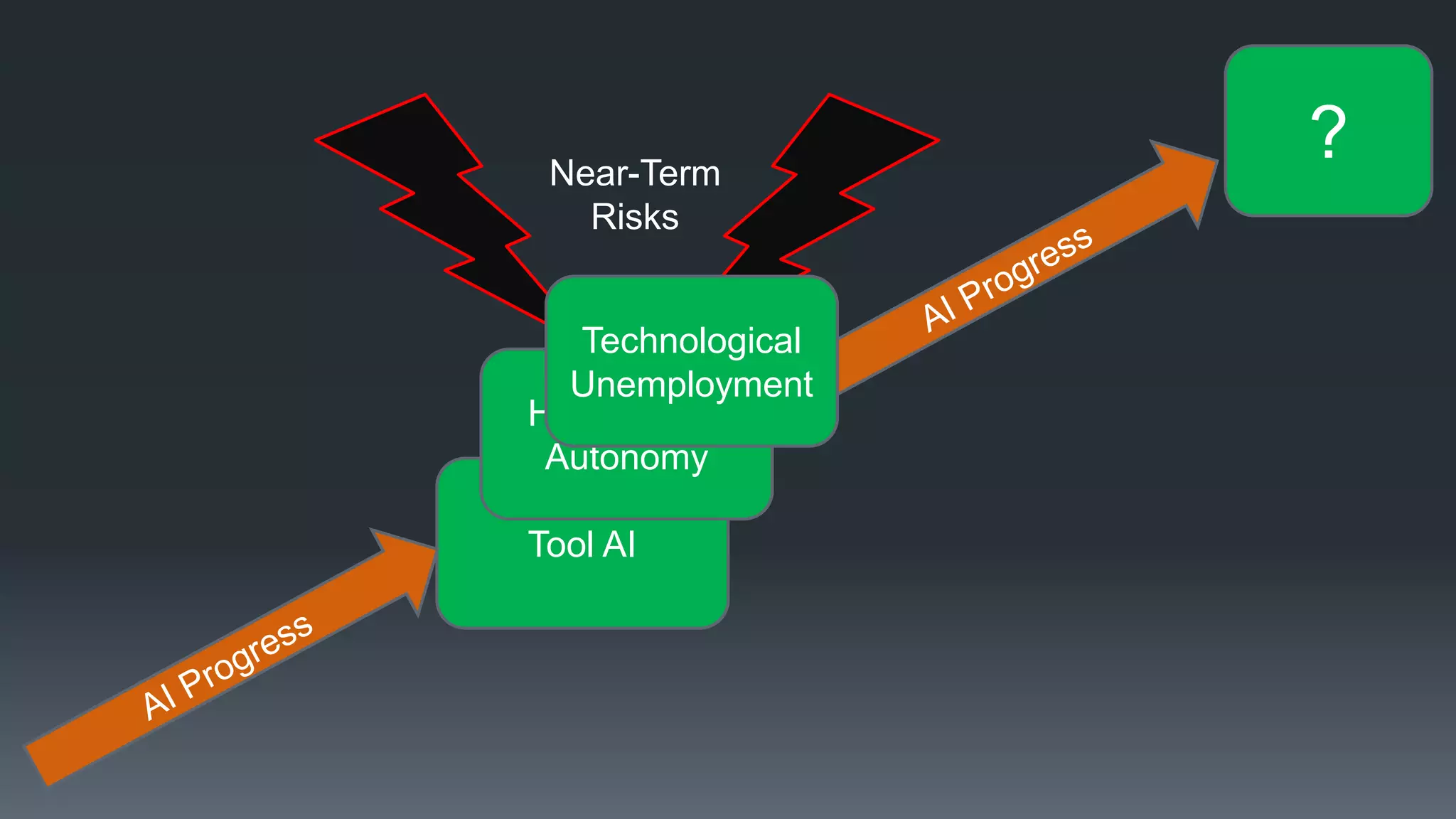
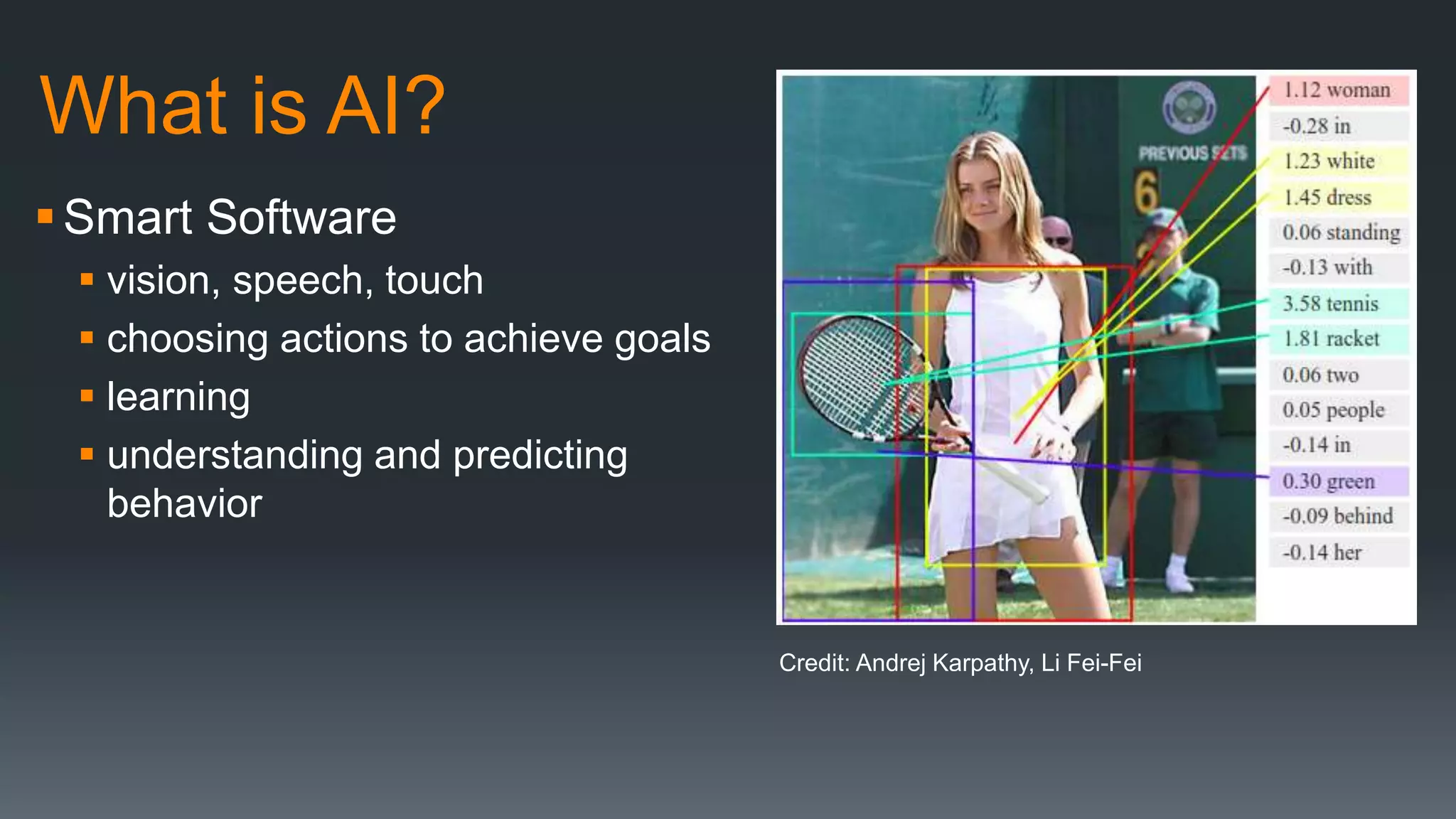
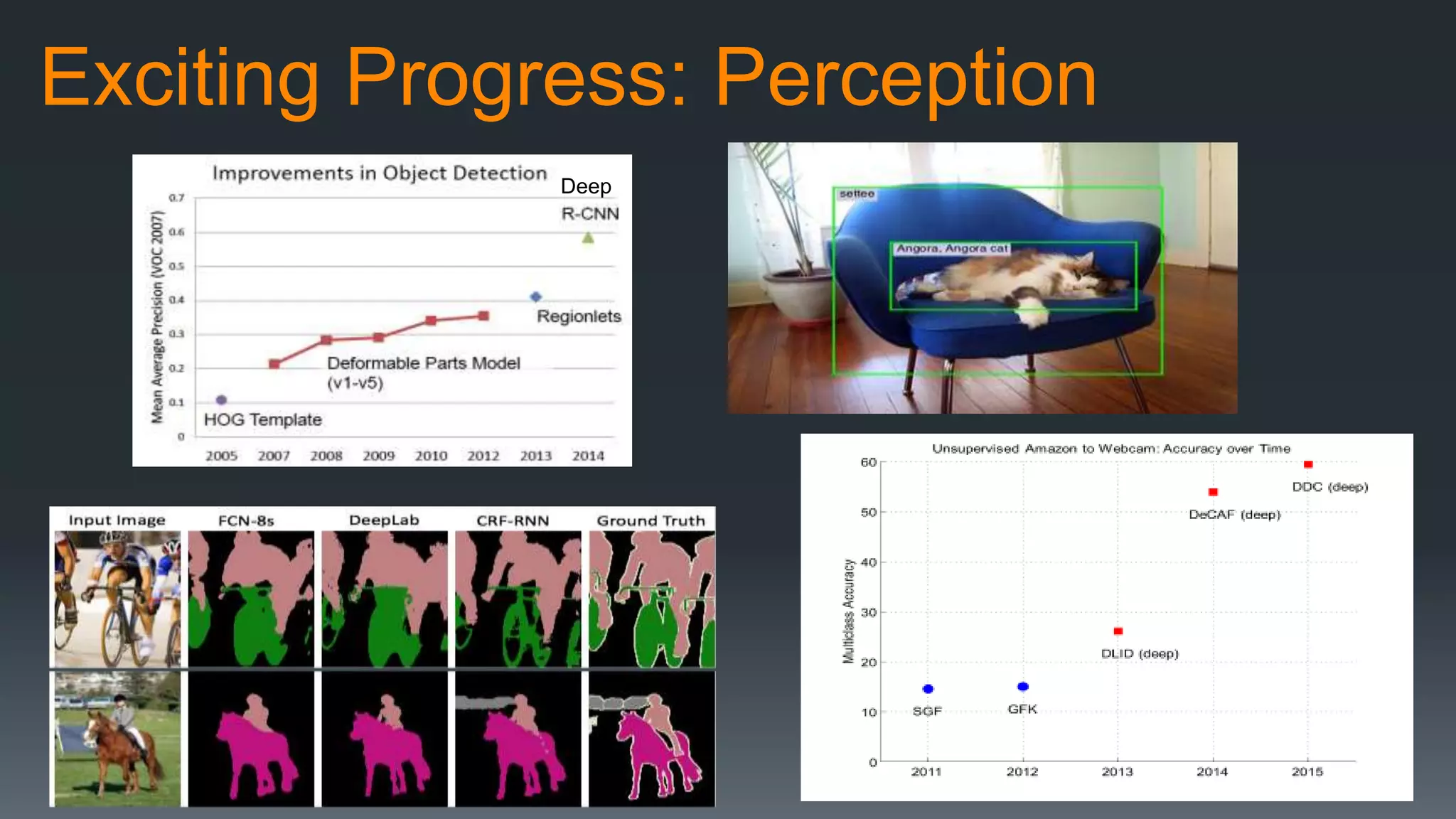
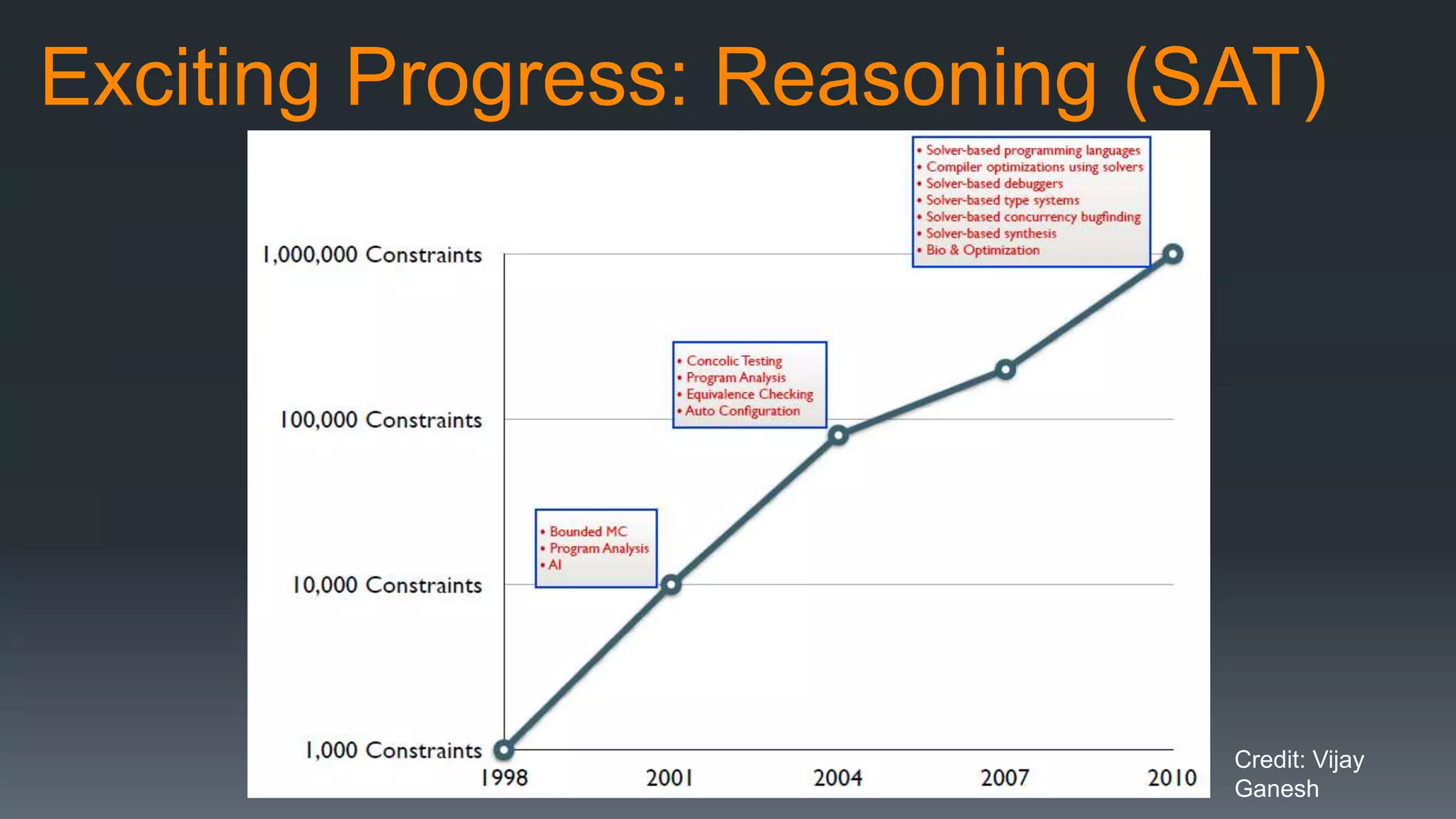
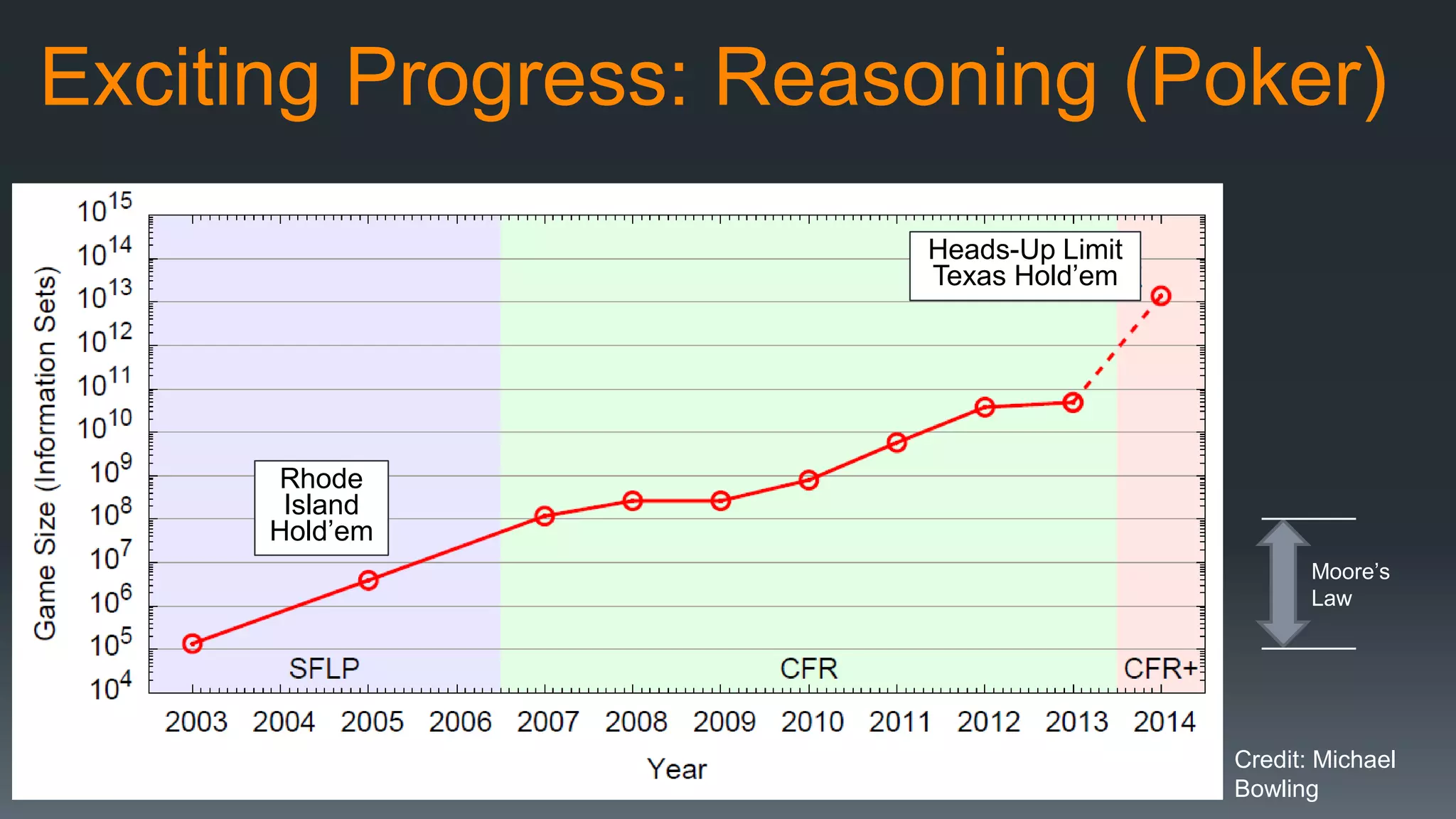
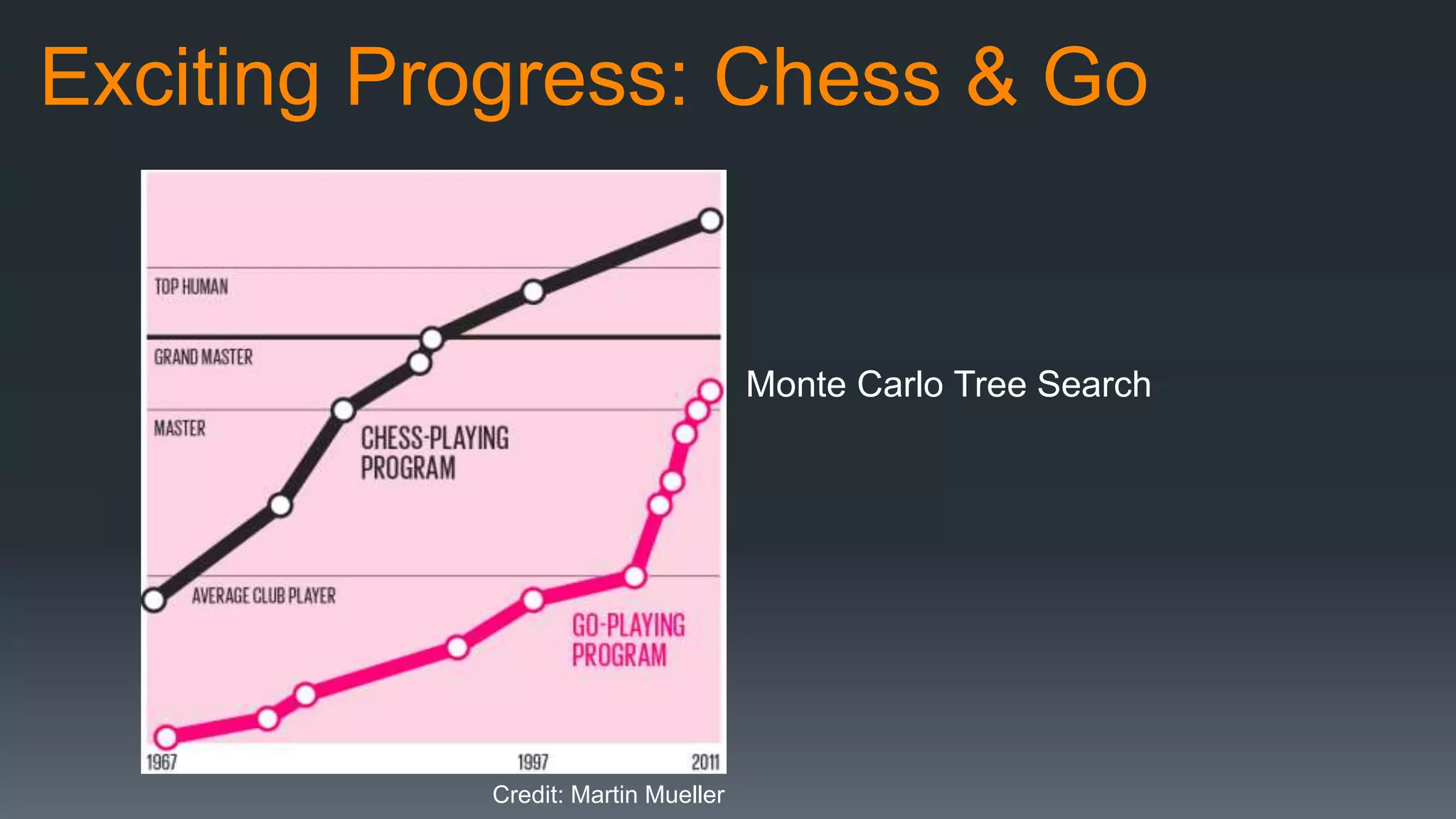
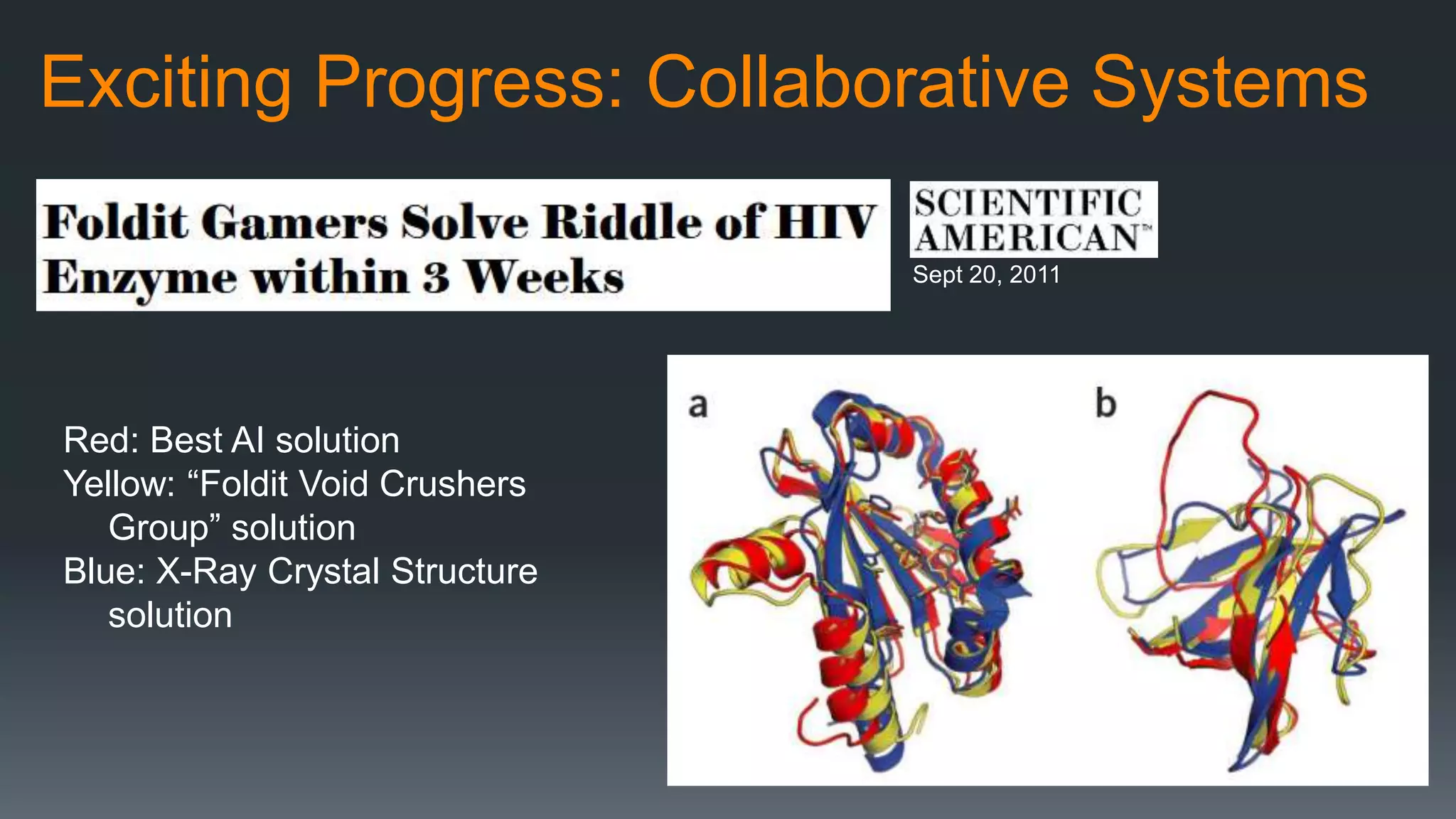
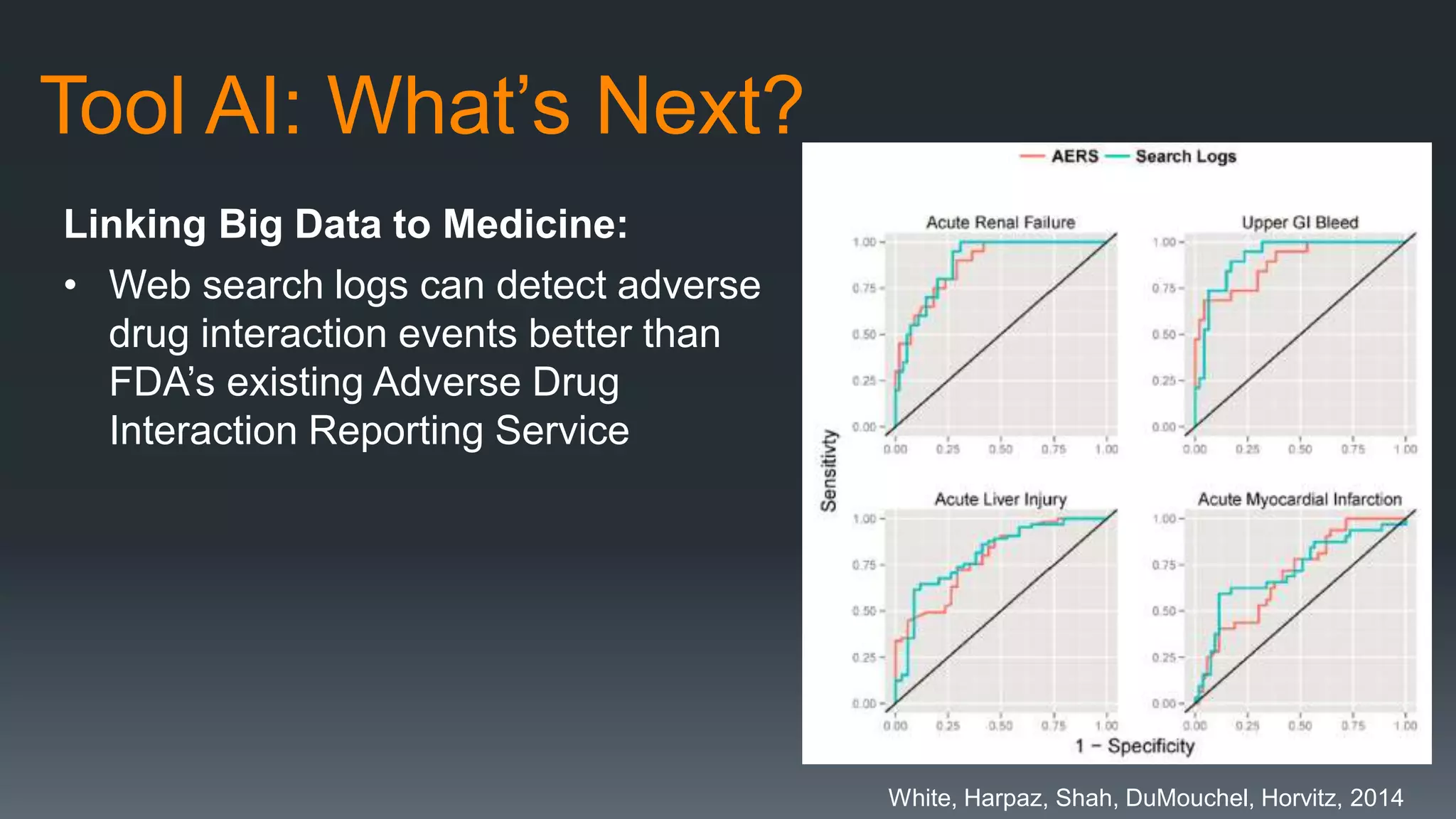
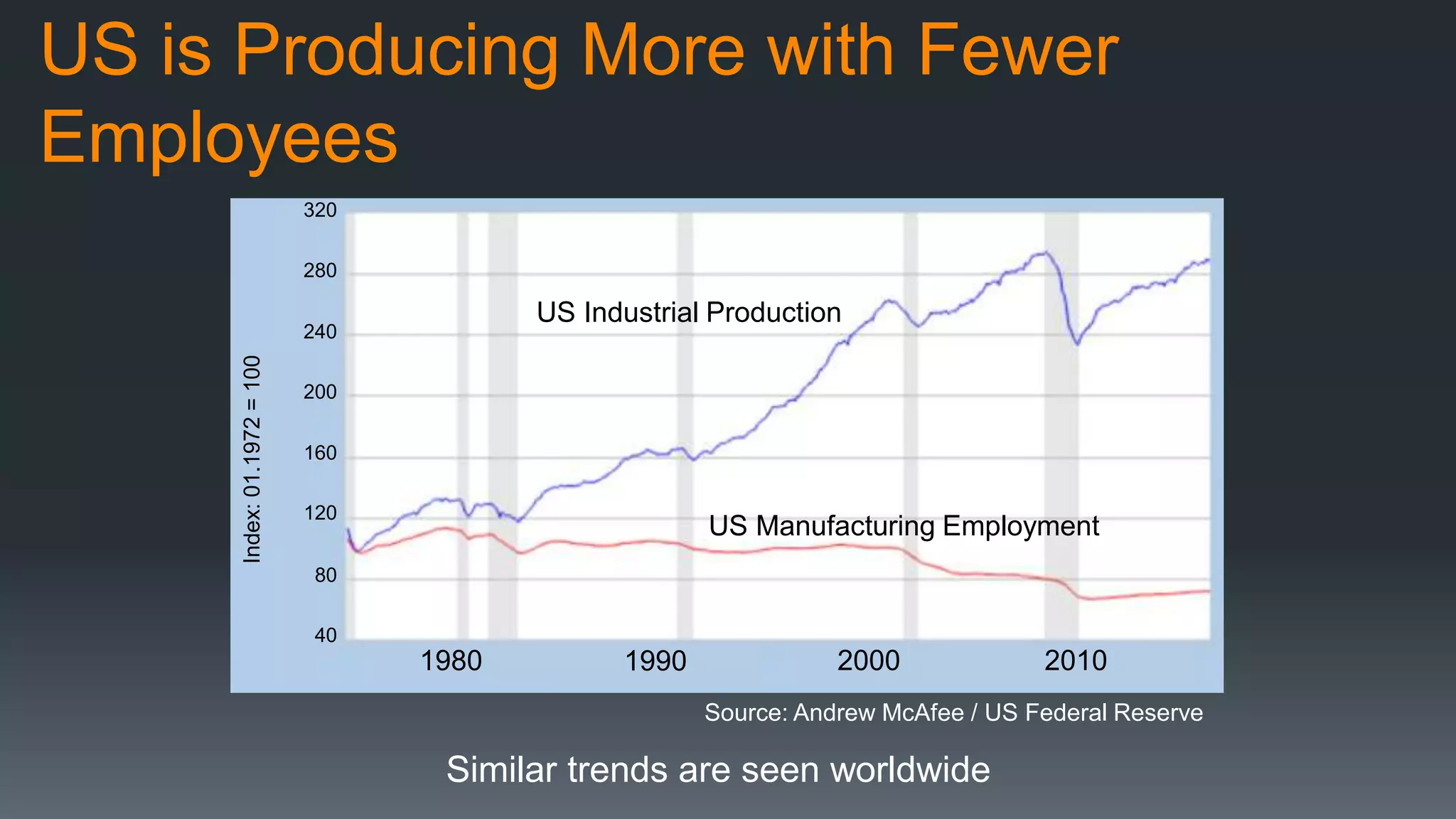
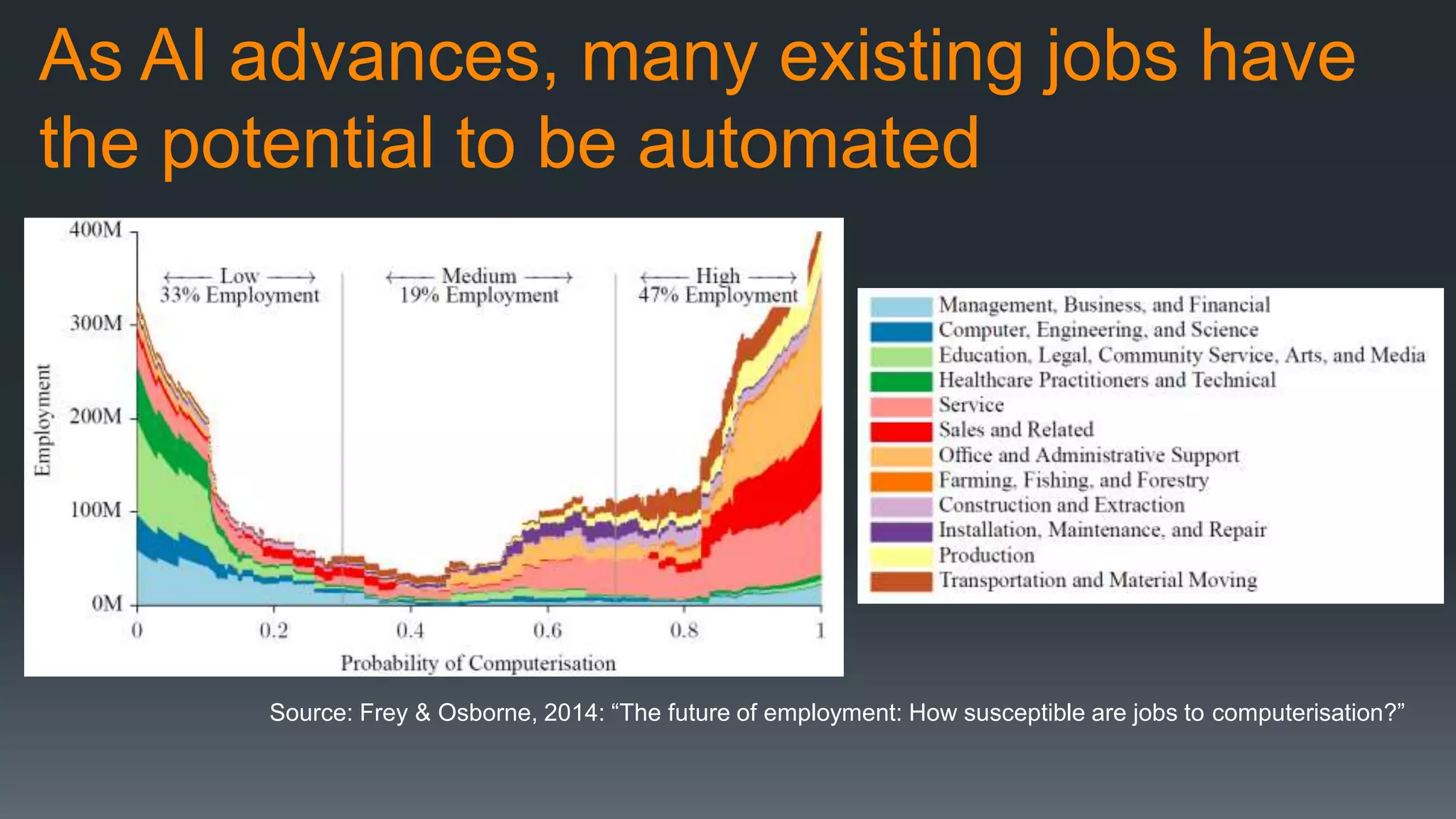
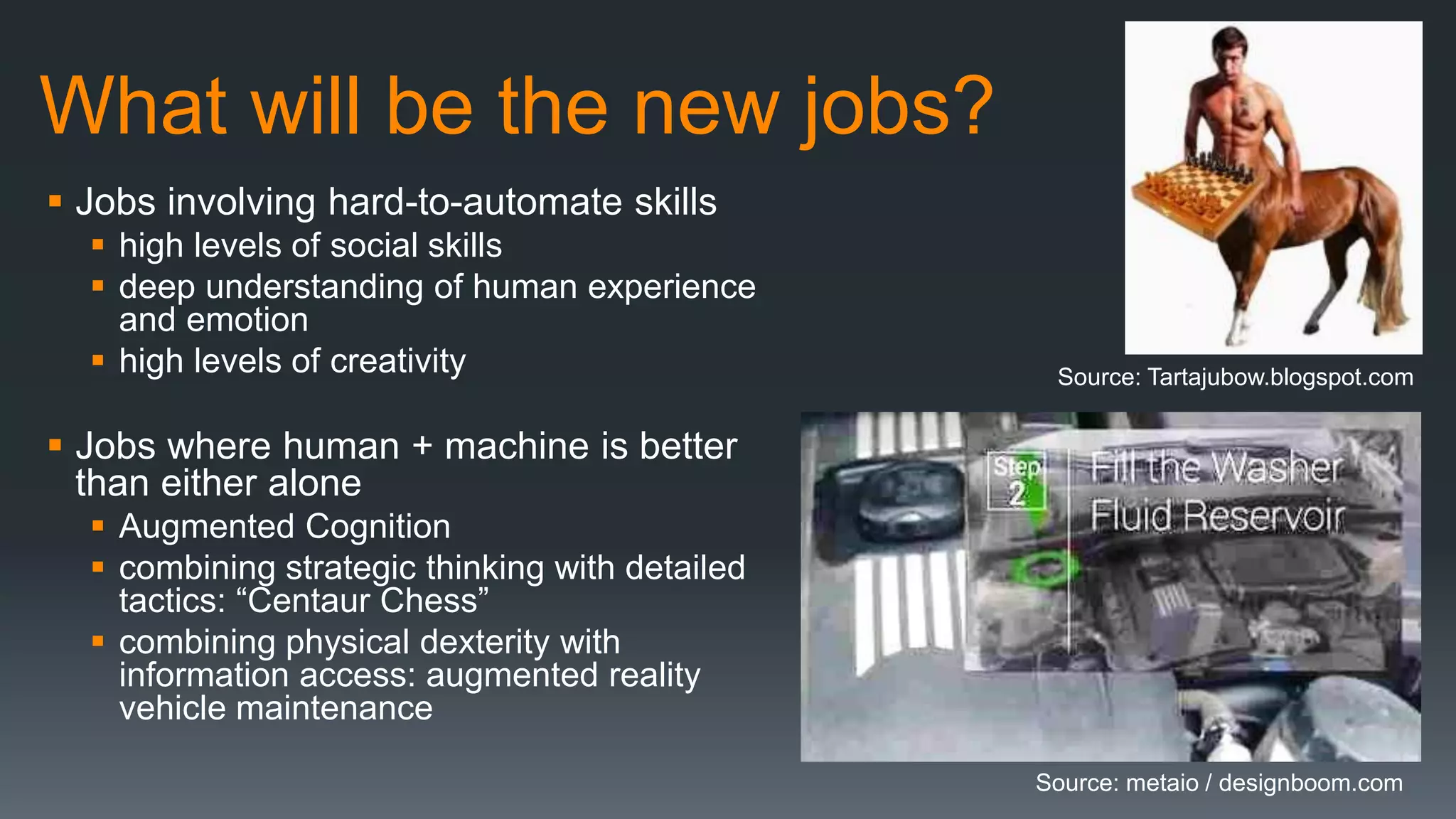
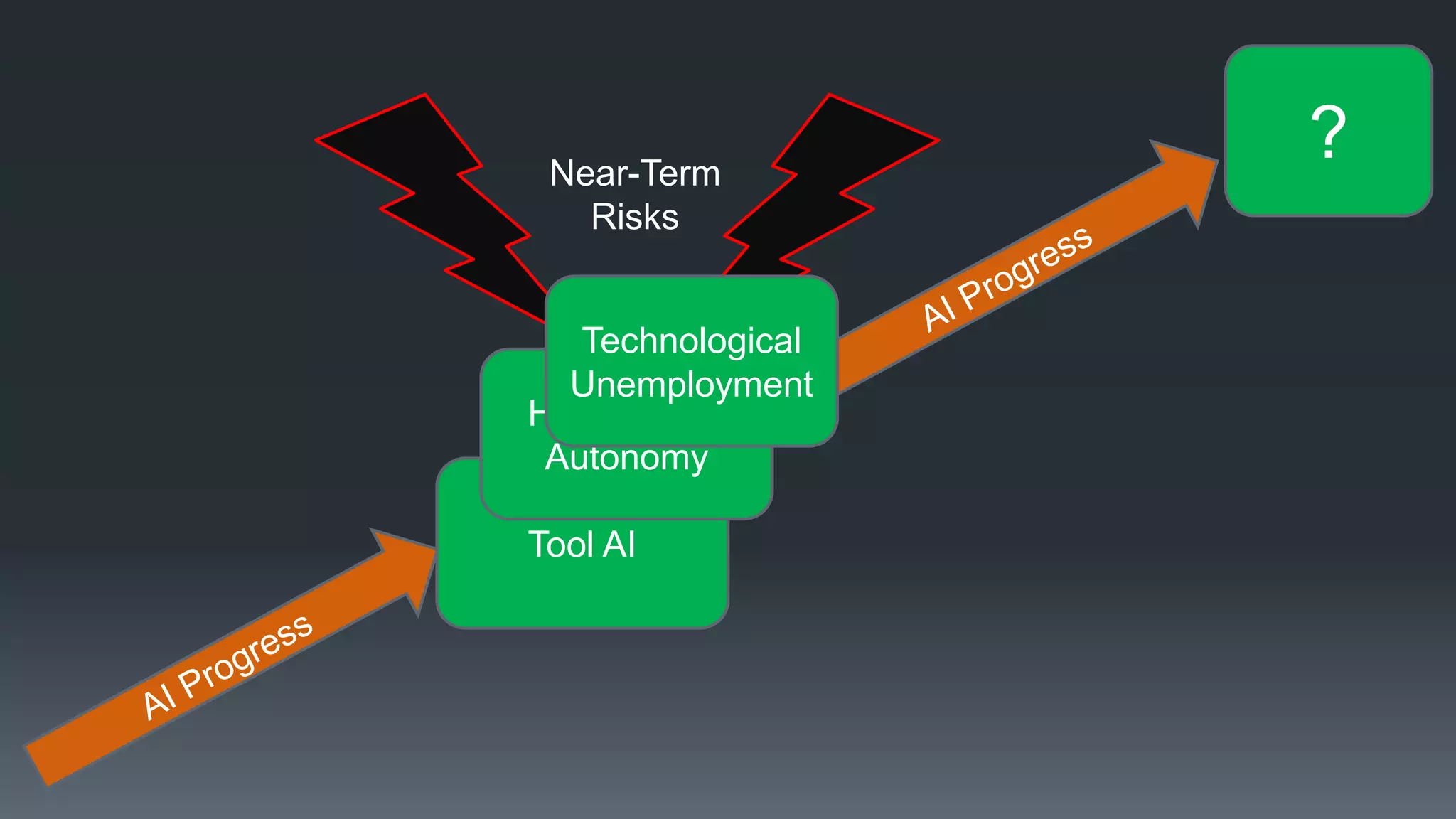
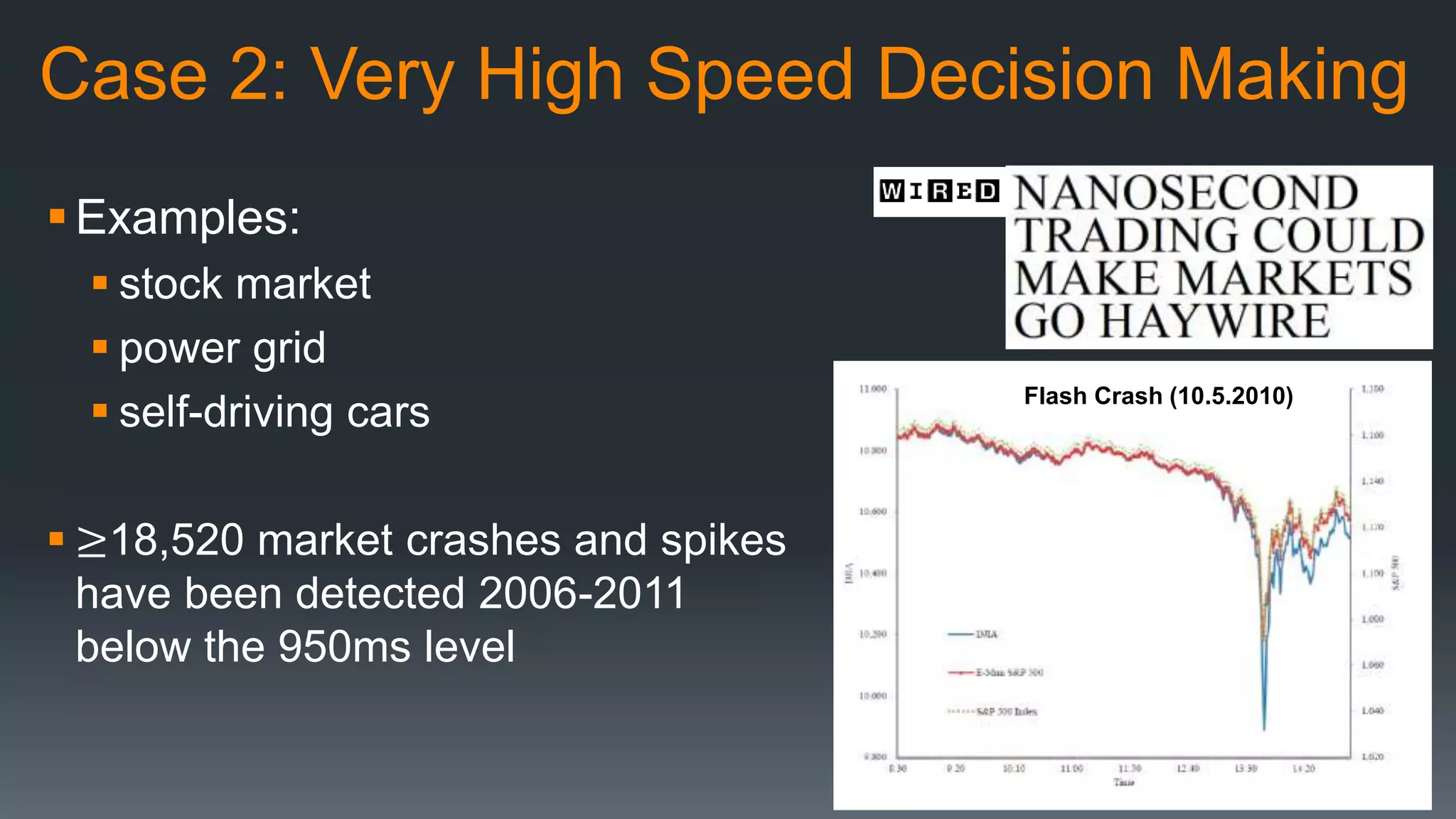
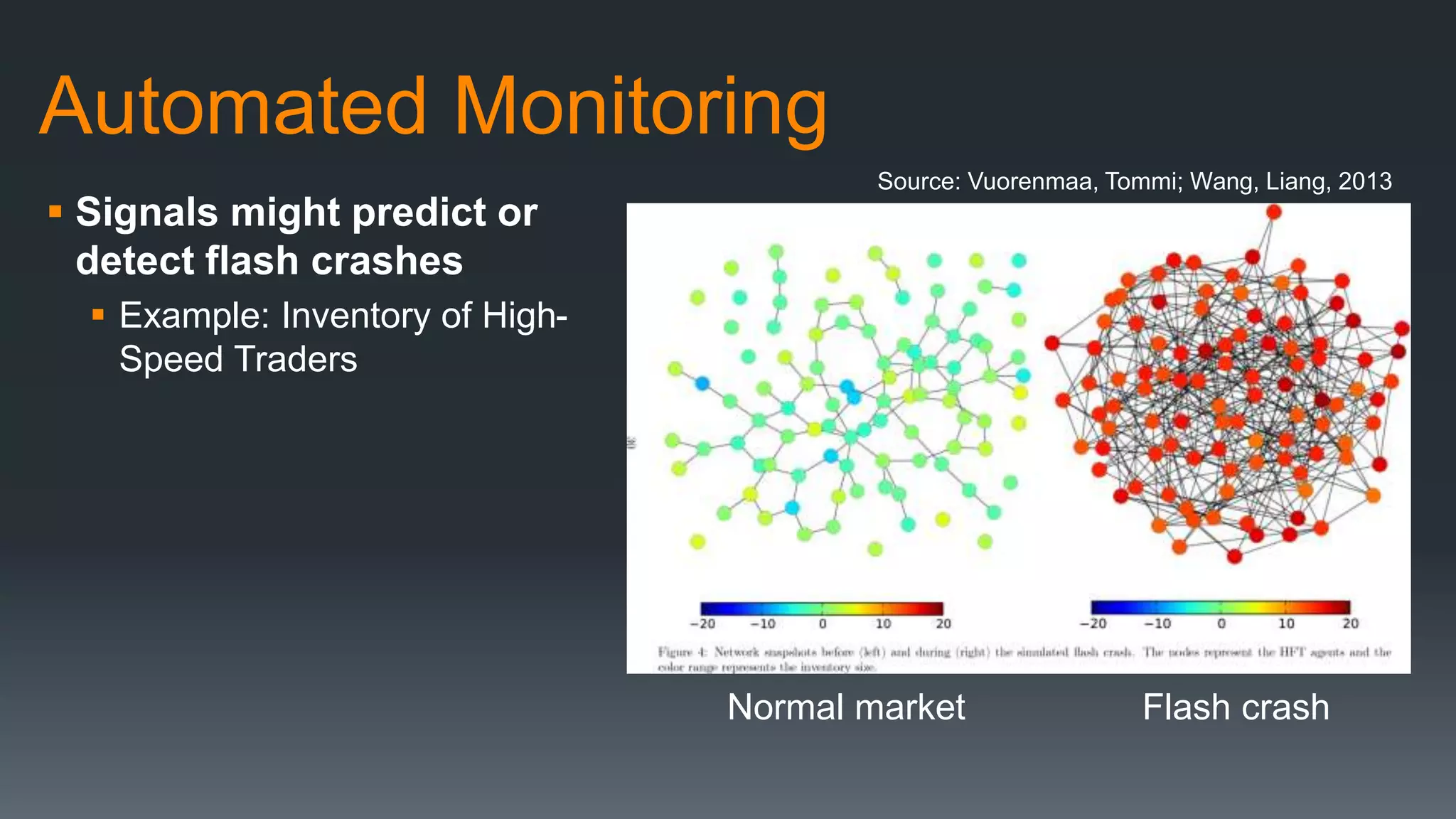
The document discusses the progress and challenges of artificial intelligence (AI), highlighting advancements in perception, reasoning, and collaborative systems. It addresses the risks associated with autonomous AI, such as cybersecurity threats and issues of trust and control, emphasizing the need for research on safe performance. Technological unemployment is also examined, noting the potential for AI to displace jobs while arguing for optimism due to potential new job creation and the complementary nature of humans and AI.