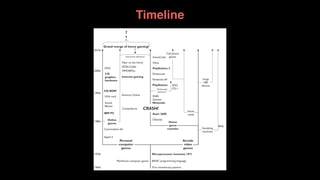
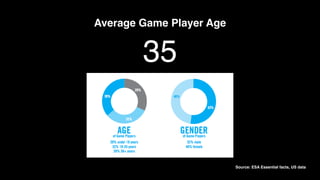
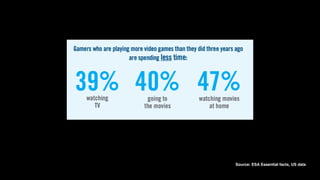
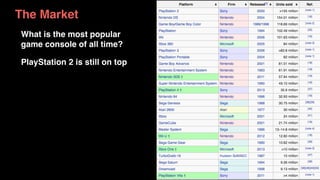
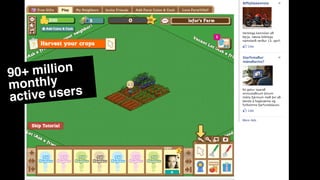
The document discusses the history and evolution of computer games, highlighting their impact on culture and industry. It covers the transition from early games like 'Spacewar!' and 'Pong' to modern interactive experiences, including multiplayer and 3D games, and explores various market trends and gaming genres. Additionally, it examines monetization strategies, the rise of casual games, and the significance of gaming in contemporary society.