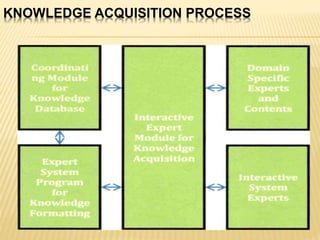
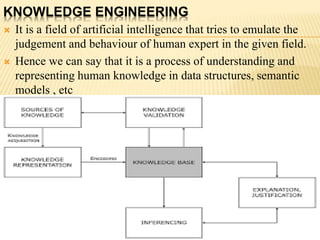
The presentation by Aditya Sarkar focuses on knowledge acquisition, which is the process of extracting, structuring, and organizing knowledge from various sources, while also highlighting the challenges and methodologies involved. Key issues include the difficulty of extracting knowledge from experts and the continually evolving nature of knowledge, which can lead to incomplete or incorrect information. The document emphasizes the importance of effective knowledge validation and representation in artificial intelligence systems, concluding that successful knowledge acquisition is crucial for knowledge engineering projects.