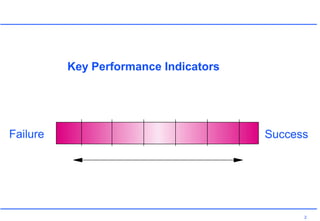
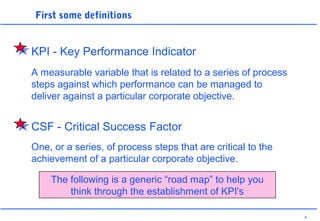
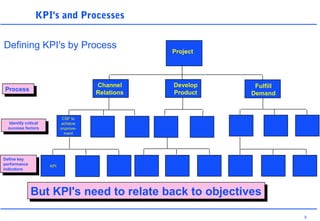
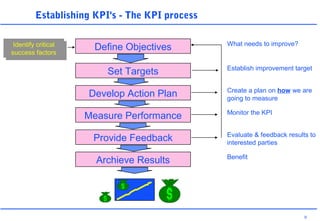
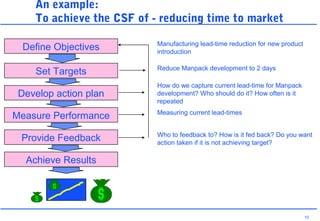
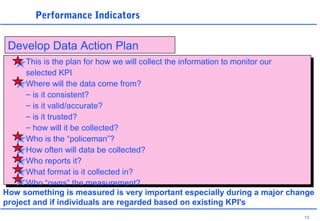
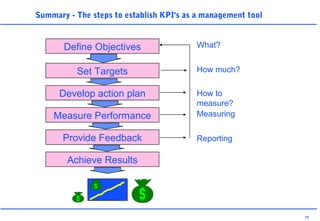
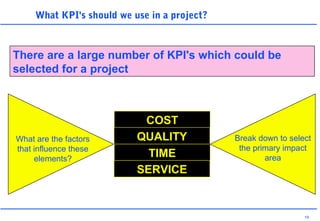
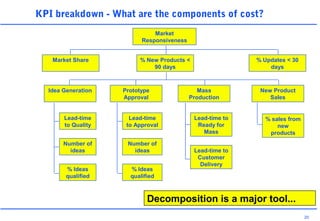
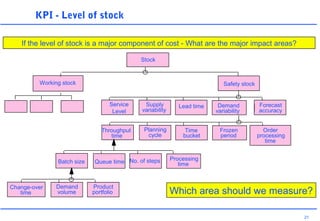
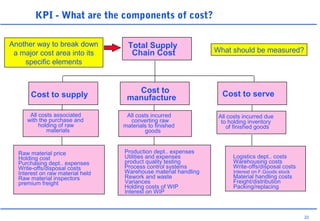
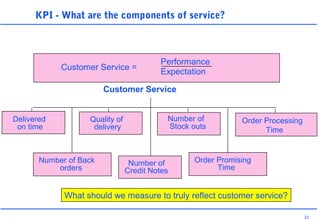
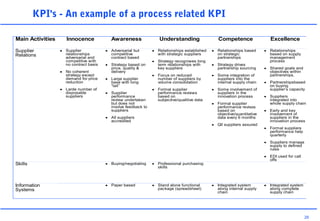
This document discusses key performance indicators (KPIs) and how to establish them for projects and processes. It defines KPIs and critical success factors. The objectives are to demonstrate how KPIs relate to projects, define some examples of KPIs, and show how to measure against them. It provides examples of using KPIs to measure costs, quality, time, service and processes. It emphasizes selecting KPIs linked to objectives, setting targets, developing measurement plans, monitoring performance, and providing feedback.