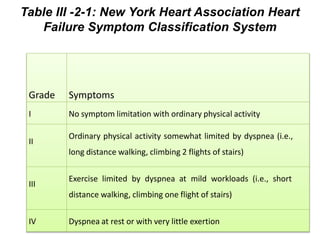
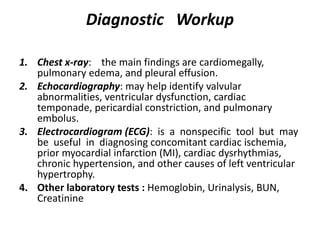
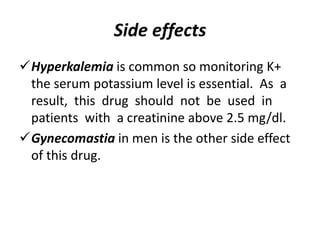
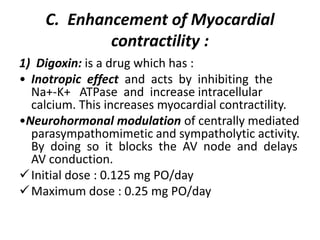
This document discusses congestive heart failure (CHF), including its definition, causes, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. CHF is characterized by inadequate systemic perfusion due to cardiac abnormalities. The most common cause is left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Clinical manifestations include dyspnea, edema, fatigue, and reduced exercise tolerance. Diagnosis involves imaging, labs, and assessing symptoms according to the NYHA classification system. Management focuses on controlling congestion with diuretics, enhancing contractility with drugs like digoxin, preventing worsening with ACE inhibitors and beta blockers, and treating the underlying cause.












![Physical findings:
• Tachycardia and Tachypnea and signs of respiratory
distress including use of accessory muscles of
respiration
• Jugular venous distention (JVD) frequently is present
and engorged neck veins
• Pulsus alternans (alternating weak and strong pulse
indicative of depressed left ventricle[LV] function
• Wheezing or rales may be heard on lung auscultation
and there may be bilateral basal dullness.
• Apical impulse frequently is displaced laterally
• Cardiac auscultation may reveal aortic or mitral
valvular abnormalities, S3 or S4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2-170220113143/85/L2-ccf-16-320.jpg)