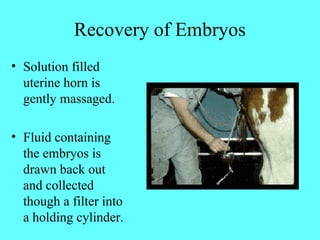
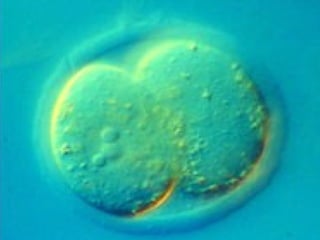
This document discusses the process of embryo transfer in beef cattle. It involves collecting embryos from a superovulated donor cow through artificial insemination and flushing, and then transferring the embryos to synchronized recipient cows to complete gestation. The key steps are superovulating the donor cow, artificially inseminating her, flushing her uterus 7 days later to collect embryos, processing and evaluating the embryos, and then transferring high quality embryos into synchronized recipient cows 16 days after their estrus cycles have been aligned through hormone treatments.