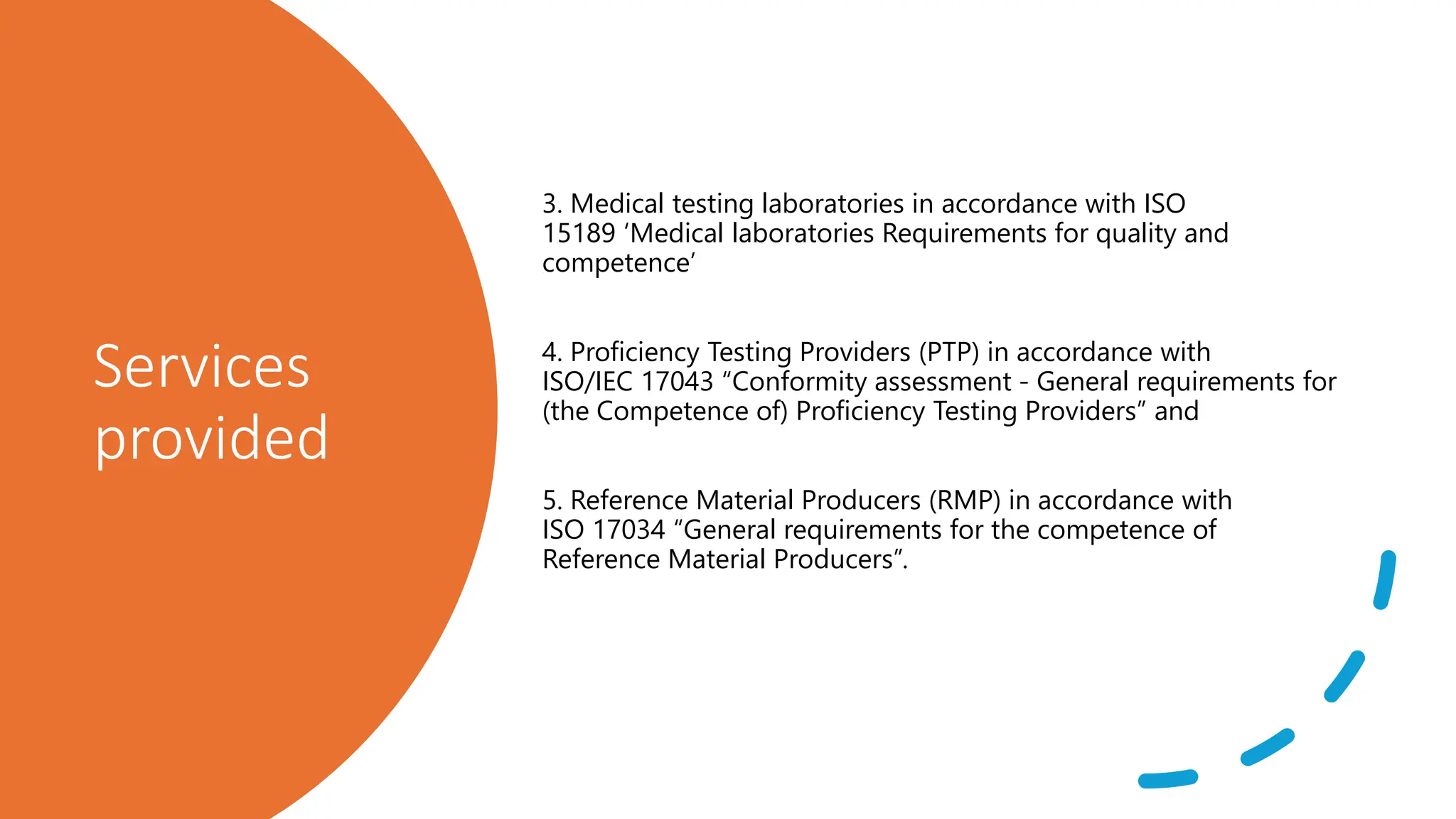
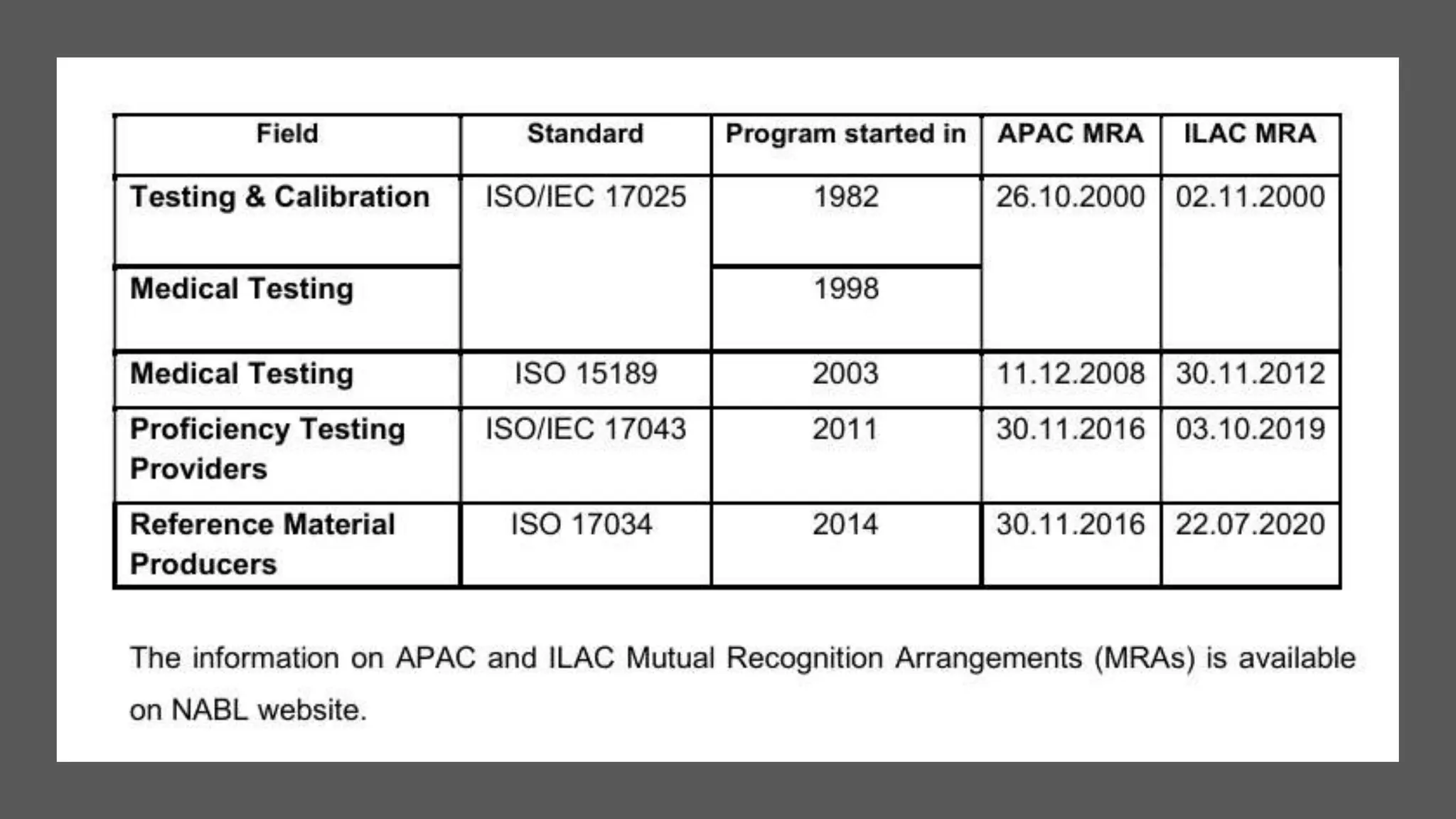
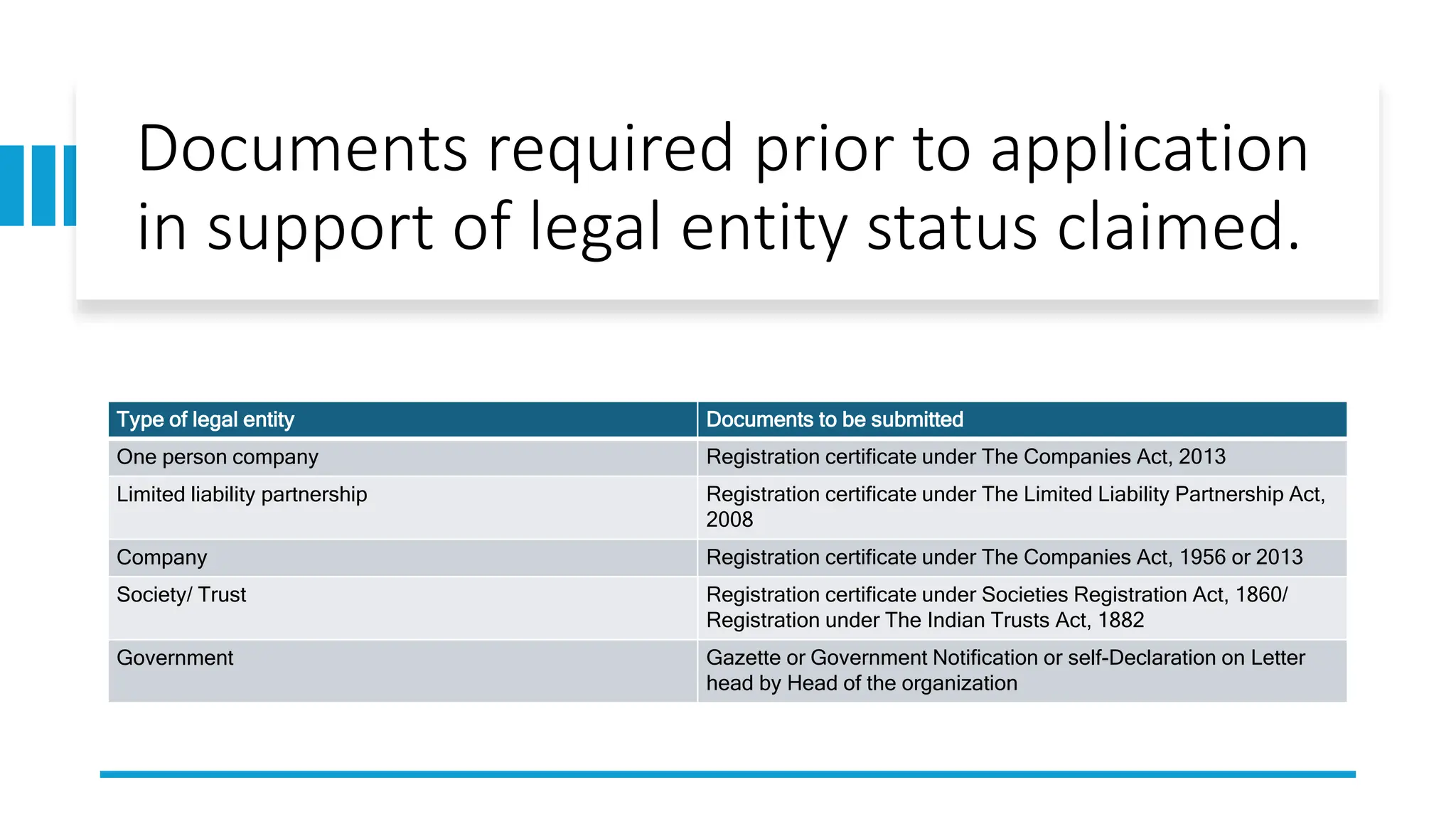
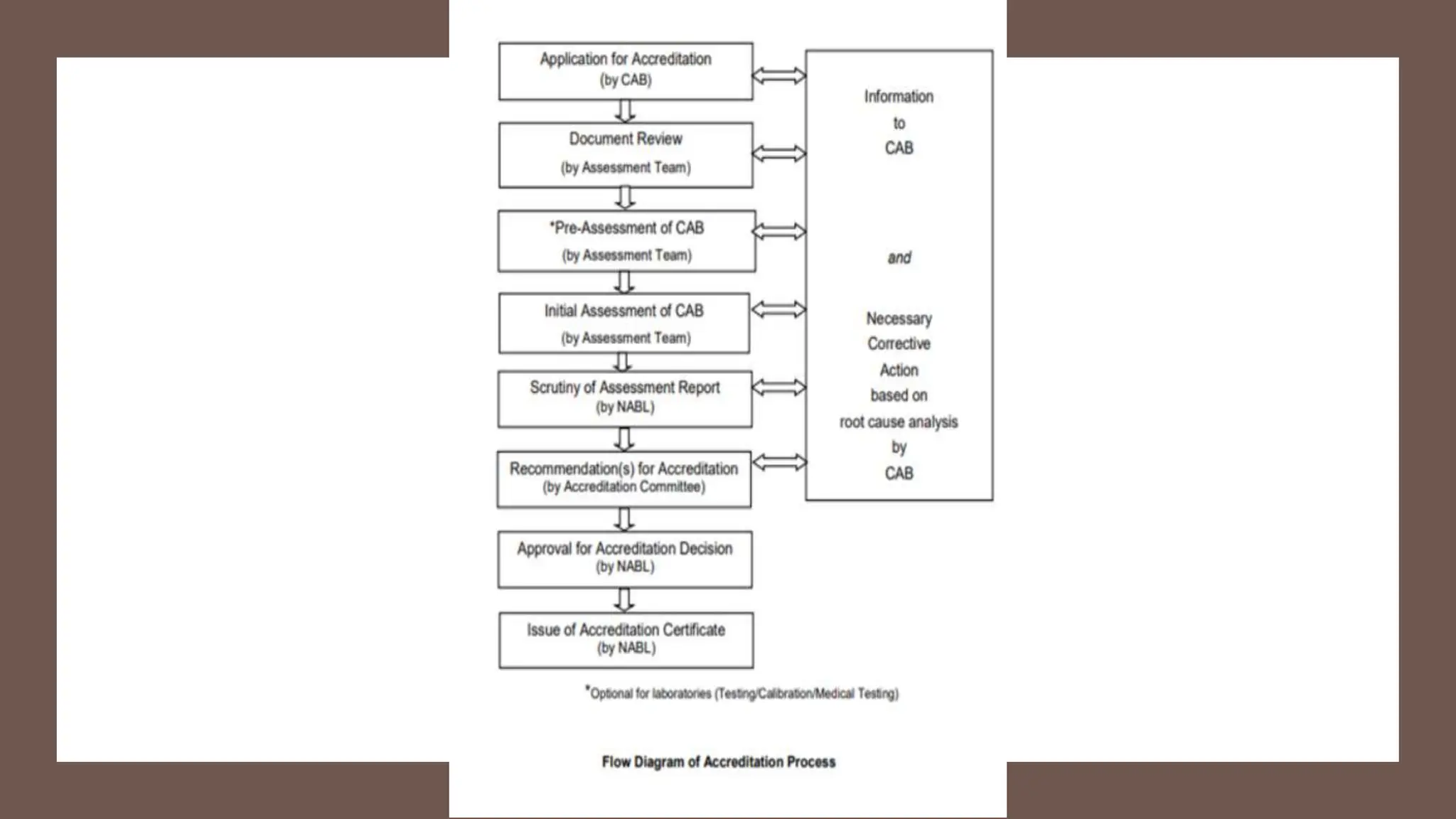
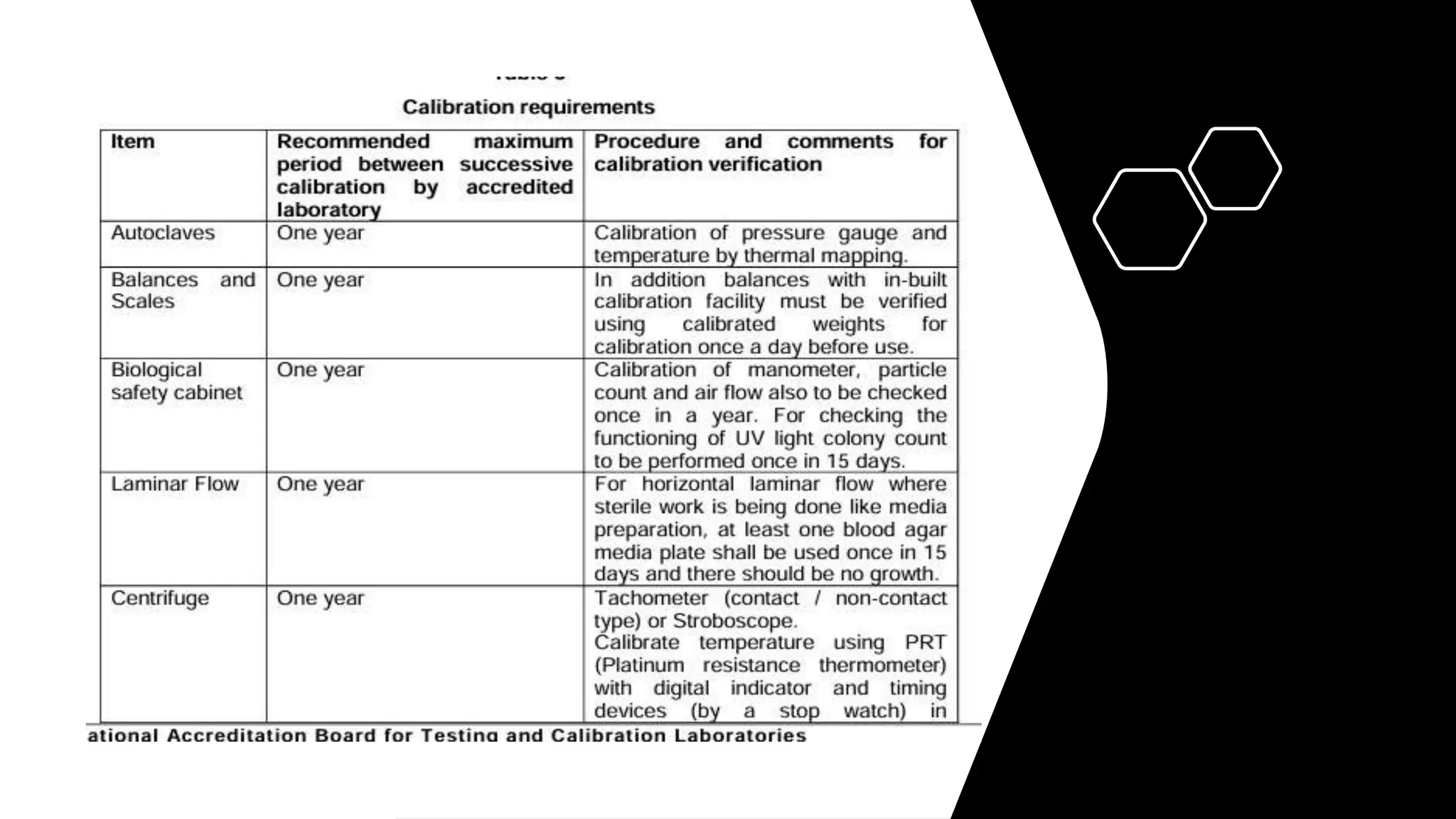
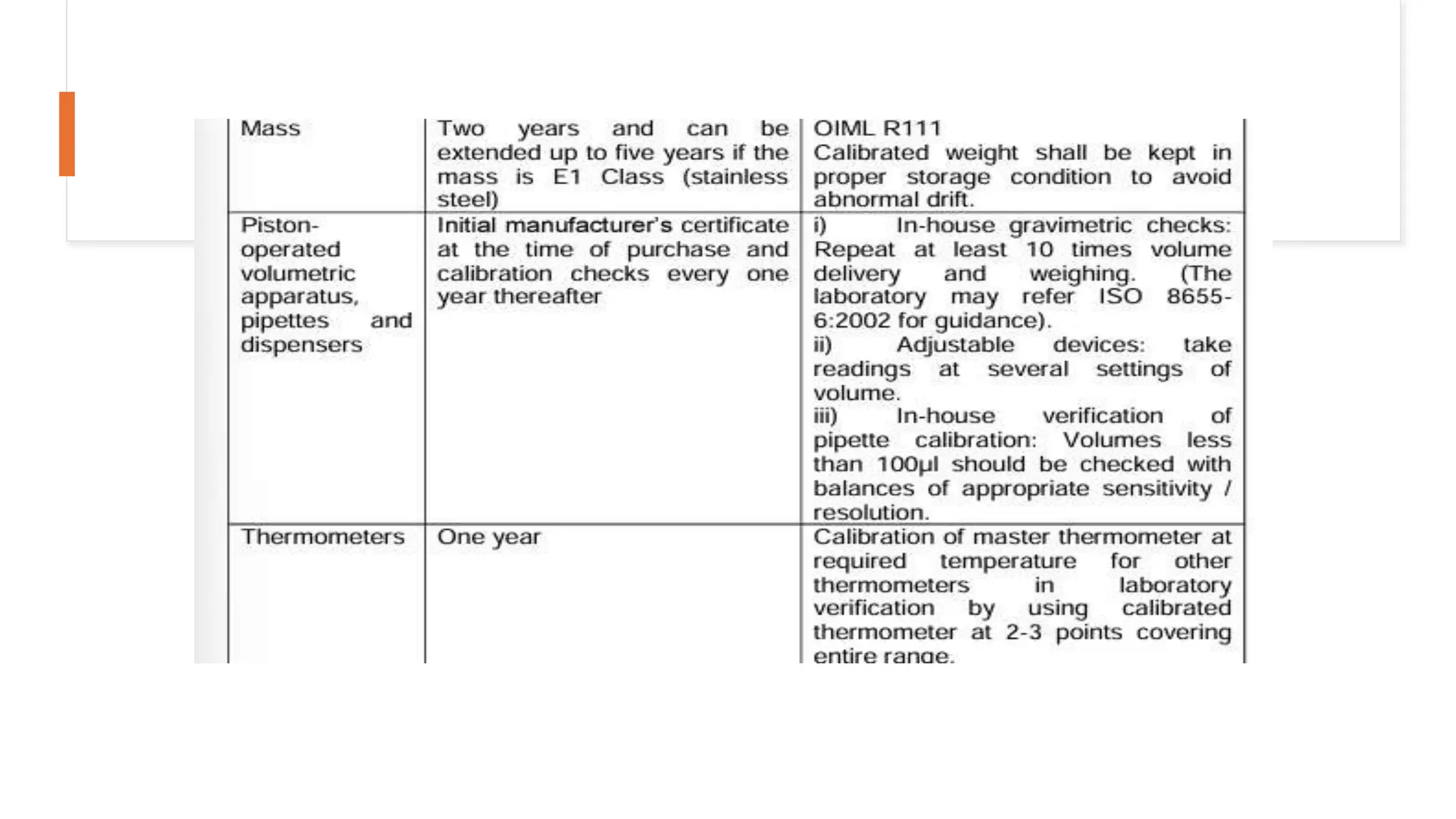
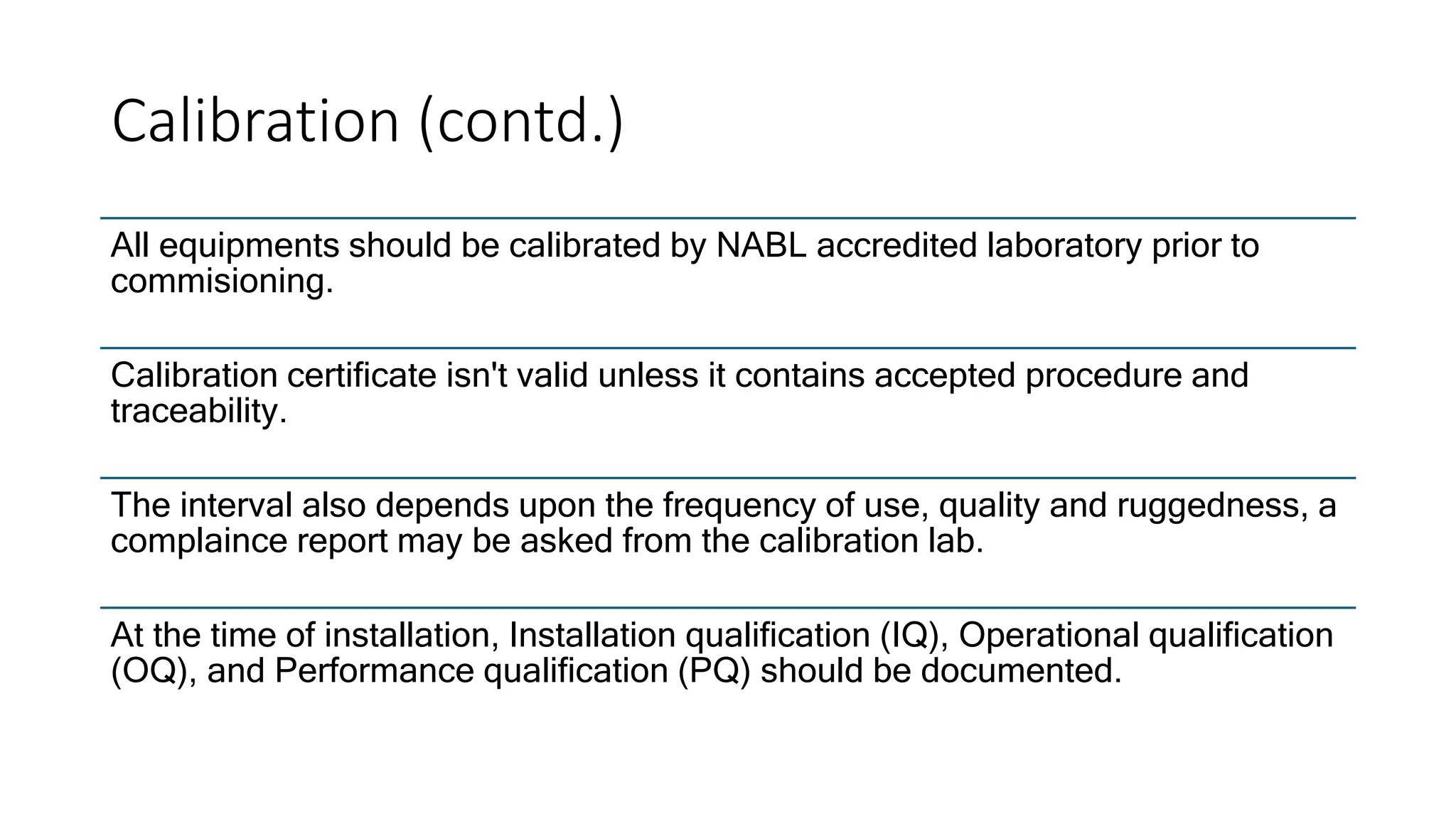
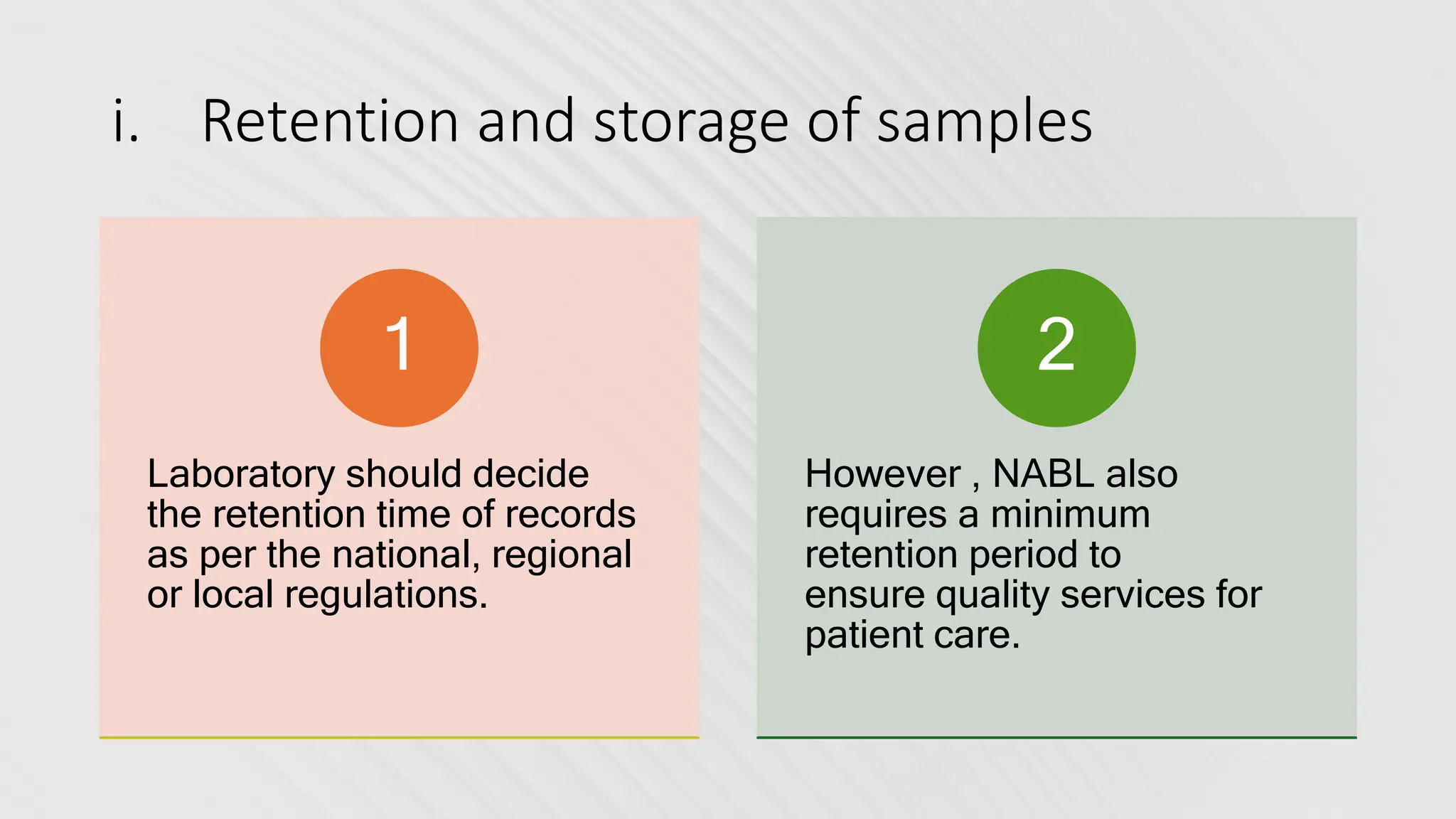
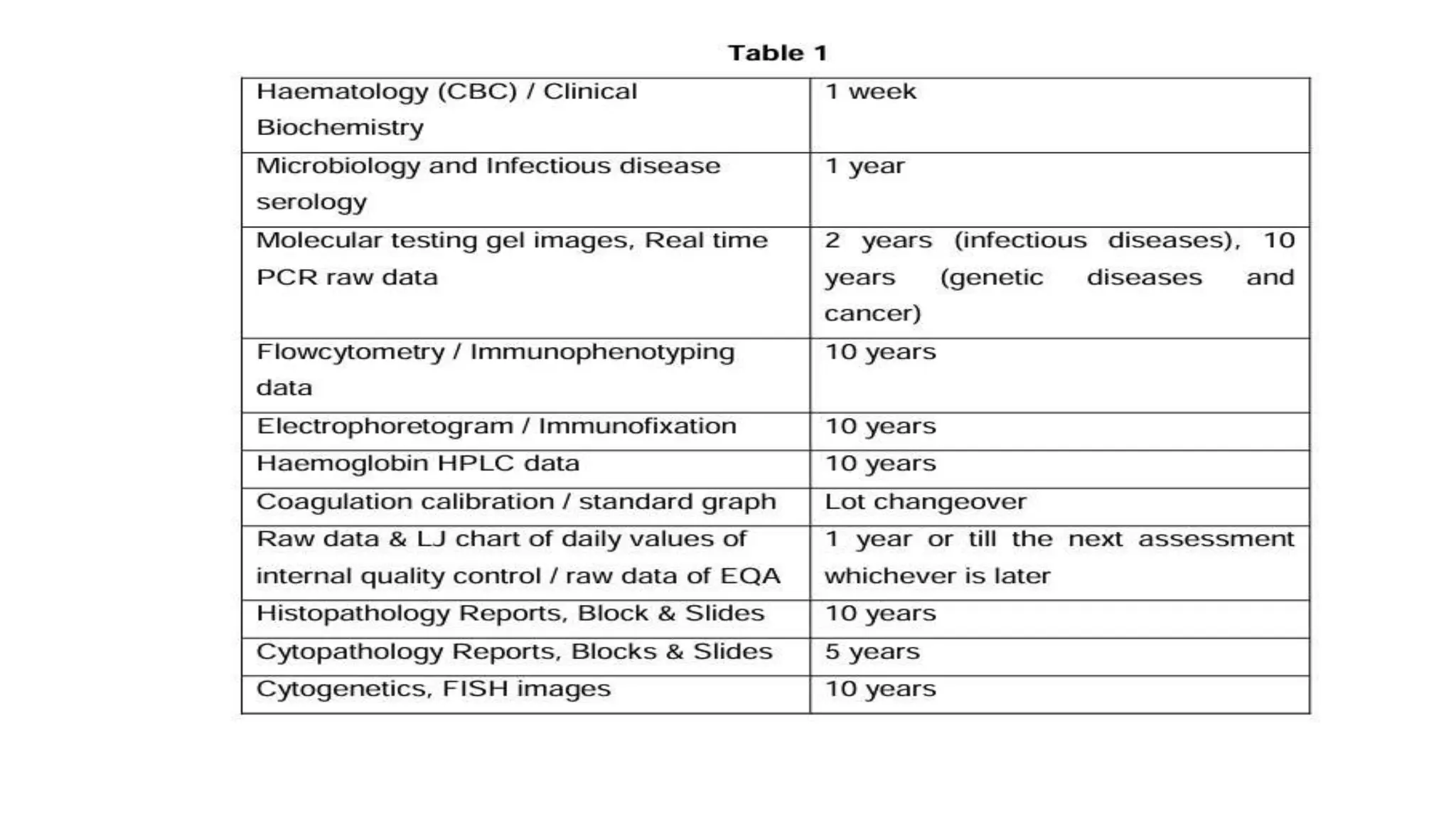
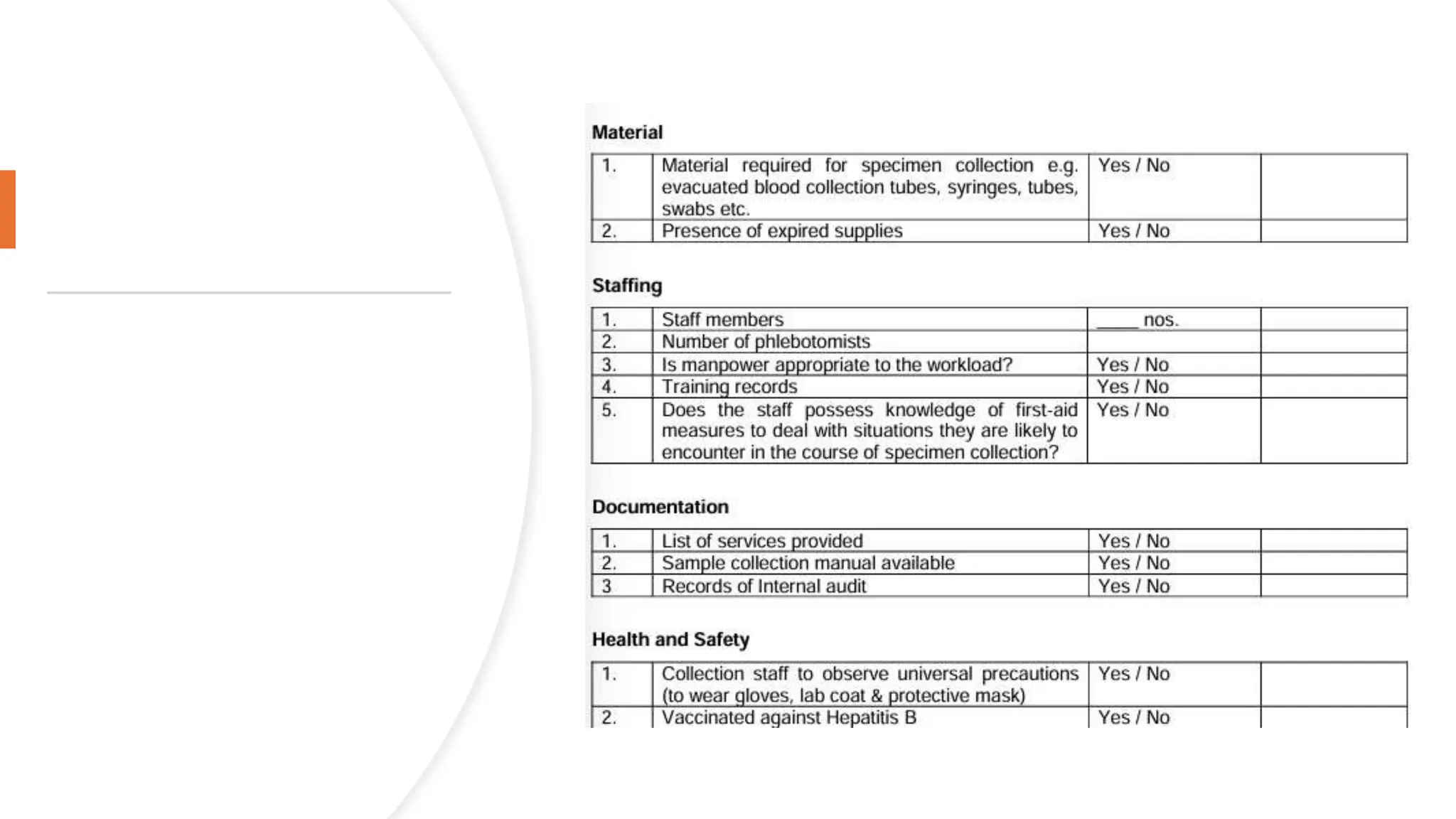
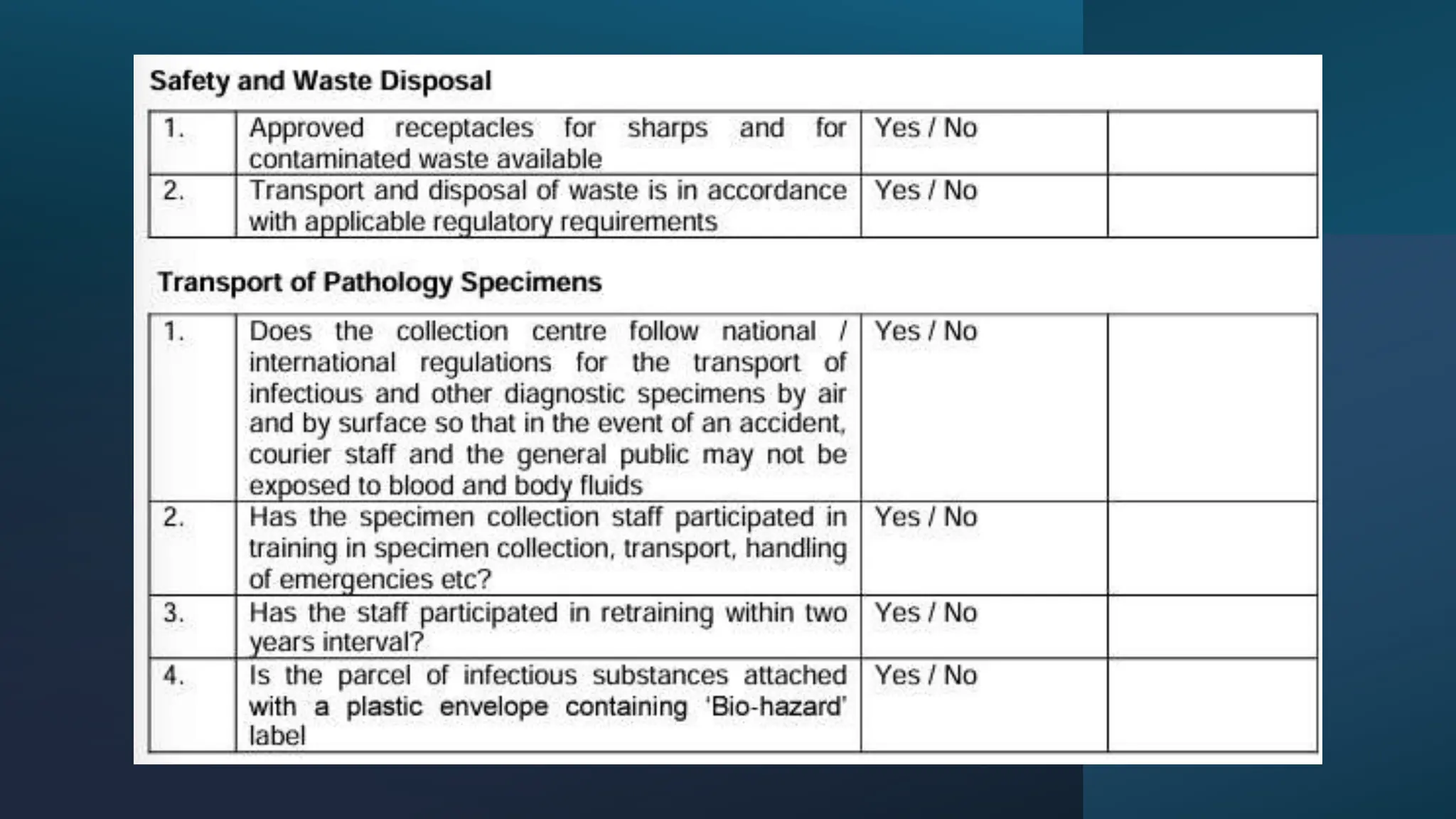
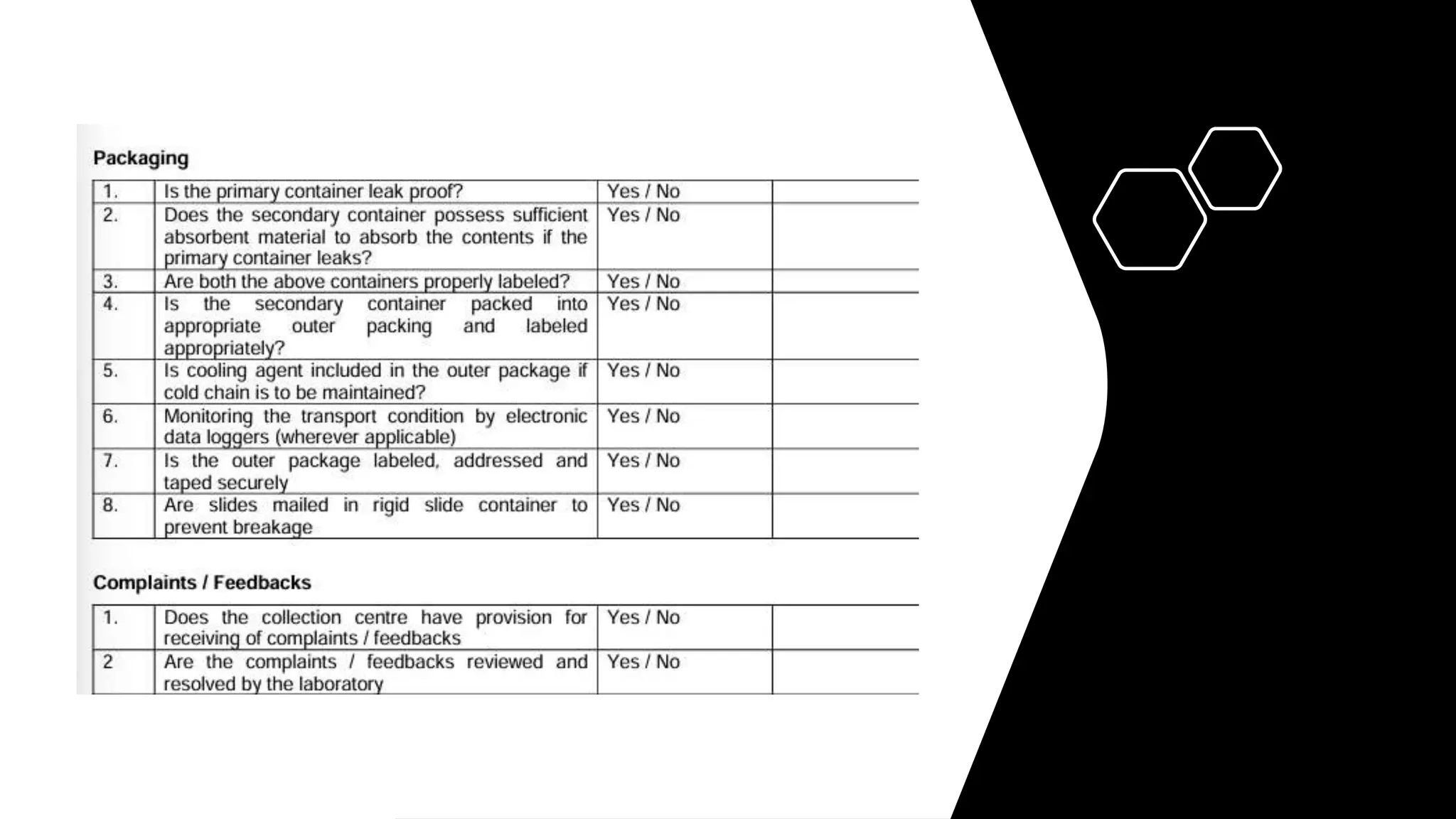
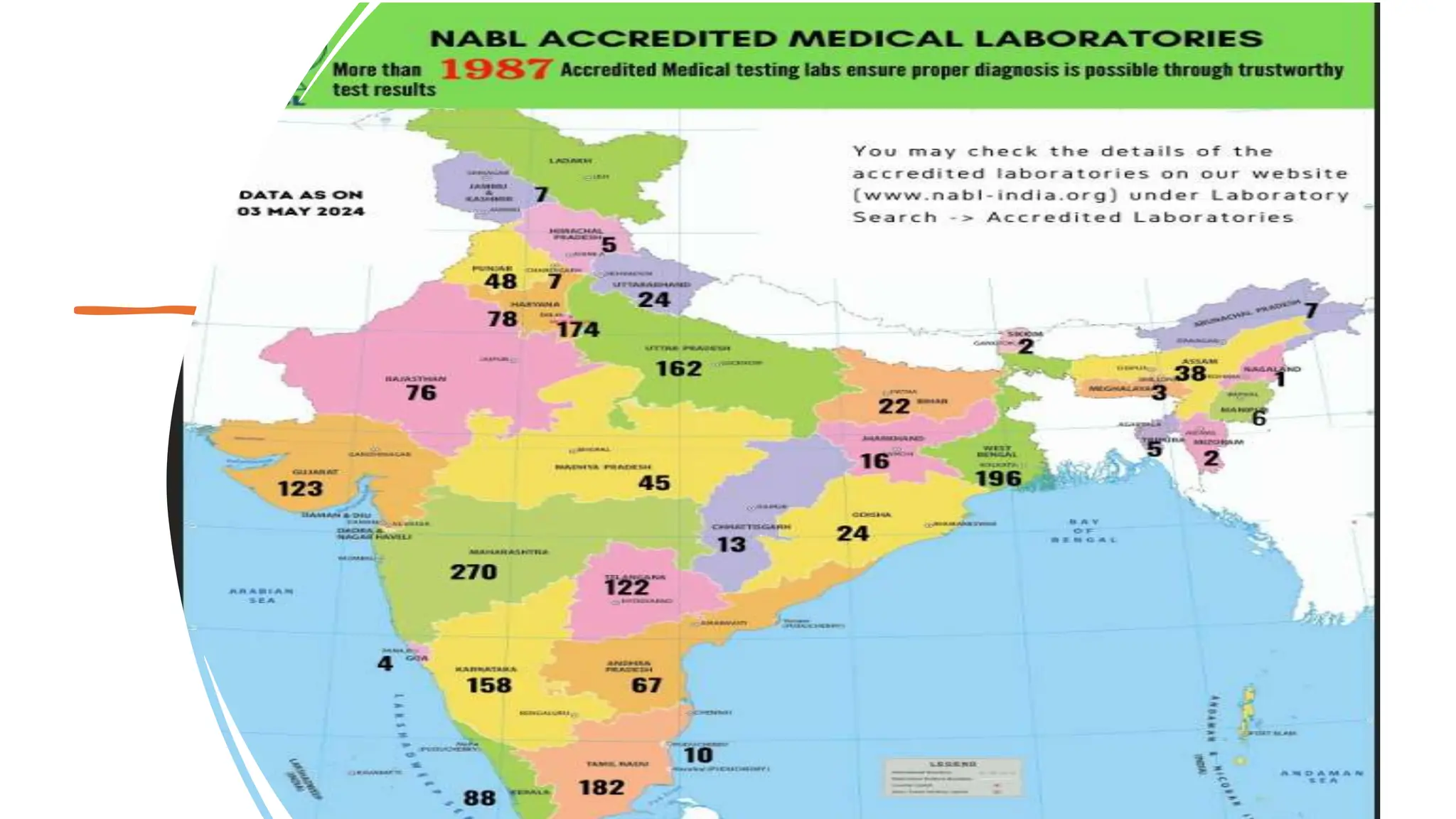
The document provides an overview of the National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL), including its history, services, and the importance of laboratory accreditation for maintaining international standards. NABL offers voluntary accreditation services for testing and calibration laboratories, ensuring quality and competence in various fields, including medical testing. It emphasizes the significance of proper calibration, waste management, and maintaining sample integrity to ensure reliable test results.