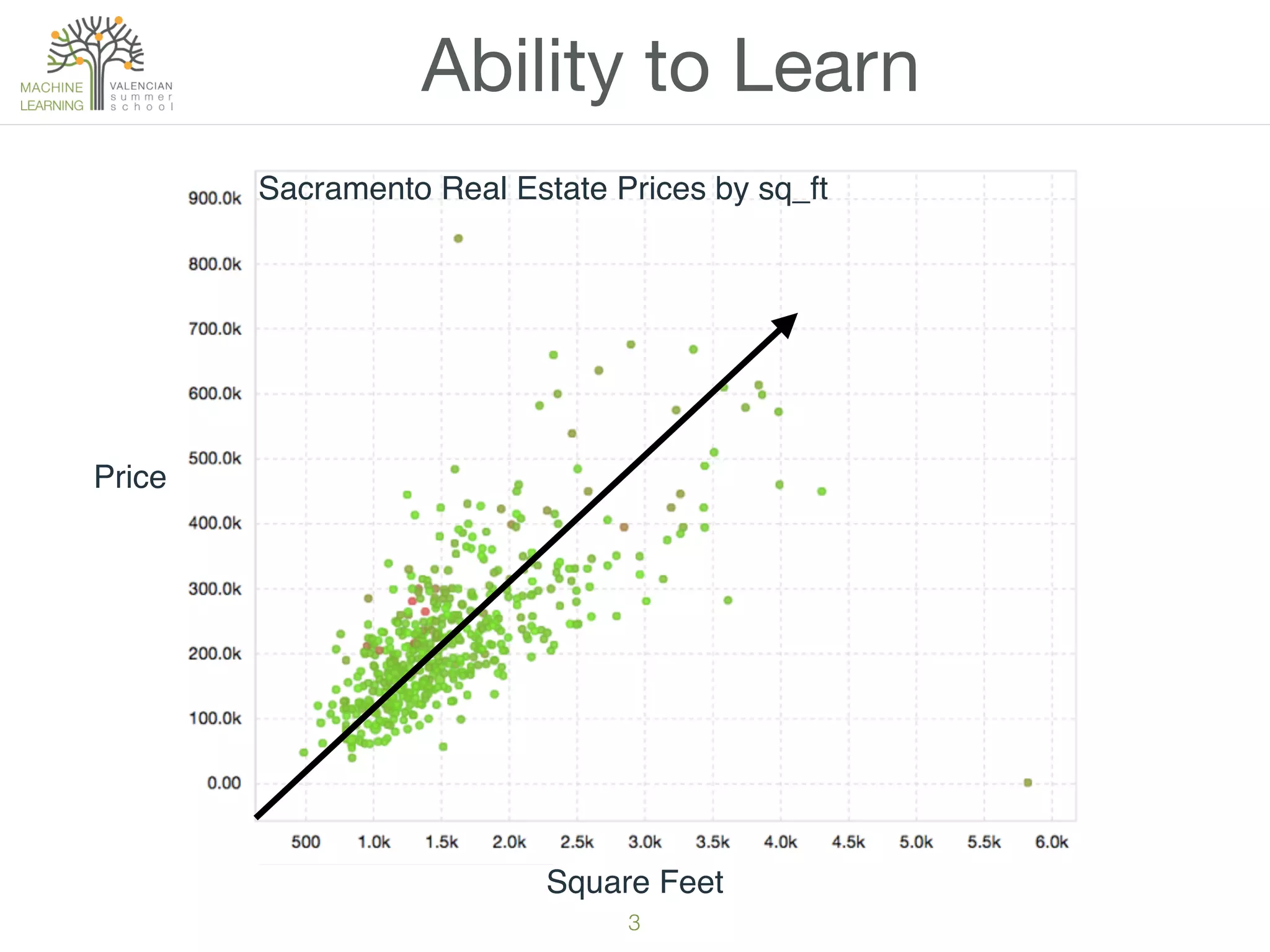
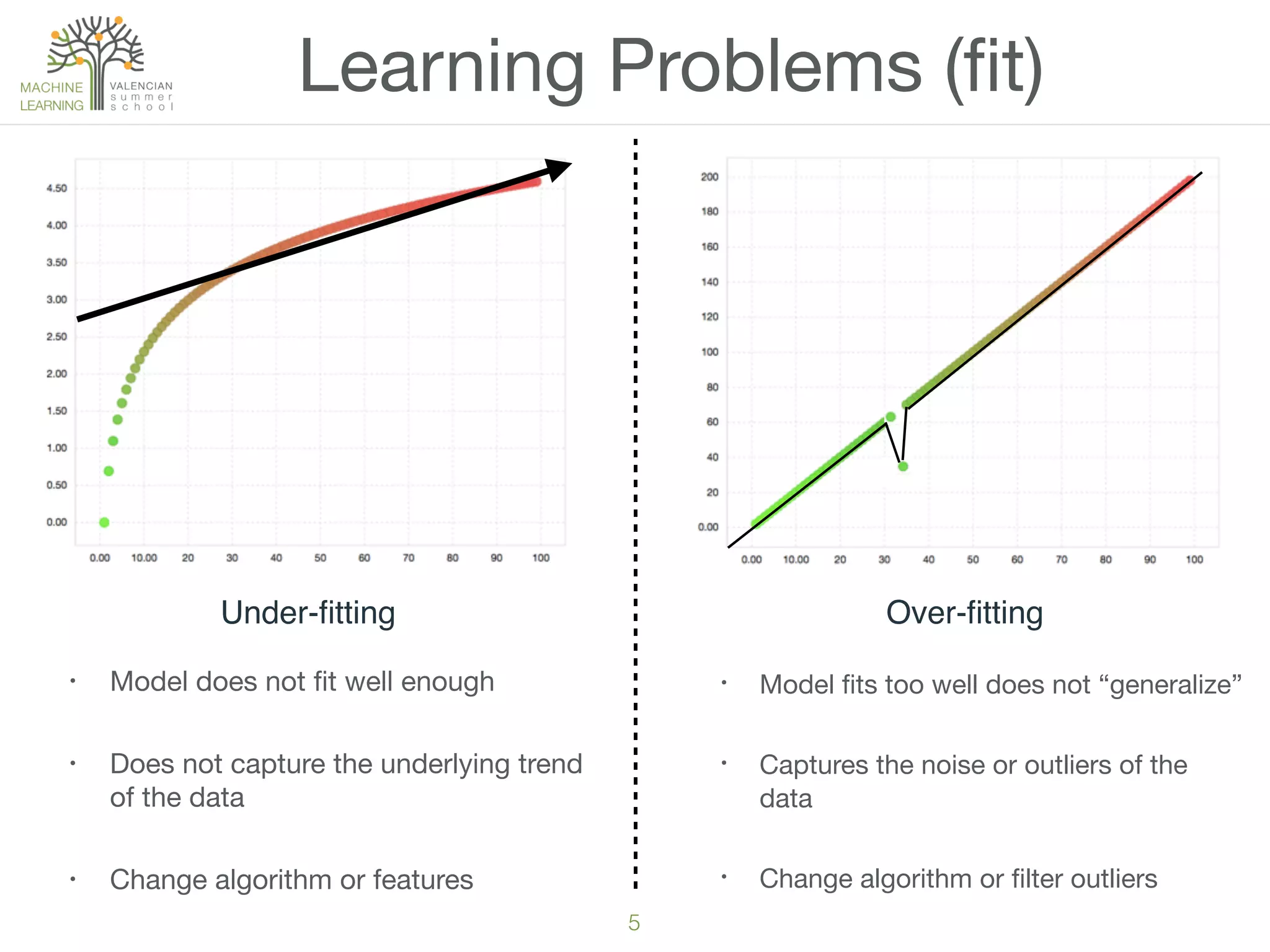
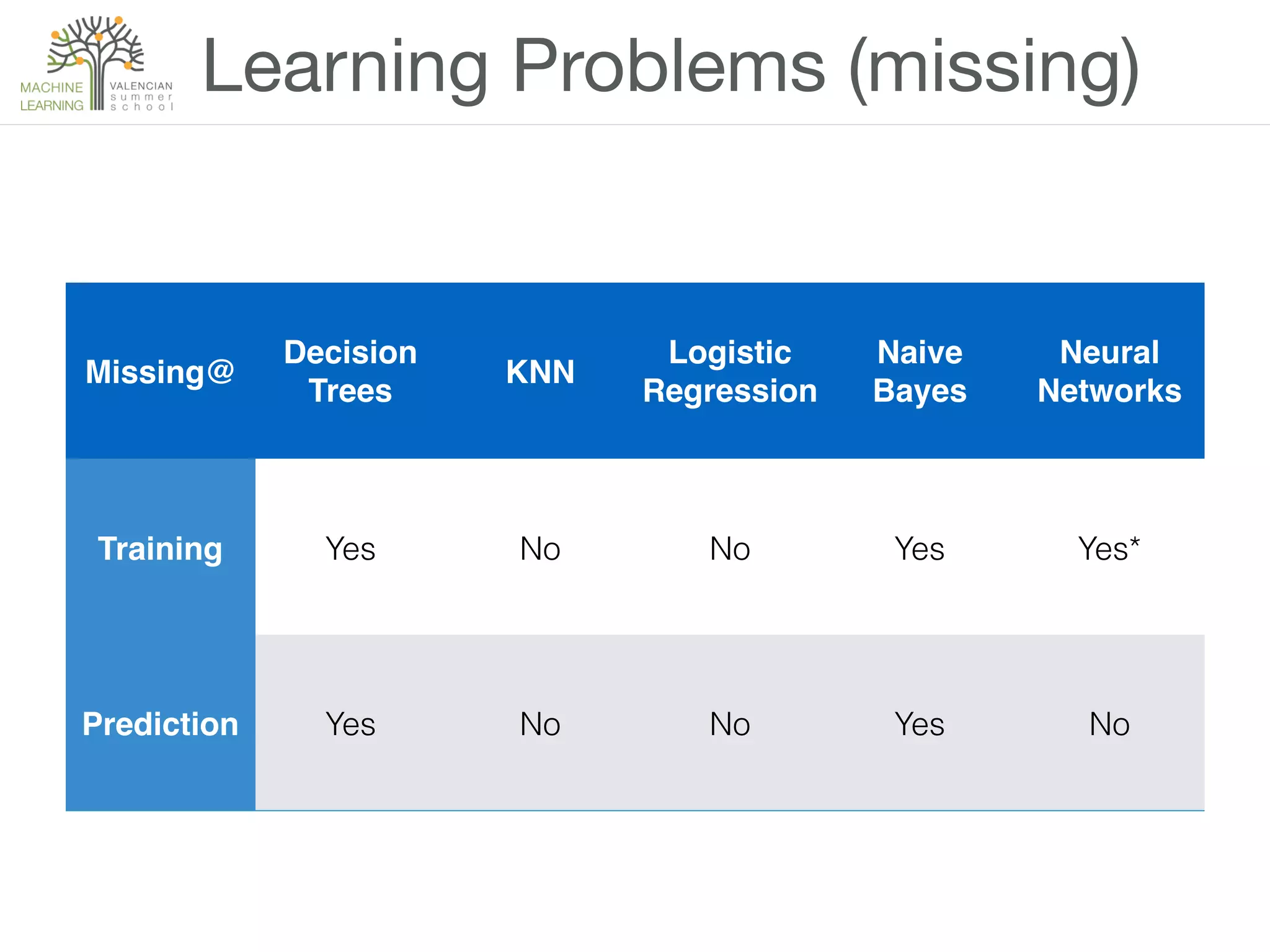
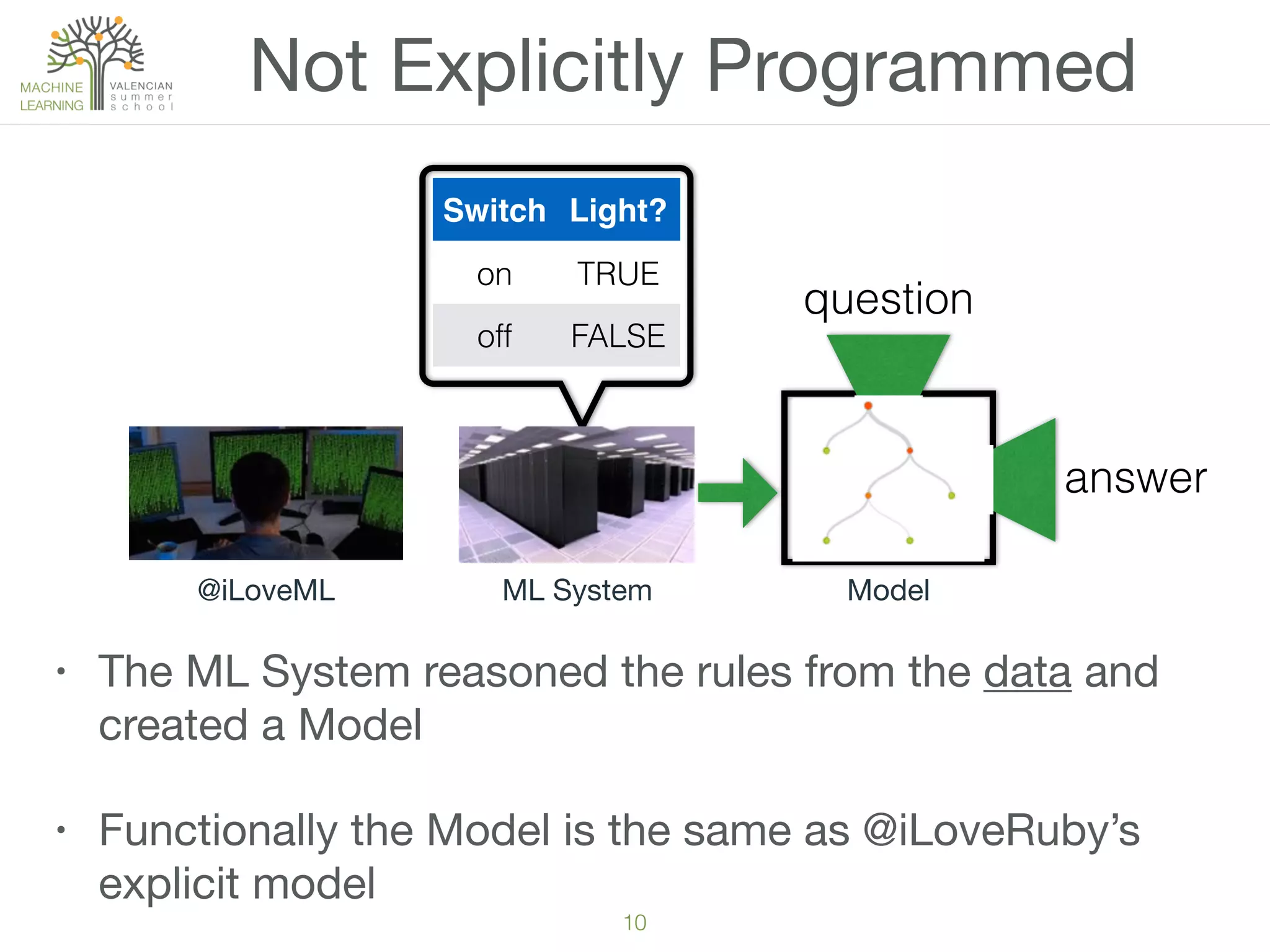
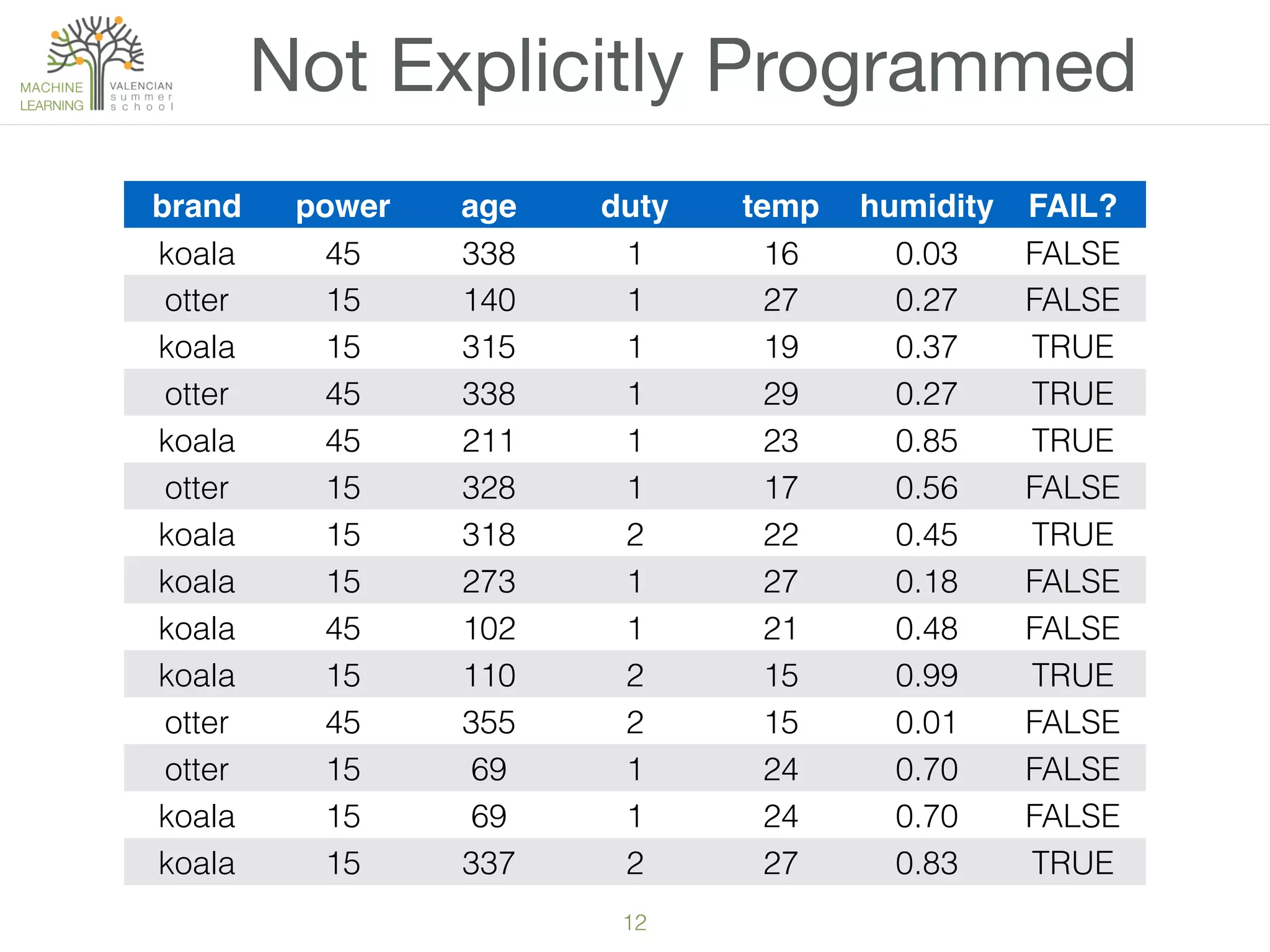
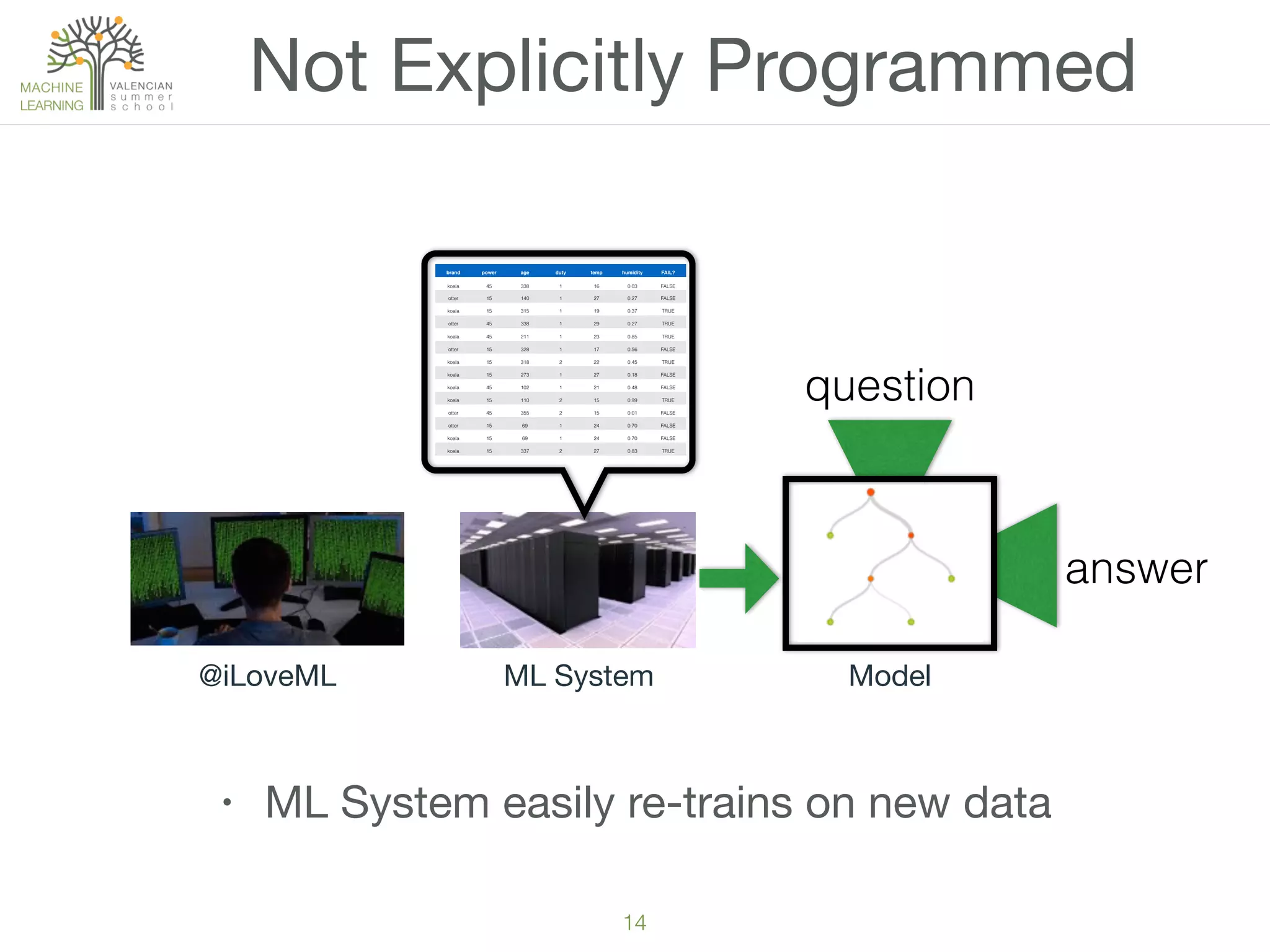
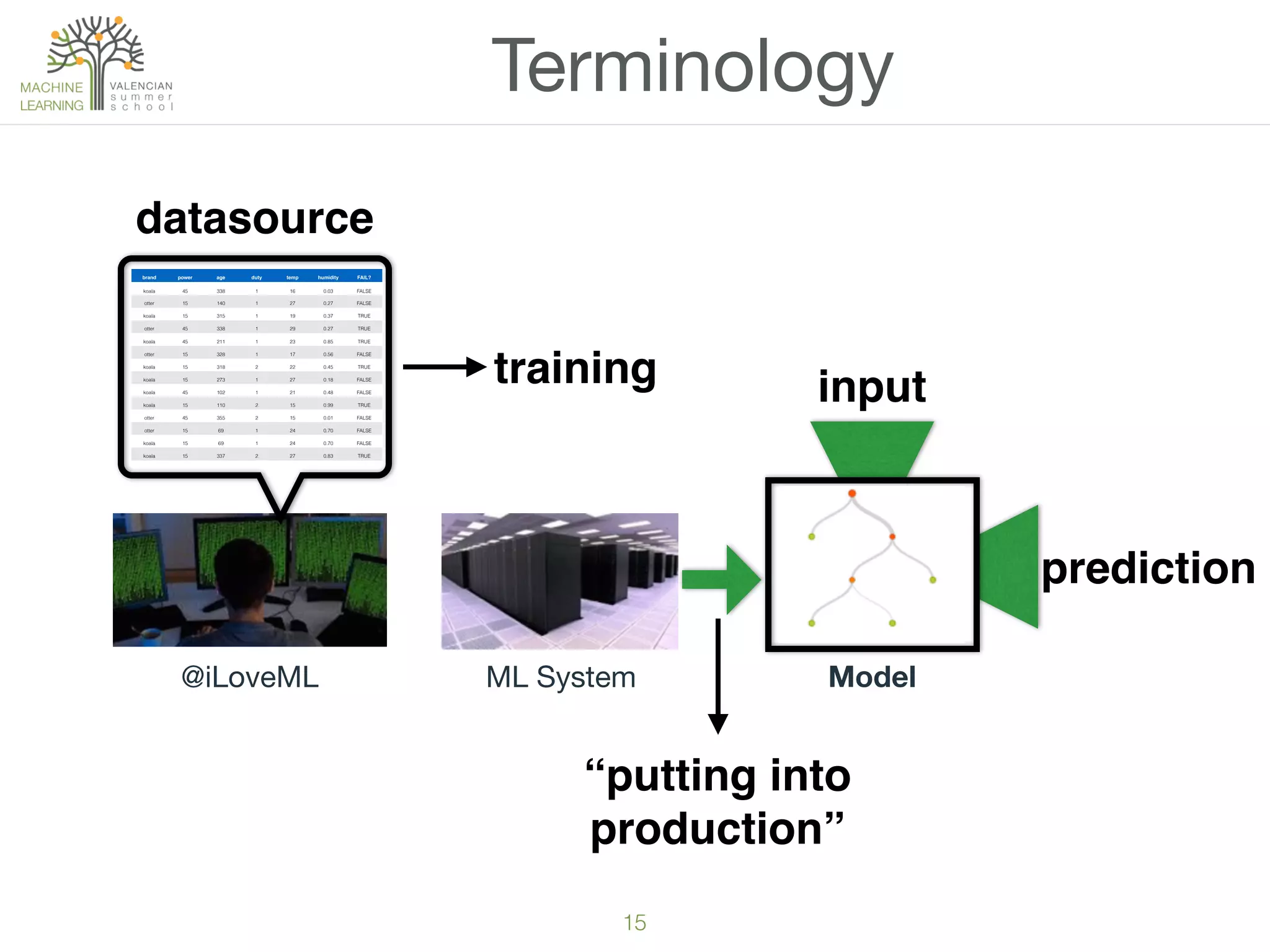
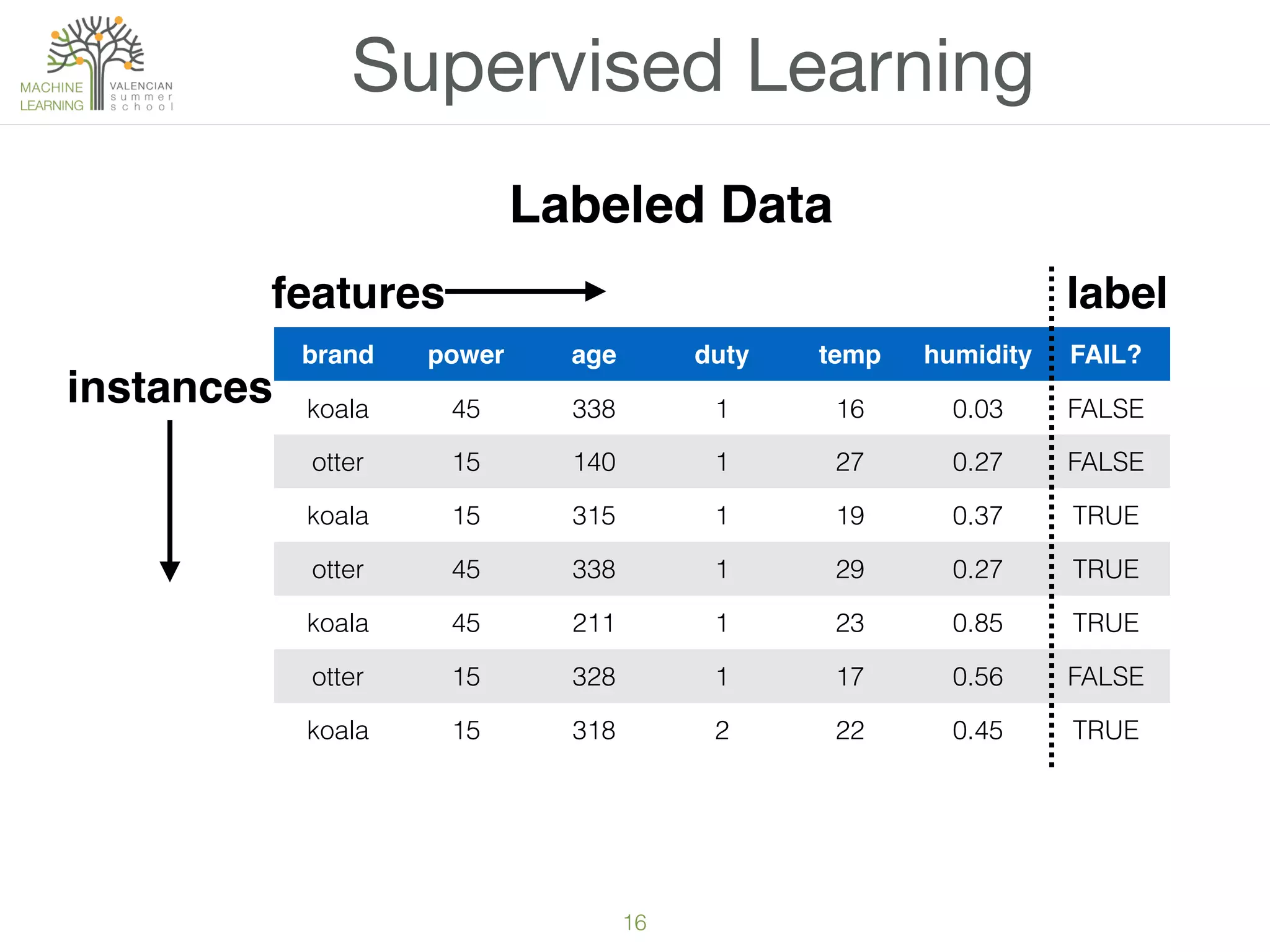
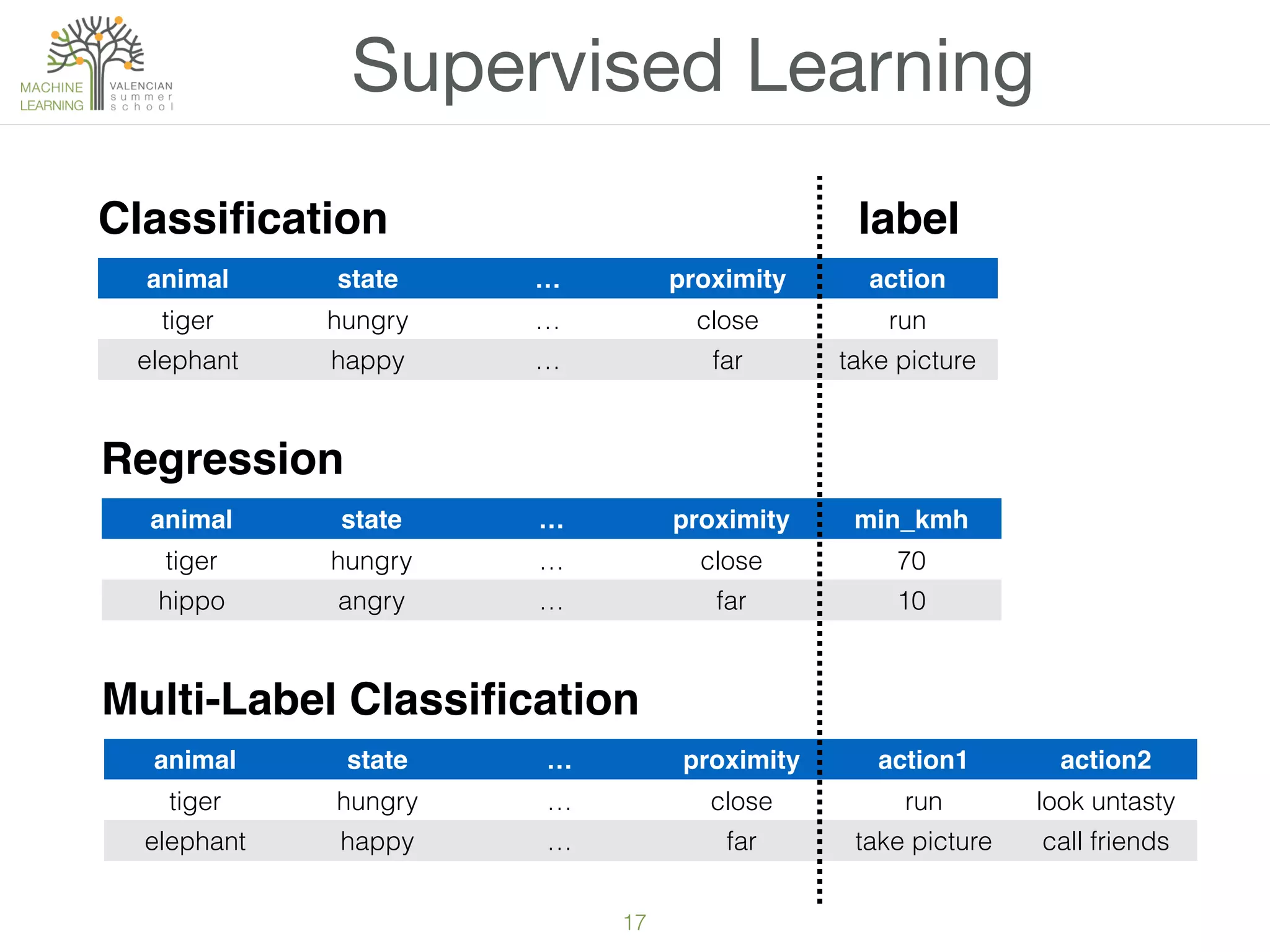
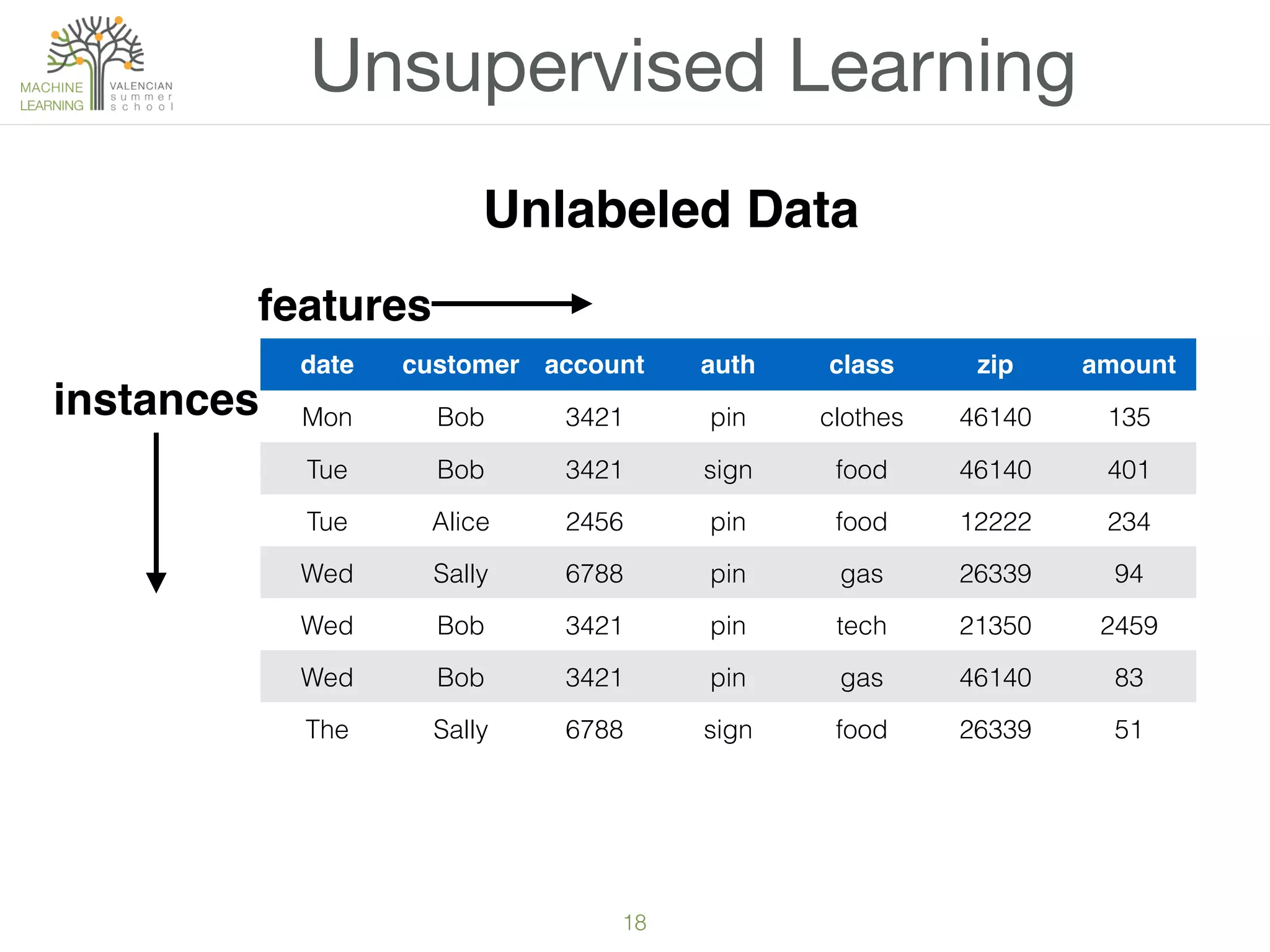
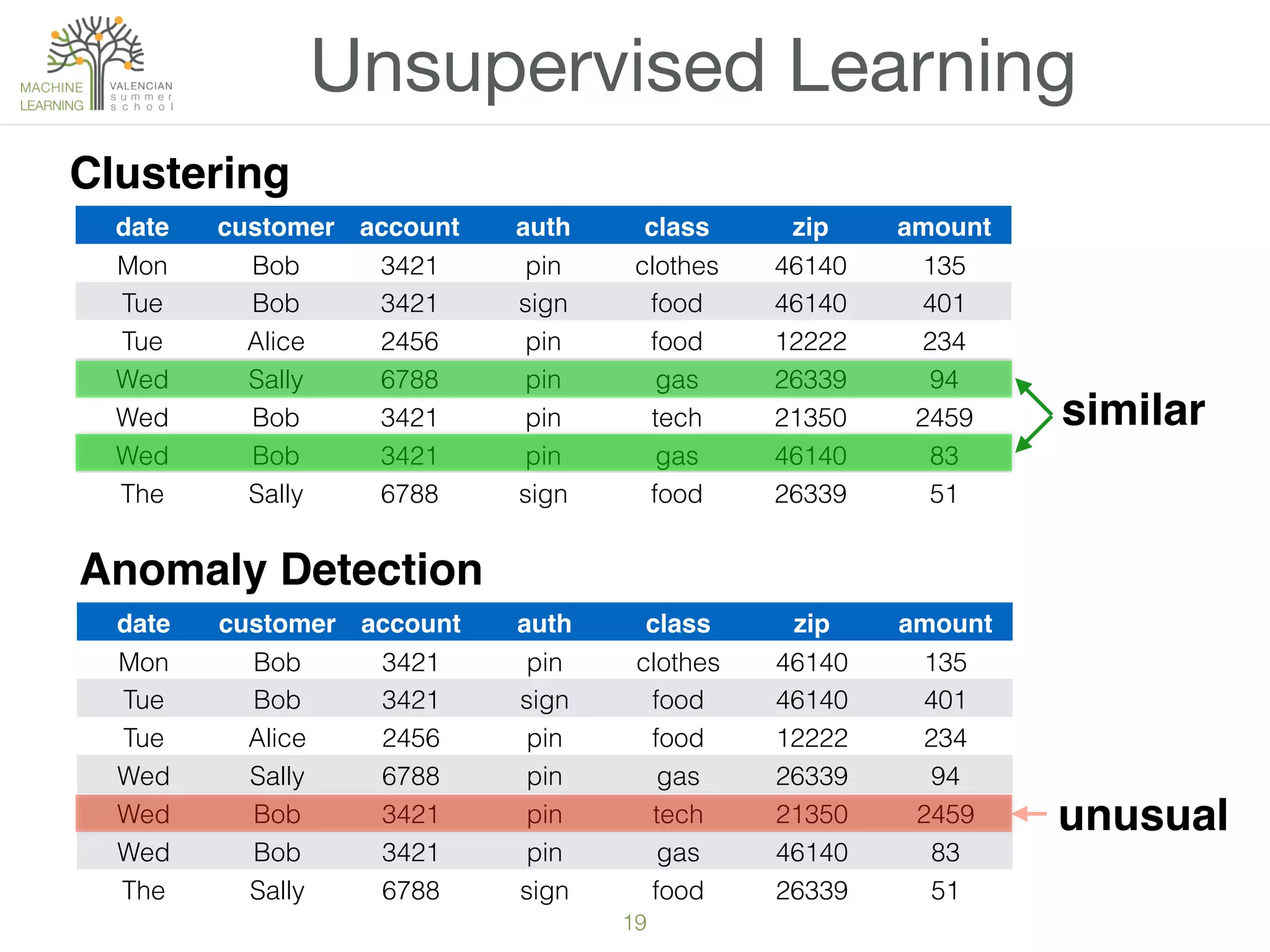
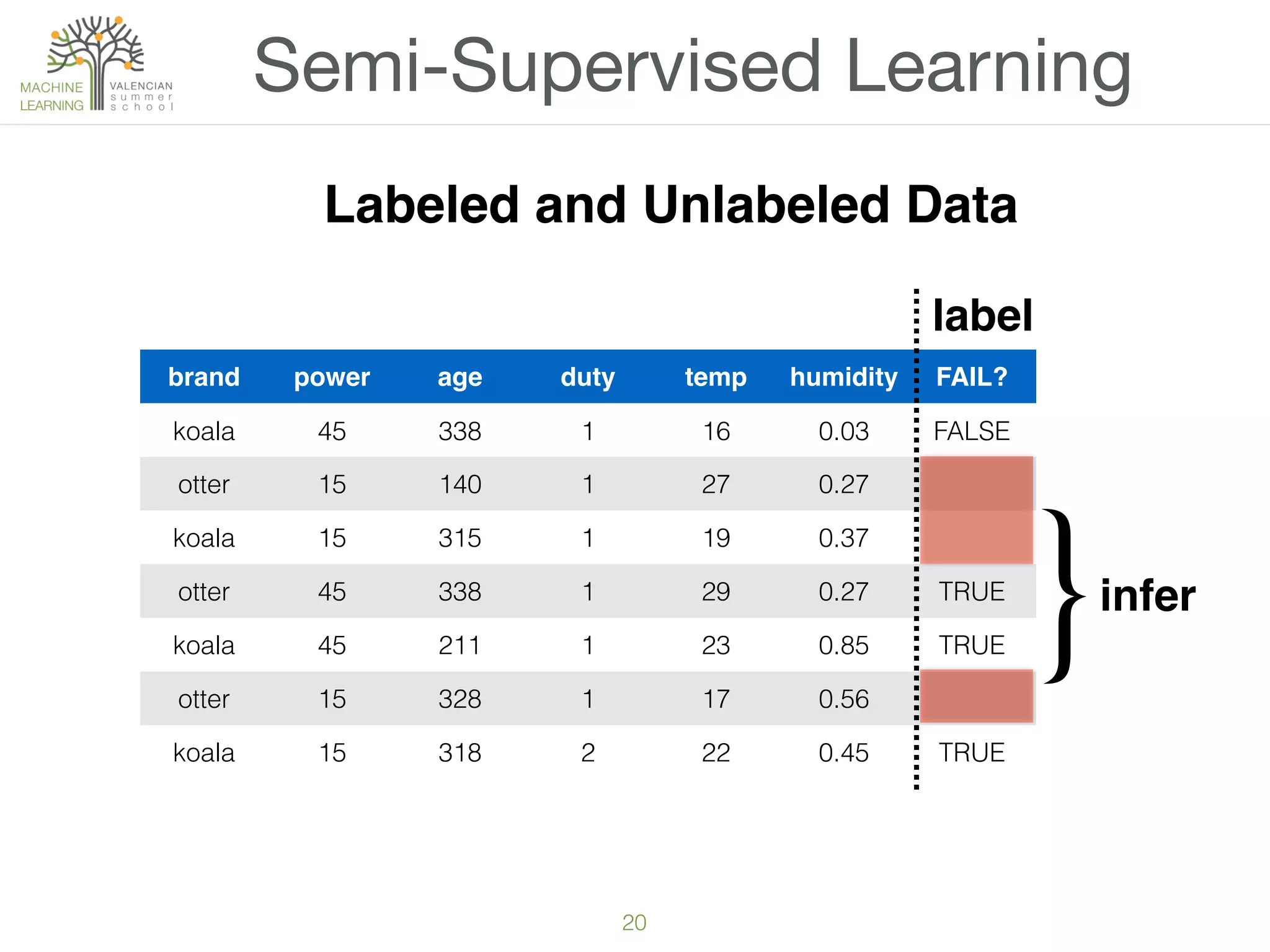
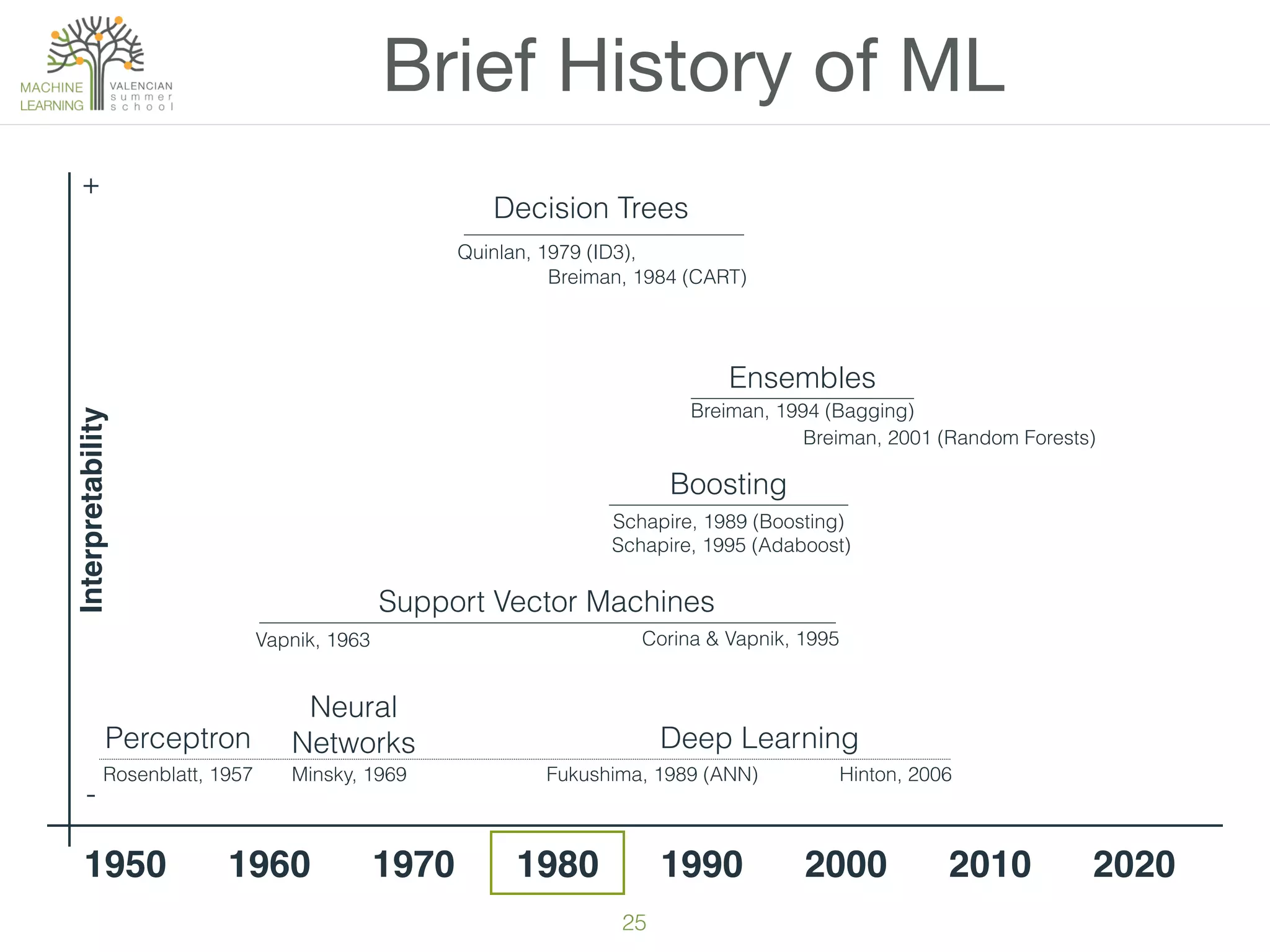
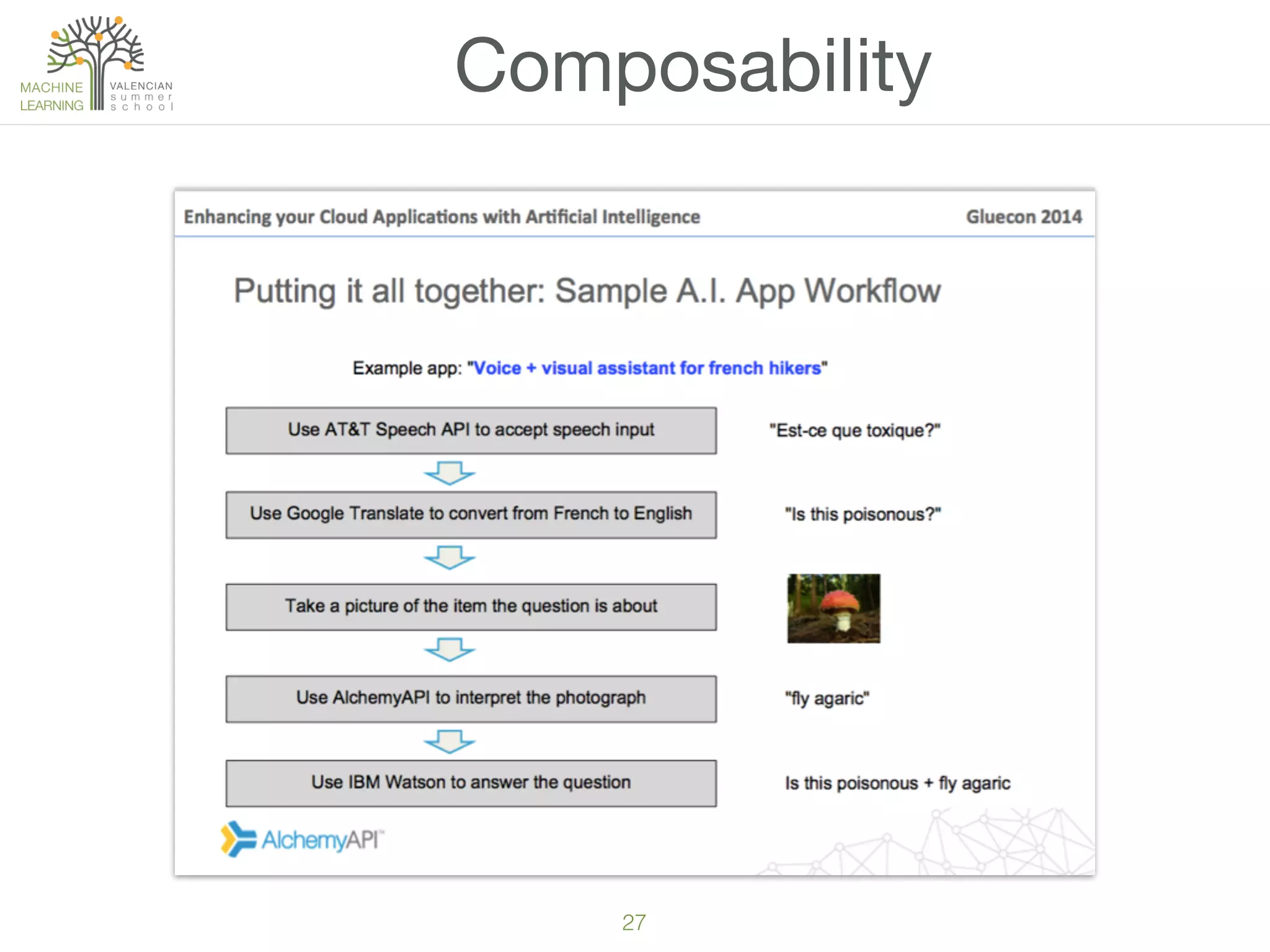
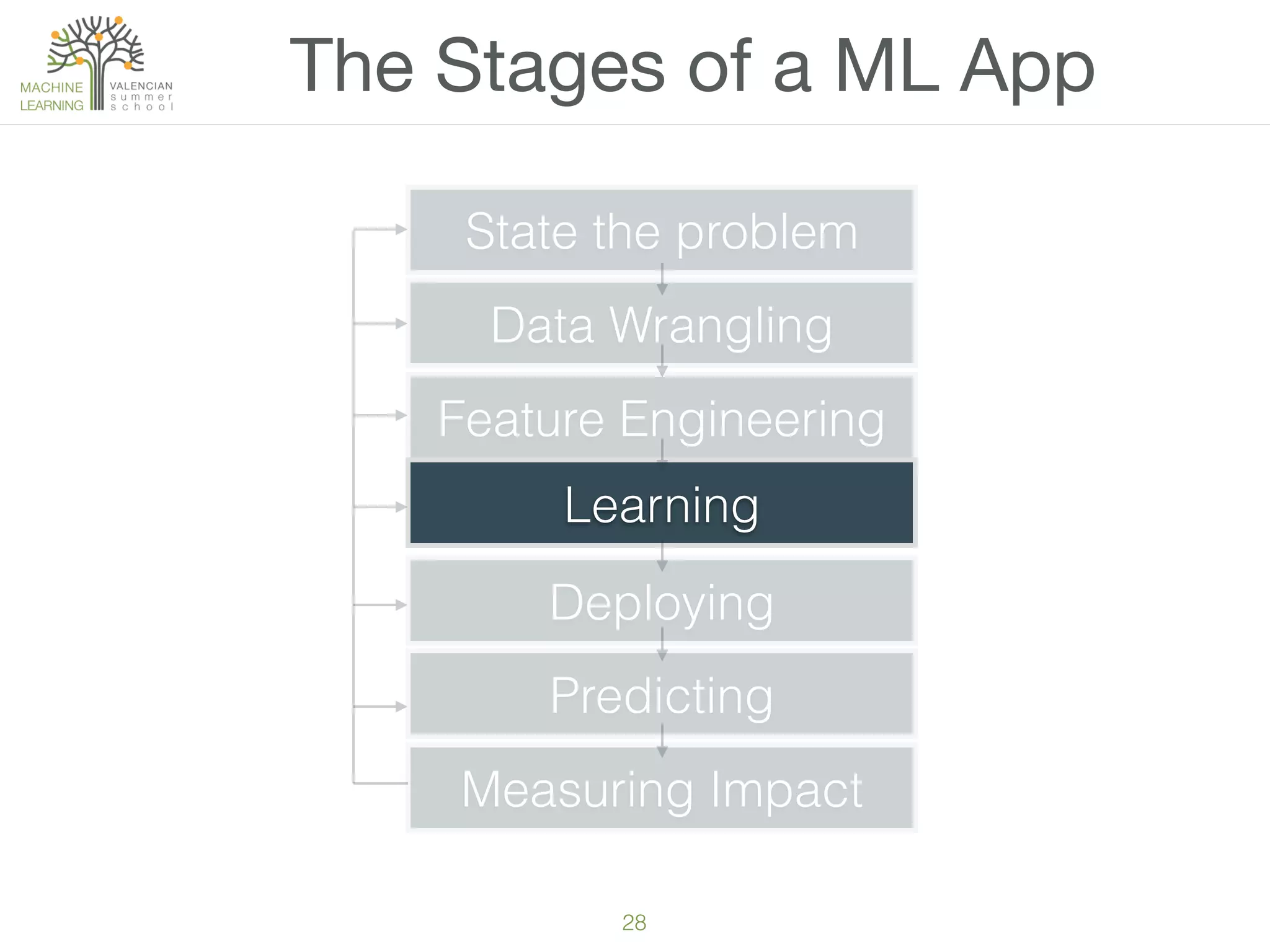
The document provides an overview of machine learning (ML), defining it as a field enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming. It discusses the types of learning problems such as underfitting and overfitting, various ML models, and the significance of data management, including handling missing values. Additionally, it traces the evolution of ML techniques from the 1950s to present, highlighting the reasons for its current prominence and outlining the stages involved in developing an ML application.