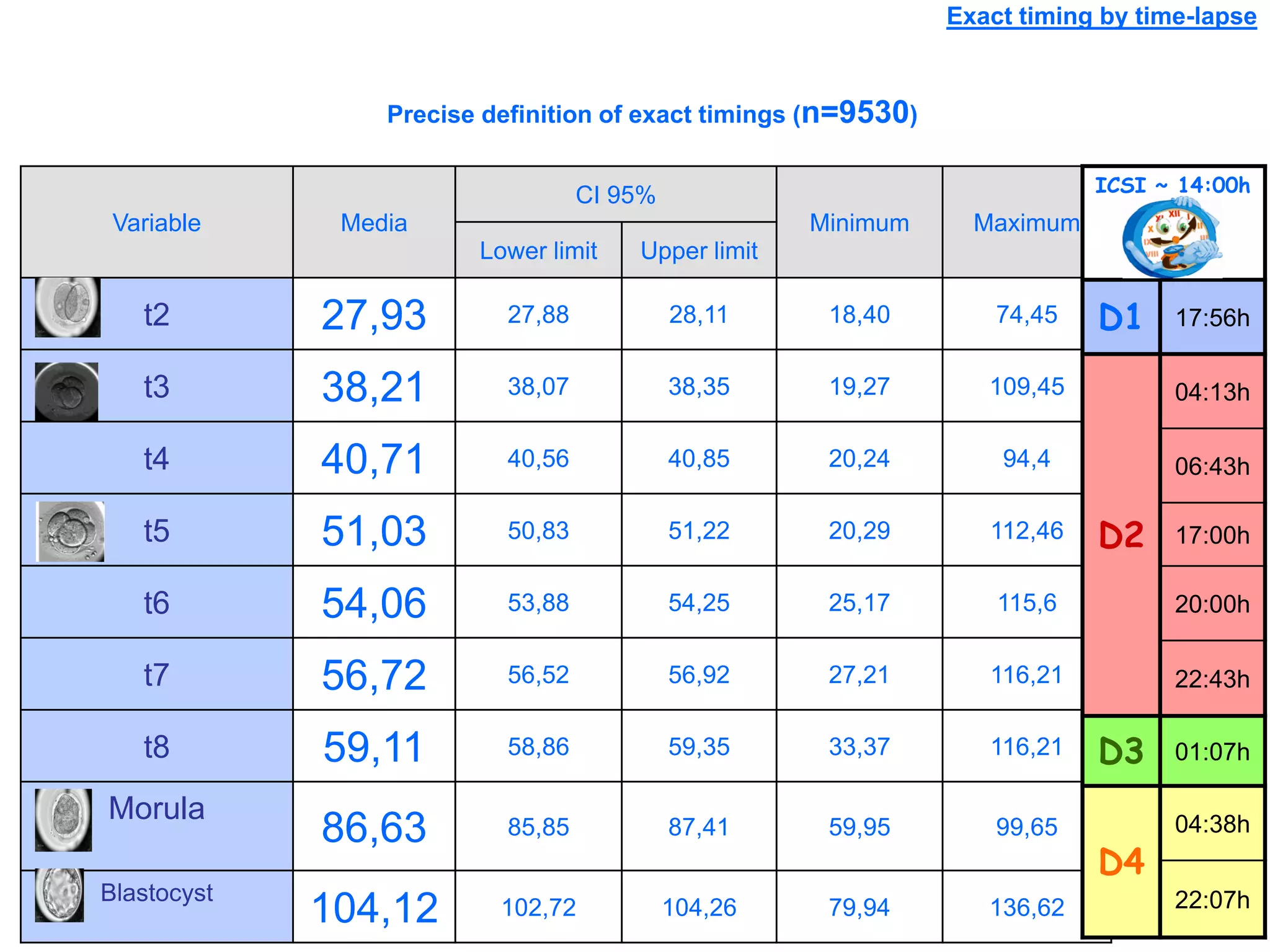
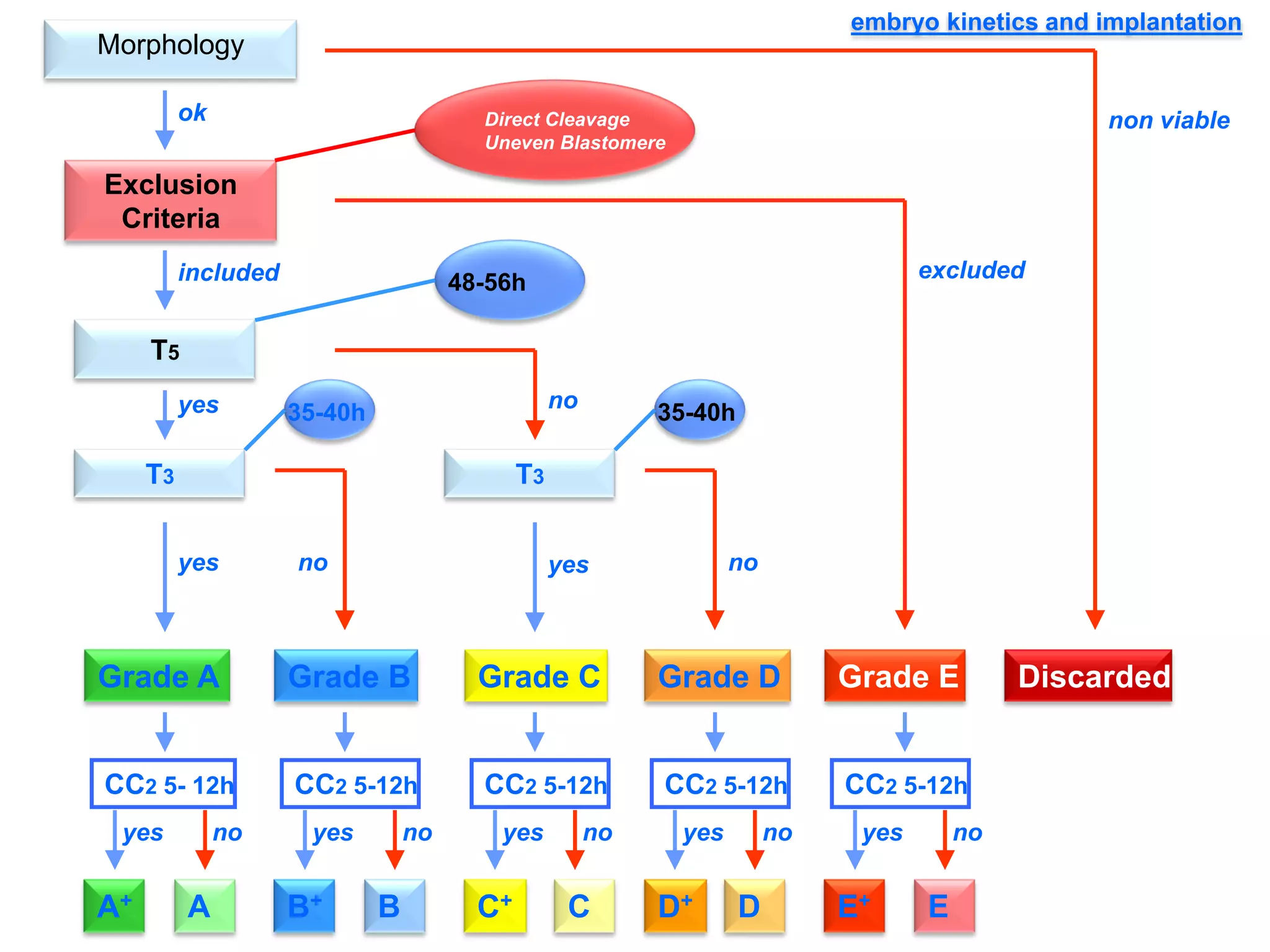
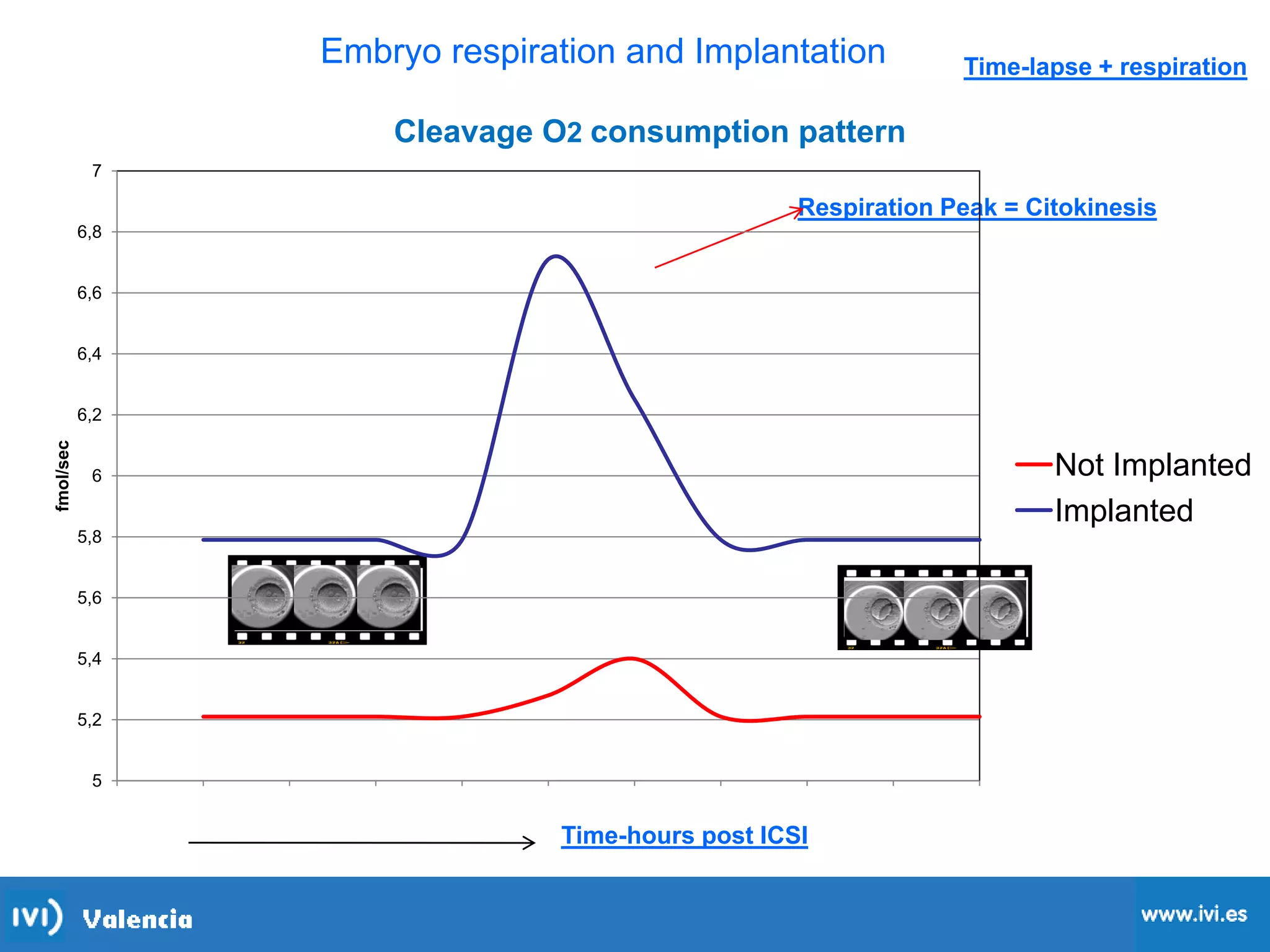
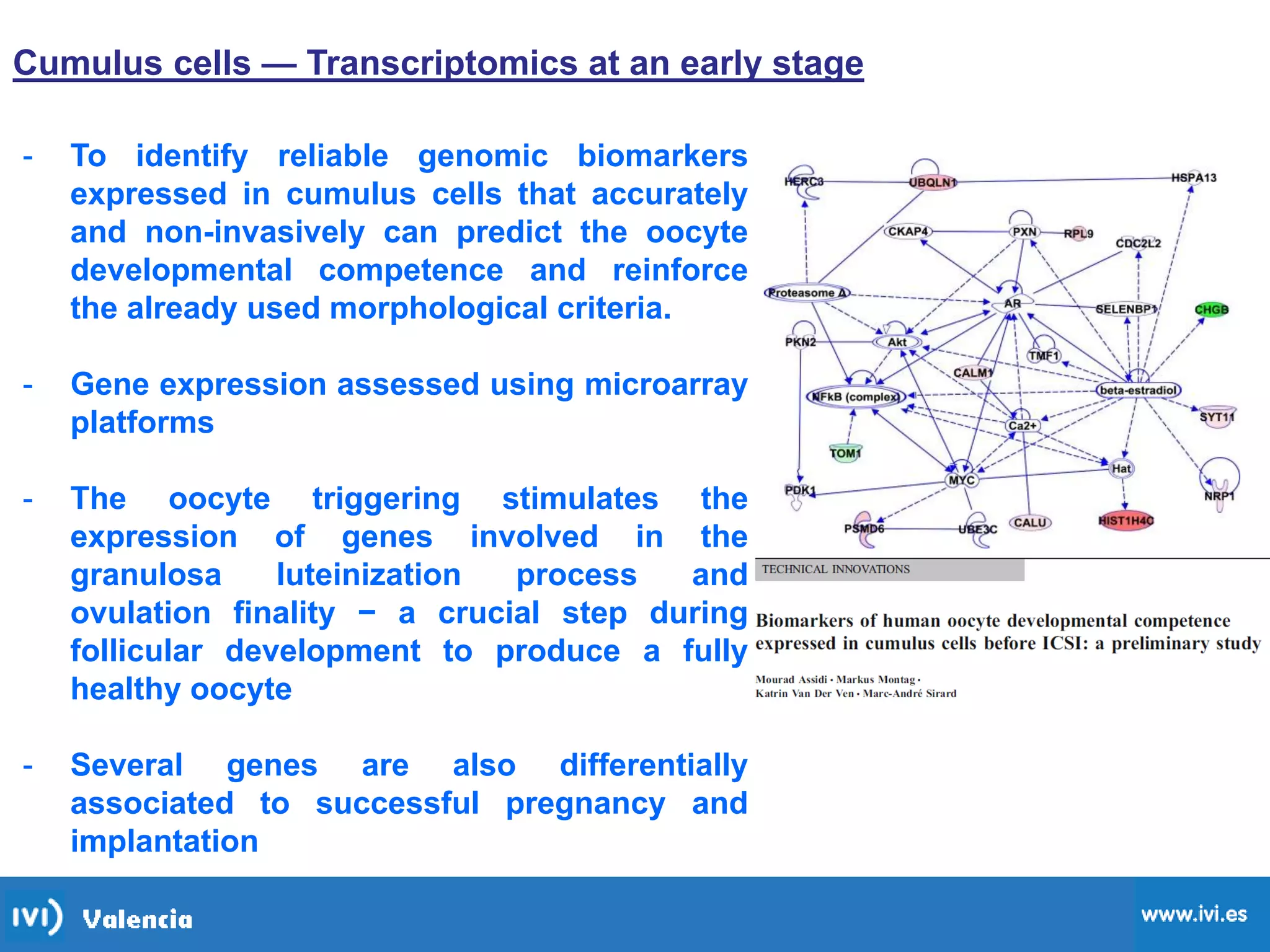
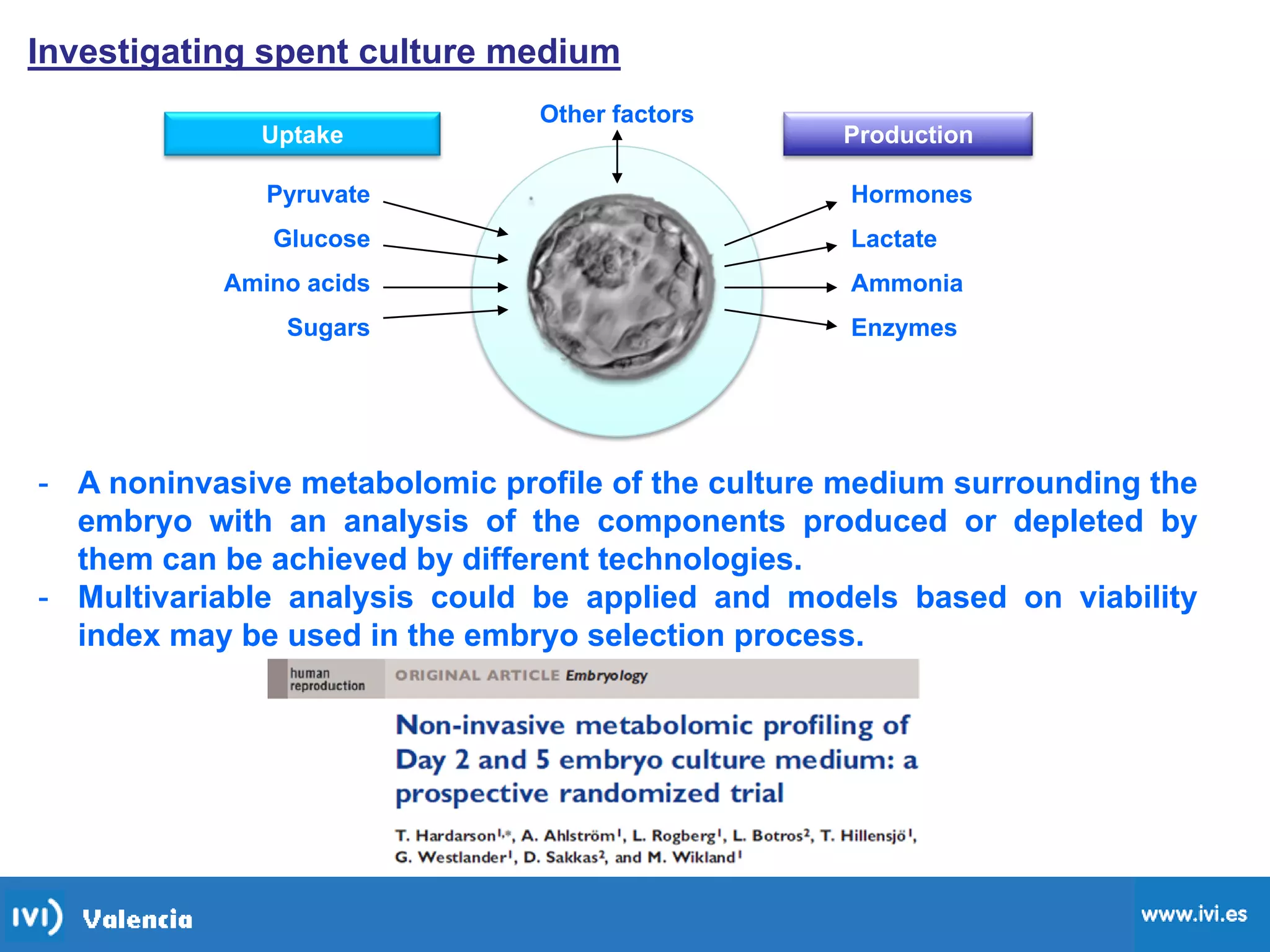
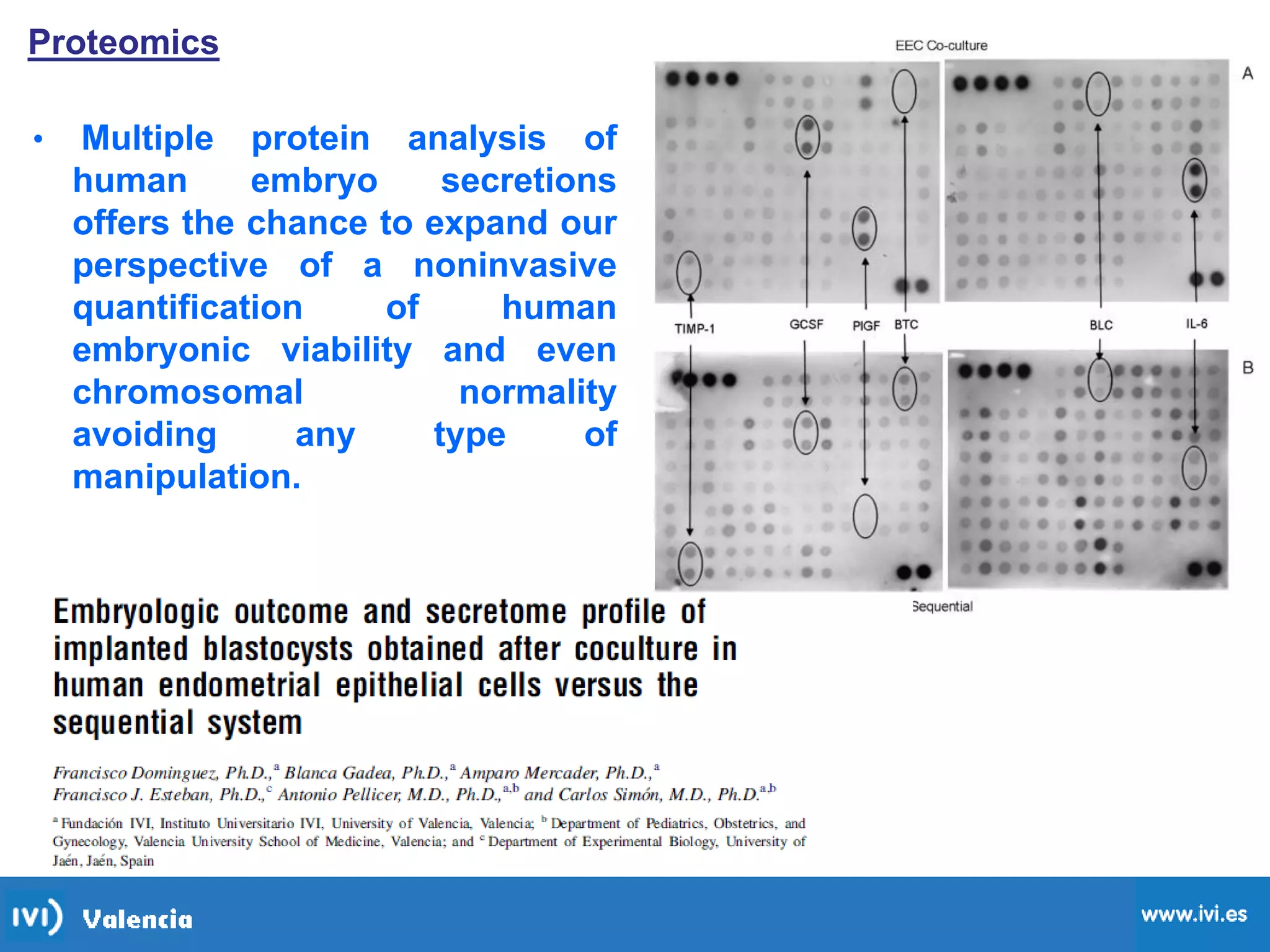
This document discusses how time-lapse imaging allows for quantification of the exact timing of each cell division during embryo development. It notes that conventional grading may miss subtle differences between embryos, but time-lapse can detect variations in the time it takes embryos to progress from one cleavage division to the next. The use of automated time-lapse imaging permits the collection of data on individual embryos over time.