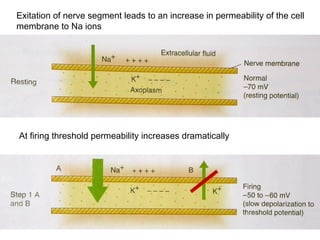
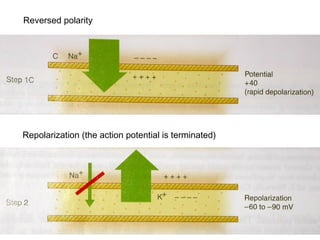
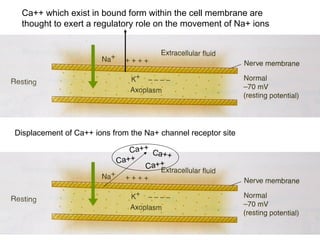
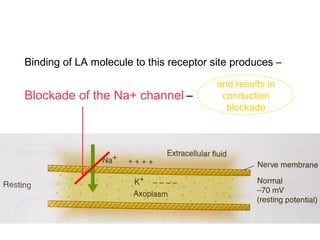
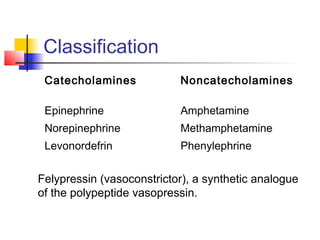
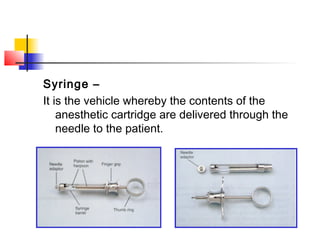
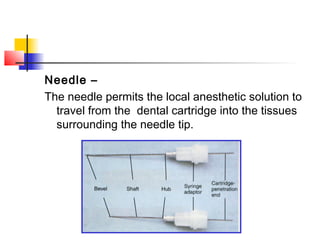
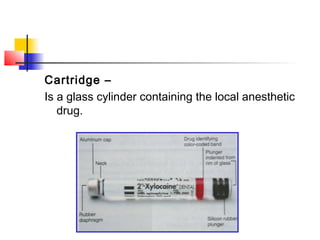
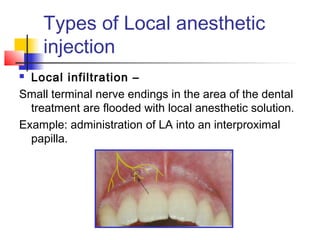
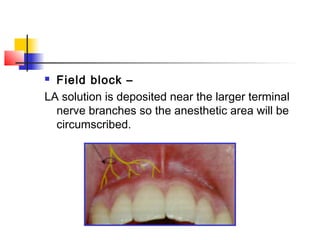
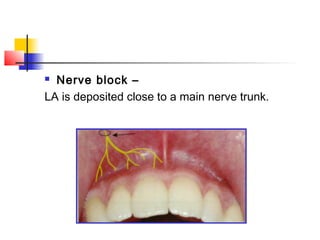
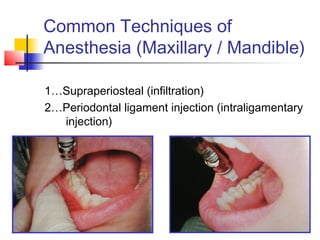
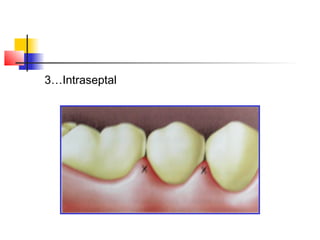
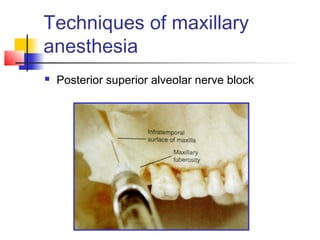
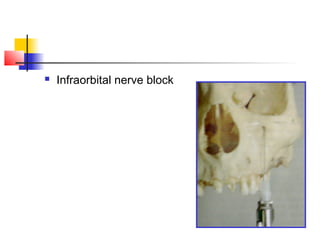
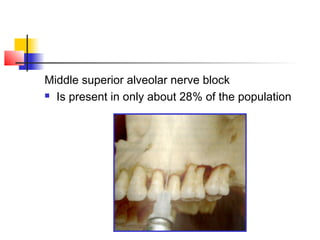
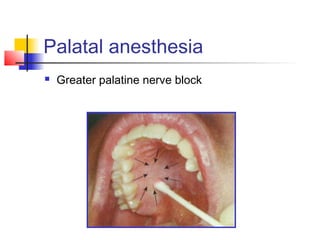
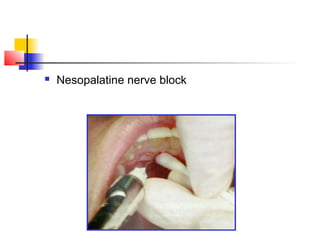
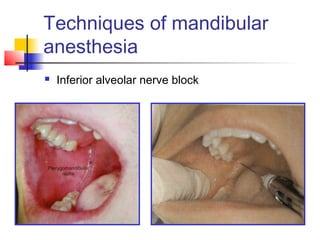
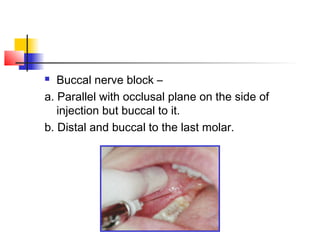
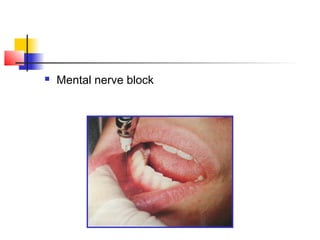
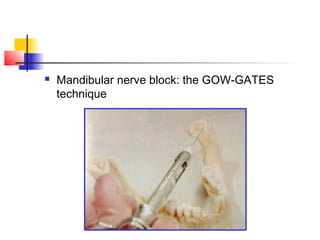
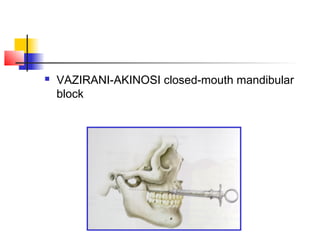
This document discusses local anesthesia used in dental procedures. It defines local anesthesia and describes the desirable properties of local anesthetic solutions. These include being non-irritating, not permanently altering nerve structures, having low systemic toxicity, and providing effective anesthesia regardless of injection site. The document outlines the electrophysiology of nerve conduction and how local anesthetics work by blocking sodium channels. It classifies local anesthetics and discusses vasoconstrictors used to prolong their effects. Complications of local anesthesia are described, including both local issues like needle breakage and hematoma, and systemic concerns like overdose and allergic reactions.