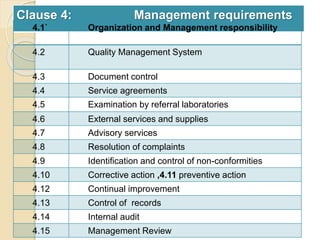
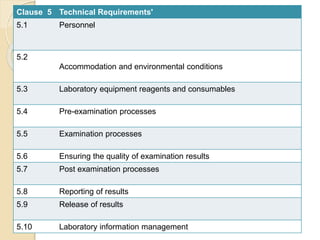
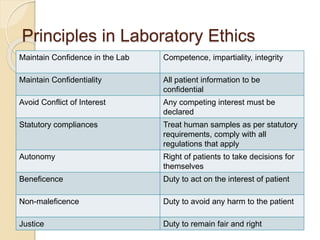
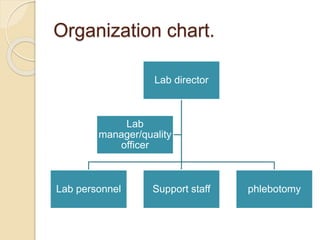
Here are the key responsibilities of the roles you asked about:
Quality Manager:
- Oversee implementation and maintenance of quality management system
- Lead internal audits and monitor corrective/preventive actions
- Ensure staff are trained and competent
- Compile and analyze quality indicators and trends
- Advise management on quality improvements
Quality Director:
- Establish quality policy and objectives with management
- Allocate resources needed for quality management
- Review quality system, audit reports and indicators at management reviews
- Ensure continual improvement of quality management system
Quality Officer:
- Assist quality manager in implementing quality systems
- Conduct internal audits and record non-conformities and actions
- Monitor day